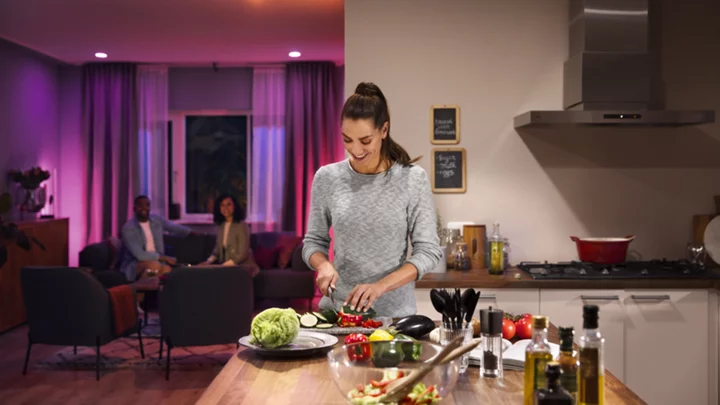

The Best Smart LED Light Bulbs for 2023
Light bulbs have grown exponentially smarter in recent years. You can now replace your standard
2023-07-06 04:47
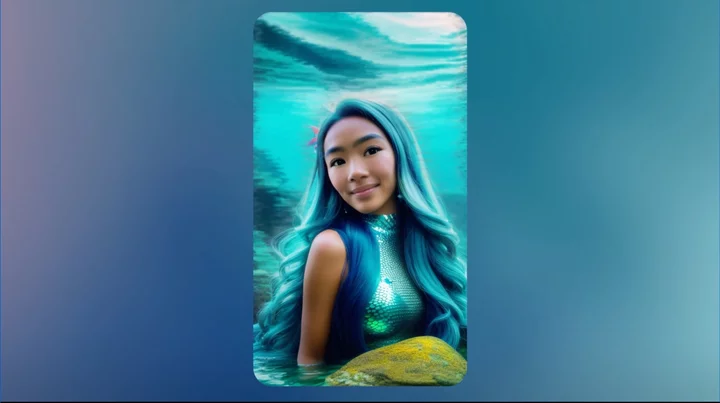

Snapchat Dreams conjures up fantastical AI-generated selfies
Snapchat is barreling ahead with generative AI features with a new selfie tool called Dreams.
2023-08-30 00:50
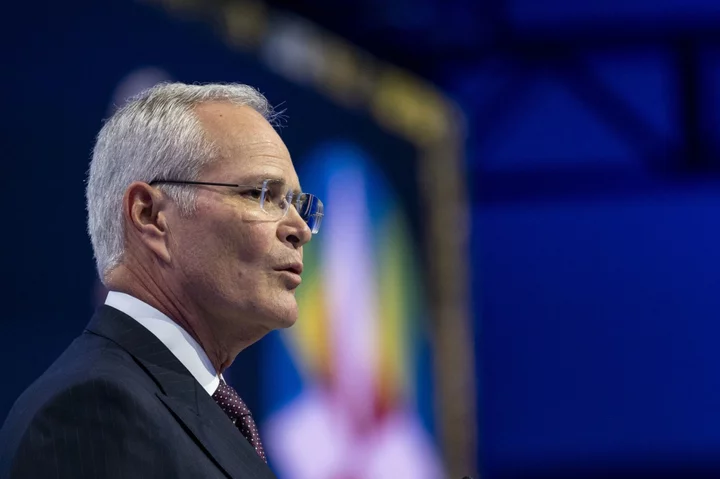

Exxon CEO, a Climate Villain to Many, Makes His Debut at COP
Exxon Mobil Corp. CEO Darren Woods cuts a strange figure at the COP28 climate summit — an oil
2023-12-02 21:22
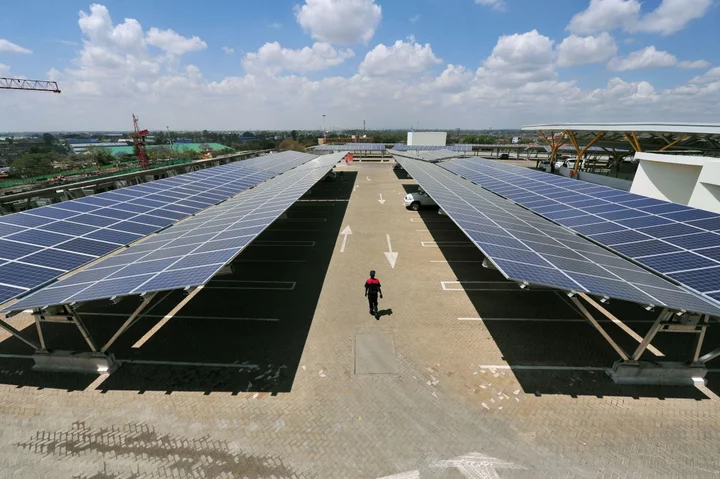

