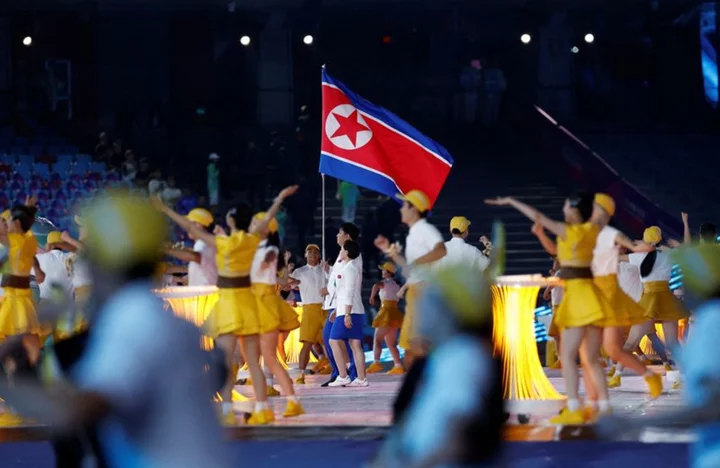

Games-Asia Olympic body backs North Korea flag at Hangzhou despite WADA ban
By Ian Ransom HANGZHOU, China The Olympic Council of Asia (OCA) says it is happy for the North
2023-09-24 20:27

IShowSpeed confronts unruly fan who yelled hurled slurs at him during live stream: 'Y’all embarrassing'
During an August 25th live stream, IShowSpeed was left enraged after encountering a fan who spewed hateful slurs and racial remarks
2023-08-27 15:17
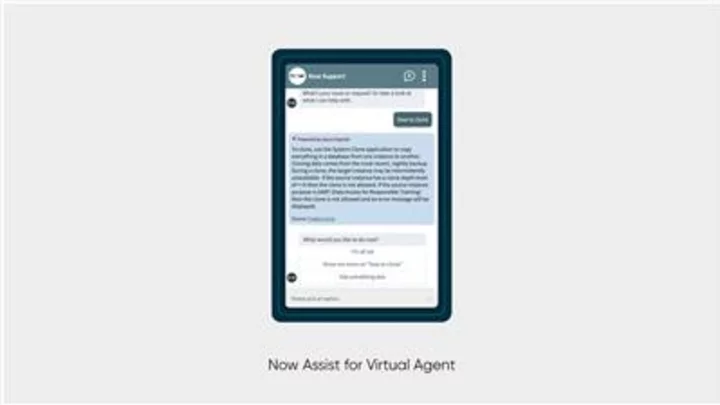
ServiceNow introduces new generative AI solution, Now Assist for Virtual Agent, to create conversational experiences for more intelligent self-service
SANTA CLARA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-13 15:25
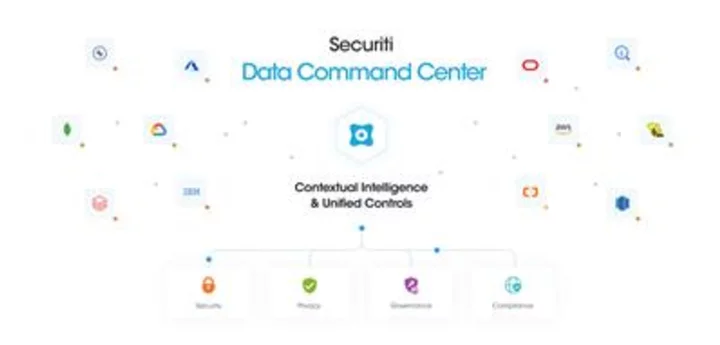
Securiti Named a Worldwide Leader in IDC MarketScape for Data Privacy Compliance Software
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 7, 2023--
2023-09-08 00:59
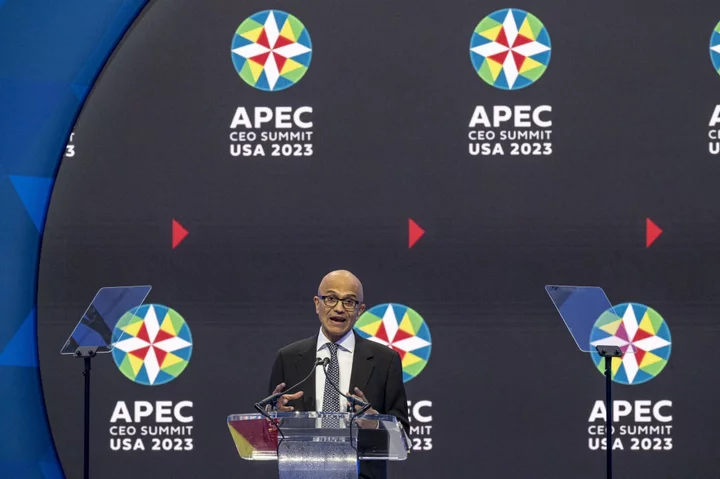

