Spotify Is in Talks to Test Full-Length Music Videos in App
Spotify Technology SA is considering adding full-length music videos to its app, which could help the streaming service
2023-07-01 03:27
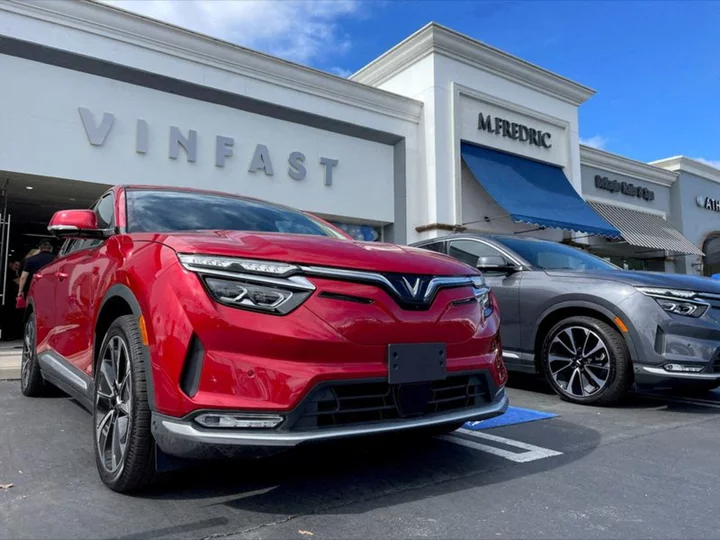

VinFast revenues jump on EV sales to Vietnam affiliate
By Phuong Nguyen and Chavi Mehta (Reuters) -Vietnamese electric car maker VinFast said on Thursday its third-quarter revenue more than
2023-10-05 22:47
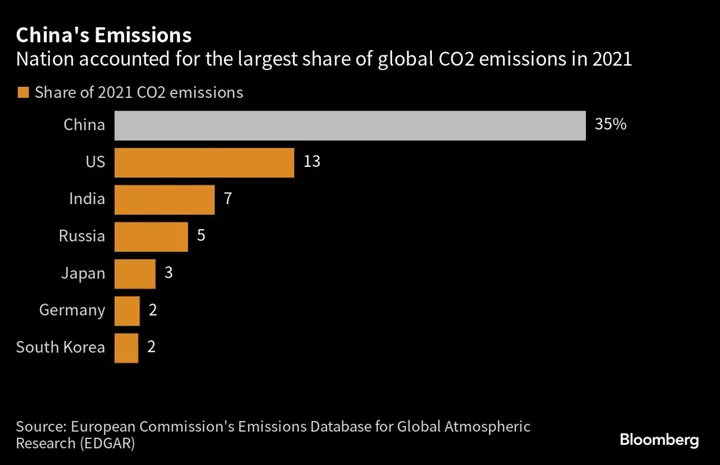
Xi Calls for a Shift Toward Controlling China’s Carbon Emissions
China’s President Xi Jinping has called for greater efforts to control carbon emissions, while also stressing the role
2023-07-12 12:53
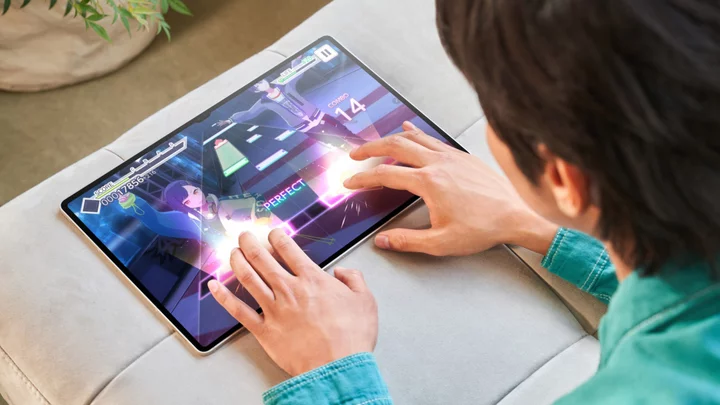

Pre-Order Galaxy Tab S9 Tablet, Get Free Storage Credit and Trade-In Credit
Today’s Samsung Unpacked event was good news for those who love the Galaxy line of
2023-07-27 08:18

