
CRN’s 2023 Women of the Channel Honors Francesca El Attrash-Ukaejiofo of Iron Bow
HERNDON, Va.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 8, 2023--
2023-05-08 22:48

Oracle Tops Sales Estimates as AI-Frenzy Spurs Cloud Demand
Oracle Corp. reported quarterly revenue that topped estimates, signaling the software maker’s cloud business is benefiting from heightened
2023-06-13 04:52

World's First Brokerage-as-a-Service Platform Breaks The Mold, Pinnacle Realty Advisors Enters California
DALLAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 18, 2023--
2023-07-19 03:58
Irish Times removes opinion article about ‘problematic’ fake tan amid concerns over AI hoax
Ireland’s newspaper of record has removed an article it said “may not have been genuine”, amid suspicions of a hoax using artificial intelligence (AI). The comment piece was published by The Irish Times on Thursday with the headline, “Irish women’s obsession with fake tan is problematic”. But the opinion article was taken down the following day, after reaching second place in the paper's most read online articles that day, according to broadcaster RTE, and sparking discussions about fake tan on a lunchtime radio show. An initial message on Friday reportedly said the article’s text had “been removed pending checks”. By Saturday, the paper had issued a “corrections and clarifications” note under the original headline, reading: “The Irish Times has become aware that the article originally published on this page may not have been genuine. “The article’s text was removed on Friday, May 12th, 2023, and a review has been initiated.” Claiming to be from “a strict Catholic family” in Ecuador who moved to Ireland in 2015 during the vote to legalise gay marriage, the purported author argued that Ireland’s “widespread use of fake tanning products” jarred with their vision of the country as at the “forefront of progressive social change”. “To me, fake tan represents more than just an innocuous cosmetic choice; it raises questions of cultural appropriation and fetishisation of the high melanin content found in more pigmented people,” the now-deleted article stated. But while the original headline and image remain online, the text and author’s byline has now been removed from the page, after journalists questioned whether the image of the author had also been created by AI. The Independent has approached the newspaper for comment. In a statement reported by the Irish Examiner, a spokesperson said: “On Friday, The Irish Times became aware that an article published online under the headline ‘Irish women’s obsession with fake tan is problematic’ may not have been genuine. “The story has been removed from irishtimes.com, and a review has been initiated.” Read More AI pioneer warns UK is failing to protect against ‘existential threat’ of machines Disturbing research warns AI may be ‘Great Filter’ that wipes out human civilisation Artificial intelligence could ‘transform’ heart attack diagnosis, scientists say ChatGPT user in China detained for creating and spreading fake news, police say
2023-05-14 00:48
Radiant Security Announces Revolutionary AI-Powered SOC Co-Pilot
LAS VEGAS & SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 9, 2023--
2023-08-10 00:19

X, the former Twitter, lets users hide once-vaunted blue check
Users on the social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, will now be allowed to hide their once-prized blue...
2023-08-03 06:54

OpenAI's ChatGPT will 'see, hear and speak' in major update
OpenAI's ChatGPT is getting a major update that will enable the viral chatbot to have voice conversations with
2023-09-25 22:56