APEC Latest: Xi Says China Will Not Fight Hot or Cold War
President Xi Jinping said China wants to be friends with the US and said his nation won’t fight
2023-11-16 14:16

Siren Marine Becomes Standard IoT Solution on Select 2024 Grady-White, Regulator, Suncatcher by G3 and Skeeter Boat Models
KENNESAW, Ga.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 8, 2023--
2023-08-08 20:27

OpenAI’s Q-Star Breakthrough – the Theories and Why Elon Musk Isn’t Worried
Speculation OpenAI has achieved a significant breakthrough in artificial intelligence might have been overblown - at least if you listen to Elon Musk.
2023-11-27 20:50

Snapchat's My AI chatbot posted a Story then stopped responding. Users freaked out.
Snapchat users have reported that the messaging app's AI chatbot had a few issues on
2023-08-16 12:49

Gamescom: The biggest announcements at the show
Gamers saw this autumn's biggest new releases, including Call of Duty, Starfield and Assassin's Creed
2023-08-23 20:59

How to switch to Mastodon from Twitter now that it's X
Twitter – now known as X – is going through some turmoil at the moment...to
2023-07-25 03:49

Nasa receives signal from 10 million miles away in space
Nasa has received a signal from a spacecraft 10 million miles away. The message, delivered using a distant laser, could “transform” communications with spacecraft, the space agency has said. It represents a successful test of Nasa’s Deep Space Optical Communications or DSOC experiment. It is also the first time that data has been successfully relayed through a laser from further away than the Moon – and marks a rapid increase, at more than 40 times the distance from the lunar surface. At the moment, almost all communications with craft in deep space is achieved through radio signals, sent and received from vast antennas on Earth. They have proven reliable but their bandwidth is limited, meaning that it is slow or impossible to send large files such as high-definition photos and videos. Nasa’s work on DSOC is an attempt to use optical communications through lasers instead. The technology could improve data rates by as much as 100 times, the space agency says. The first attempt to test the technology beyond the Moon left the Earth on Nasa’s Psyche mission, which left Earth last month on a mission to study a distant asteroid. The spacecraft is carrying a laser transceiver than can both send and receive laser signals in near-infrared. Last week, that equipment locked onto a Nasa laser beacon in California. Nasa says that “first light” breakthrough is one part of a host of experiments that they hope will prove the laser technology can work. “Achieving first light is one of many critical DSOC milestones in the coming months, paving the way toward higher-data-rate communications capable of sending scientific information, high-definition imagery, and streaming video in support of humanity’s next giant leap: sending humans to Mars,” said Trudy Kortes, director of technology demonstrations for the Space Technology Mission Directorate at Nasa Headquarters in Washington. Nasa likens the precision pointing of the laser signal to trying to point a light at a coin from a mile away. What’s more, the laser and its target are constantly moving: in the 20 minutes it will take for the light to travel to Earth from Psyche’s furthest distance, both the planet and the spacecraft will have moved significantly. The team will now work to refine the systems that ensure the spacecraft is pointing its lasers in the right direction. When that happens, Nasa will try an experiment to demonstrate that the spacecraft is able to maintain high-bandwidth data transfer at different distances from Earth. It will do so by breaking the data into bits that can be encoded in the photons of light sent by the spacecraft. That light then arrives at the telescope on Earth and can be reassembled into images or other important data that will be sent by spacecraft – and perhaps humans – in the future. Read More SpaceX hints next Starship launch attempt could be soon SpaceX to launch world’s biggest rocket again after first attempt ended in explosion Nasa spots collection of shocking materials on distant planet
2023-11-23 00:50