First Floor or Top Floor? How to Decide Where to Live in an Apartment Building
Pets, noise tolerance, and how much you like rats can all help determine which floor is right for you.
2023-05-17 23:18

Gatik’s Chief Technology Officer and Co-founder, Arjun Narang, Honored as a 2023 Automotive News Rising Star
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 11, 2023--
2023-09-12 00:57
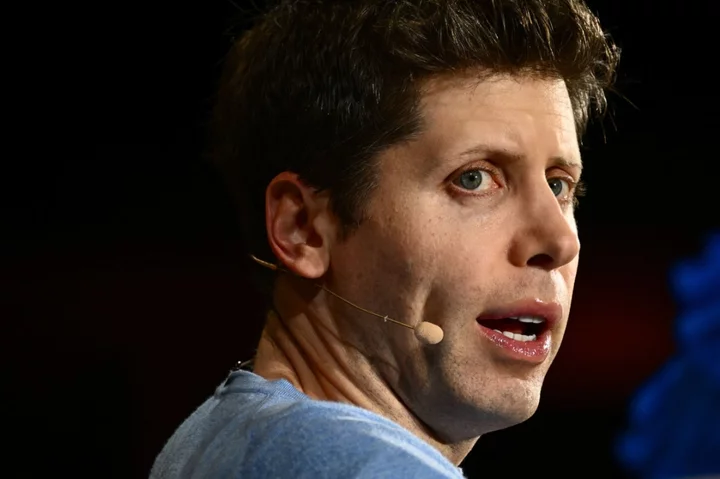

OpenAI in talks to bring Sam Altman back days after CEO ouster, reports say
Just days after Sam Altman was fired as OpenAI’s CEO, the board might be considering bringing him back, according to reports. Anonymous sources told both the Wall Street Journal and New York Times that the board is considering walking back on its dramatic firing of Mr Altman. Both outlets reported that Microsoft, a prominent investor in the company, was leading the charge to reinstate Mr Altman. The company announced the leadership change on Friday. “Mr. Altman’s departure follows a deliberative review process by the board, which concluded that he was not consistently candid in his communications with the board, hindering its ability to exercise its responsibilities,” the company wrote. “The board no longer has confidence in his ability to continue leading OpenAI.” While publicly citing communication issues, behind closed doors, the board and Mr Altman appeared to diverge when it came to OpenAI’s future. Mr Altman was hoping to push development more aggressively than the board, CNN reported. Greg Brockman, the president and cofounder of OpenAI who was asked to leave the board, wrote on X that the operation to upend the leadership happened quickly. Mr Altman was asked to join a video call with the board at noon on Friday and was immediately fired. Mr Brockman was not a part of the video meeting, he said. Twenty minutes later, Mr Brockman was told that he could stay in his role, but was being removed from the board, he wrote. “We too are still trying to figure out exactly what happened,” Mr Brockman wrote. He later announced he was quitting “based on today’s news.” Following his exit, Mr Altman wrote on X: “i loved my time at openai. it was transformative for me personally, and hopefully the world a little bit. most of all i loved working with such talented people. will have more to say about what’s next later.” The Times also reported that Mr Altman and Mr Brockman have plans to launch a new startup in the wake of his ouster and are speaking to investors. Those plans have not been made public. Read More OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman ousted as CEO ChatGPT Plus stops signups after major update ChatGPT creator mocks Elon Musk in brutal tweet
2023-11-20 01:29
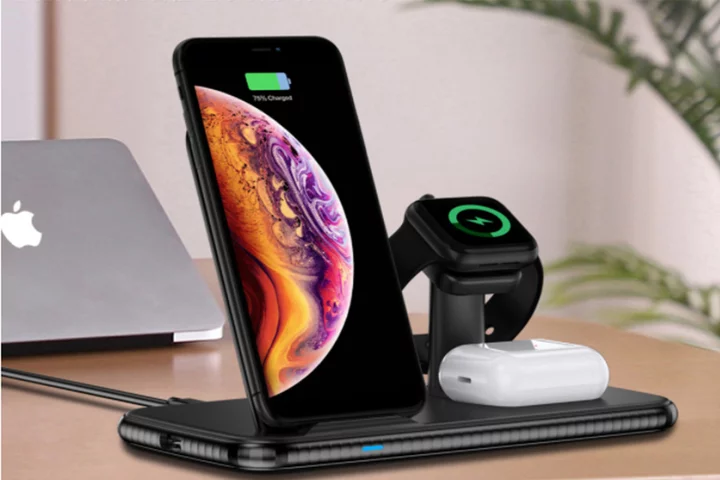