US sues to block Xbox takeover of Call of Duty developer Activision Blizzard
The US Federal Trade Commission has sued to stop Microsoft buying Call of Duty developer Activision Blizzard. It is just the latest problem for the deal, which has already been blocked by UK regulators. If completed, it will become one of the largest takeovers ever – but has faced scrutiny from regulators around the world, who argue that it might cause problems for the gaming market. The FTC's Monday filing in a federal court in San Francisco seeks a restraining order and injunction to stop Microsoft's $69 billion purchase of the California gaming company behind hit franchises such as Call of Duty and World of Warcraft. Microsoft, maker of the Xbox game system, has been struggling to win worldwide approval for the deal with just over a month before the deadline to close it, according to the contract it signed with Activision. “We welcome the opportunity to present our case in federal court," said a statement Monday from Brad Smith, Microsoft's vice chair and president. "We believe accelerating the legal process in the U.S will ultimately bring more choice and competition to the market.” The FTC already took Microsoft to court to block the merger, but that was before the U.S. agency's in-house judge in a trial set to start on Aug. 2. That administrative process doesn't preclude the parties from closing the deal. The contract between Microsoft and Activision required the deal to close by July 18, but the FTC's latest action seeks to stop that from happening. “Microsoft and Activision Blizzard have represented in the past that they cannot close their deal due to antitrust reviews of the transaction in other jurisdictions," the FTC said in a statement Monday. "But Microsoft and Activision have not provided assurances that they will maintain that position. In light of that, and public reporting that Microsoft and Activision Blizzard are considering closing their deal imminently, we have filed a request for a temporary restraining order to prevent them from closing while review continues.” Microsoft's other main obstacle is in the United Kingdom, where antitrust regulators have also taken action to block the acquisition. The all-cash deal announced in January 2022 has been scrutinized by regulators around the world over fears that it would give Microsoft and its Xbox console control of Activision's hit franchises and give it an unfair boost in the emerging business of cloud-based game subscriptions. It could be the priciest tech industry merger in history. Fierce opposition has been driven by rival Sony, which makes the PlayStation gaming system. Microsoft sought to counter the resistance by striking a deal with Nintendo to license Activision titles like Call of Duty for 10 years and offering the same to Sony if the deal went ahead. European regulators representing the 27-nation bloc approved the deal last month on condition that Microsoft make some promises meant to boost competition in the cloud-based gaming market. A number of other countries, including China, Japan, Brazil and South Korea, have also approved it. But the blockbuster deal has remained in jeopardy because of the surprise April decision by the U.K.’s Competition and Markets Authority and the ongoing case in the U.S. Microsoft in late May filed an appeal of the British regulator's decision and has also voiced strong public opposition directed at top government officials. U.S.-based consumer advocacy group Public Citizen, an opponent of the deal, welcomed the FTC's move Monday. “Although the agency has already used its authority to block the merger through administrative proceedings, Microsoft is pushing to culminate the purchase of Activision before the agency can finish its process," said a statement from Public Citizen's competition policy advocate Matt Kent. ""By filing in federal court to enjoin the transaction, the FTC is showing that it won’t back down in the face of Microsoft’s escalatory tactics.” Additional reporting by Associated Press
2023-06-14 02:25

Adin Ross responds to IShowSpeed's statement about ignoring texts, calls latter 'liar': 'S**k my d**k
Adin Ross accused IShowSpeed of lying about not replying to his texts, here's what all happened
2023-05-30 18:29
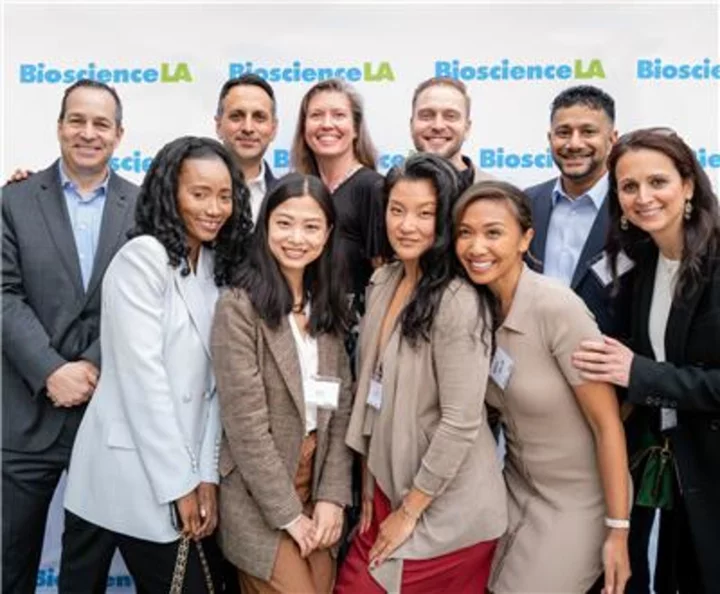