Nasa has gathered a large piece of a distant asteroid. What now?
Scientists have gathered a significant chunk of a distant asteroid, which has made its way to Earth after a mission taking millions of miles. But the really useful work will begin now. Nasa’s Osiris-Rex mission flew to the distant Asteroid Bennu, scooped up a piece of the object into a canister, and then flew back to Earth to drop it off. On Sunday, Nasa picked up that canister in the Utah desert and is now working to secure it. It will then send those samples to a variety of scientists around the world, with a chunk of it being sent to more than 200 people at 38 different institutions across the world. They hope that they can use them as a “time capsule” to peer into the early universe, telling us about where we came from. “This box when it is opened of material from the surface of Bennu can tell us untold secrets of the origins of the universe, the origins of our planet and the origins of life itself,” said Queen musician Brian May, who helped with the research by mapping out the asteroid to find a landing spot. “What an incredibly exciting day.” Sample return missions are particularly exciting to scientists because they offer a look at a pristine piece of a distant world that has been undisturbed by the environment on Earth. While some pieces of asteroids and other objects can fall down to Earth, they have to make their way through the atmosphere and can be damaged and changed in the process. They also mean that researchers are able to use all of the Earth’s latest technology to study the sample. Other pieces of distant worlds have of course been studied by spacecraft and landers, but they are only able to do so with the limited instruments they take to those planets. Another advantage of sample return missions over studying the objects at their home is that scientists can look back at those samples with new sensors and equipment invented long after the sample was actually taken. Many space missions continue for years – Curiosity is still examining Mars after arriving there in 2012, and the Voyager probes are still providing information almost 50 years after they were launched – but they are only able to do so with the technology that was available when they set off. The analysis done in sample return missions really begins when the spacecraft arrives at its target: then, it starts looking at the context of the sample, gathering information about the world from which it came that should prove useful to scientists later. Osiris-Rex arrived at Bennu in 2018, and spent two years mapping the asteroid before it set off back home with its delivery. All of that information in addition to the samples could help answer a variety of questions about our planet, scientists hope. “The asteroids in our solar system contain the raw building blocks from which the Earth was made, so working out their composition will tell us a lot of how our planet formed,” said Boris Gansicke from the department of physics at the University of Warwick. “There are many open questions, for instance, where did the water that we have on Earth come from? And where did the ingredients that made life possible to develop come from? “To answer those questions, ie measure the composition of an asteroid, you need to get your ‘hands’ on them (or in this case the arm of a space mission), and this is what Osiris-Rex achieved. “In a nutshell, it’s similar to sitting in front of a delicious dinner and wanting to have the list of ingredients.” Sample return missions are almost as old as space travel itself, and the first of them were the early Apollo missions, which brought back pieces of the Moon. Those continue to be useful to scientists. Since then, as human travel into space has declined, most of the work has been done by robots. In the early 1970s, the Soviet Union’s Luna missions gathered pieces of the Moon and brought them back, and in 2020 Japan’s Hayabusa2 mission brought back pieces of the asteroid Ryugu. Scientists have high hopes for future missions: perhaps the most discussed is a mission to Mars, which would bring back the first ever pieces of that planet. Engineers have suggested that for decades, and a number of plans have been formed, but none are likely to launch any time soon. Read More Nasa spots shocking number of galaxies like our own Nasa lands Bennu asteroid samples back on Earth Nasa just delivered a piece of a distant asteroid to Earth Pieces of a distant asteroid are about to fall to Earth Nasa to return largest asteroid sample ever as UK helps with research Massive solar flare strikes Nasa spacecraft sent to study Sun
2023-09-26 00:45
You Might Like...
Pets pose a serious health threat that we've all been overlooking

Nextdoor Announces the 2023 Neighborhood Faves Winners and Unveils Special Bell Ringing Event at the New York Stock Exchange

MGM Resorts Hackers Broke in After Tricking IT Service Desk

How to watch IPL 2023 for free from anywhere in the world

Watch this robot teach us how to cook ramen

LEAK: New Storm Point POIs Are Coming to Apex Legends
Get lifetime access to millions of podcasts for $40
TikTok: Divorce lawyer warns women to 'stay away' from 'controlling' men with these 5 'narcissistic' jobs