Save $40 on this 4-in-1 wireless charging hub
TL;DR: As of July 31, you can get the Fast Charge 4-in-1 Wireless Charging Hub
2023-07-31 17:54

JD.com’s Sales Beat Estimates Despite Chinese Economy Weakness
JD.com Inc.’s revenue accelerated in the second quarter after its signature 6.18 festival scored with shoppers, helping the
2023-08-16 18:46

Astronomers find zombie planet that ‘shouldn’t exist’
Scientists have found a new planet they shouldn’t exist, after it seemed to miraculously survived the violent death of its star. Many planets, including our own, face almost certain doom when their stars reach the end of their lives and engulf them. When our own Sun dies, for instance, it will expand to 100 times and swallow the Earth. But the new study offers hope that at least some of those planets are able to survive. The newly discovered world, a Jupiter-like planet known as Halla, managed to survive the demise of its star Baekdu, in what should have been certain death. Astronomers found the planet and discovered through follow-up observations that Baekdu had previously expanded into a red giant. When it did, it would have inflated up to 1.5 times the distance between it and Halla, engulfing the star, and then shrunk back down to its current size. Despite that dramatic and violent event, Halla has managed to persist, sticking around so that astronomers could see it using telescopes in Hawaii. “Planetary engulfment has catastrophic consequences for either the planet or the star itself - or both. The fact that Halla has managed to persist in the immediate vicinity of a giant star that would have otherwise engulfed it highlights the planet as an extraordinary survivor,” said Marc Hon, the lead author of the study. The findings are published in a new paper, ‘A close-in giant planet escapes engulfment by its star’, in the journal Nature today. Halla was found in 2015, using what scientists call the “radial velocity method”, which monitors how stars move and uses that to understand how they might be tugged around by the planets that orbit them. In the years since, scientists found that the planet must have been engulfed by the star, and conducted follow-up observations to better understand the planet. Those observations confirm that the planet had been in its stable orbit for over a decade, and that it really existed. “Together, these observations confirmed the existence of the planet, leaving us with the compelling question of how the planet actually survived,” said IfA astronomer Daniel Huber, second author of the study. But scientists still do not know how it survived. One possibility is that it started on a larger orbit before moving closer to its star, but astronomers believe that is unlikely. Another is that Baekdu was actually once two stars. They may have merged during their death, sparing Halla from being merged at all, by stopping them getting big enough to engulf it. And a separate possibility is that Halla was actually born out of the collision of the two stars. That might have produced a gas cloud that actually gave birth to Halla, and so it may be the result of the demise of its star rather than a survivor of it. Read More Nasa rover spots bizarre donut shaped rock on Mars Strange alien planet could be trapped in edge of the Solar System SpaceX Starship completes six-engine static test fire at base in Texas
2023-06-28 23:26

How to unpin Snapchat's My AI from your Chat feed
Bad news: If you aren't a Snapchat+ subscriber, you can't remove My AI from your
2023-05-10 20:54

Seoul Semiconductor Unveils 2nd-generation LED Technology for Future Displays at Display Week 2023
ANSAN, South Korea--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 24, 2023--
2023-05-24 21:28
You Might Like...

Hundreds of hoax Facebook posts are terrifying people into sharing them, fact checkers warn

Snag studio-quality Bose headphones 700 for under $300

Ninja: Which gaming headset does pro gamer use? Here's what you need to know

Disney, The New York Times and CNN are among a dozen major media companies blocking access to ChatGPT as they wage a cold war on A.I.

Ondine Biomedical Appoints Senior Pharma Executive Dr. Simon Sinclair as Chief Medical Officer
India landed on the Moon for less than it cost to make Interstellar

China's Leapmotor unveils C10 SUV at Munich car show

Anghami Files 2022 Annual Report With 37% Revenue Growth & Announces Q1 2023 Results With 60% Improvement in EBITDA