BioscienceLA Launches Leadership Catalyst Program For Emerging Leaders in the Life Sciences
CULVER CITY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 15, 2023--
2023-08-15 20:24

Valorant Rope Burn Card: How to Get for Free
Players can get the Valorant Rope Burn Card for free by linking their Riot Games and Amazon Prime accounts by Oct. 23.
2023-09-29 23:24
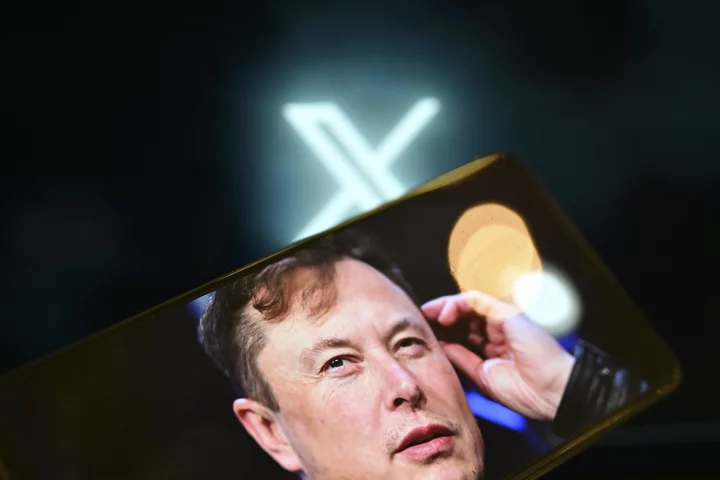

Elon Musk 'likes' trending #BanTheADL posts as white supremacist ad runs on platform
Over the past 24 hours, the hashtag #BanTheADL has been trending on X, the platform
2023-09-02 06:28
You Might Like...

X is shutting down feature to send posts to select people after privacy concern

Asahi Kasei Joins the Japan Hydrogen Forum to Support Decarbonization in the U.S.

Students: Slide into Summer Break Without Risking the Summer Slide

Google Wins Limits to Antitrust Claims at Trial Over Search Deals

E Ink Announces Sharp Corporation Is Releasing ePoster Color Electronic Paper Displays Featuring E Ink Gallery™ Plus
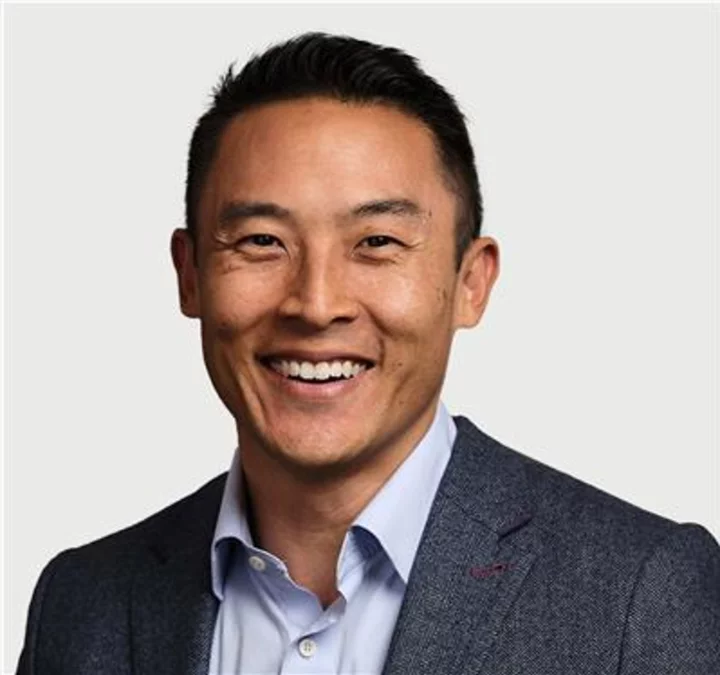

Calendly Welcomes Former Salesforce Product Executive Stephen Hsu as CPO

Chinese hack of Microsoft engineer led to breach of US officials' emails, company says

There’s a perfectly good reason why people believe conspiracy theories