Camco Fund to Mobilize $1.6 Billion for Africa Power
A UK-government backed renewable energy fund plans to mobilize $1.6 billion to help provide 16 million people and
2023-11-17 20:22

VINSSEN to Attend Nor-Shipping 2023 in Oslo, Norway
SEOUL, South Korea--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 5, 2023--
2023-06-05 15:21

Germany to Hook Up Industrial Hubs With Hydrogen Supplies
Germany unveiled plans to connect industrial hubs near the Rhine, the south and the east of the country
2023-07-12 19:24

Content Catalyst Rebrands Analyst Research Platform, Publish Interactive
CAMBRIDGE, England--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 14, 2023--
2023-07-14 18:26

Does Tristan Tate run a brothel? Controversial influencer suggests troll to 'look for job' after grave accusation: 'Nothing to do with pimping'
Tristan Tate said, 'The world is shocked to find out that although I’ve been accused of human trafficking it’s nothing to do with selling people'
2023-07-13 18:47
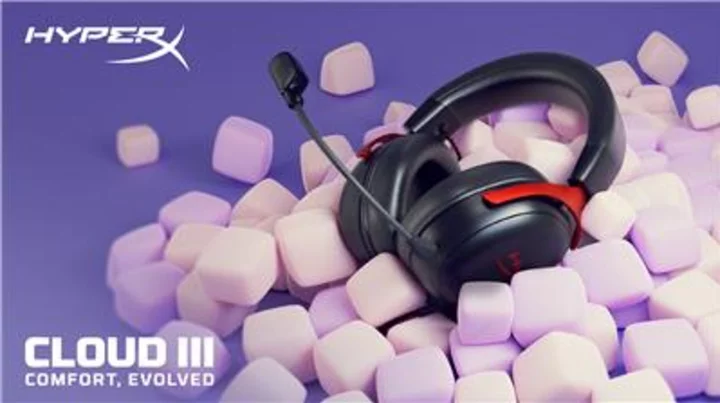

HyperX Announces Cloud III Gaming Headset
FOUNTAIN VALLEY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 30, 2023--
2023-05-30 18:18

Suspended Twitter account tracking Elon Musk's jet moves to rival Meta's Threads
Jack Sweeney, the creator of an account tracking Elon Musk's private jet in real time, has moved to
2023-07-09 00:26

Mujin Secures $85 Million in Series C Funding to Accelerate Adoption of Intelligent Robotic Automation
TOKYO & ATLANTA--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 5, 2023--
2023-09-05 22:23

How Fortnite Players Can Get Their Share of the $245M In-App Purchase Settlement
Late last year, the FTC fined Epic Games $520 million for tricking players into buying
2023-09-22 07:17
You Might Like...
StrongPoint Partners With Leading Supply Chain Solutions Provider Blue Yonder

Norway fines Facebook owner Meta over privacy breaches

SEGA Europe is set to acquire Angry Birds maker Rovio
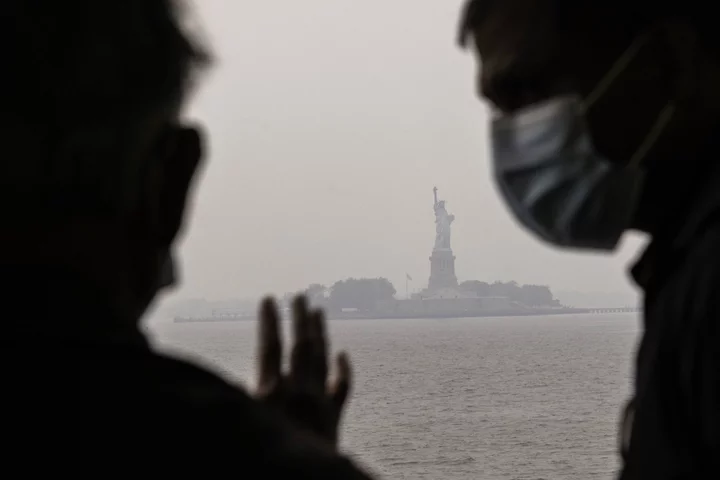

Deutsche Bank Executive Warns of Growing ‘Fat Tail’ ESG Risk
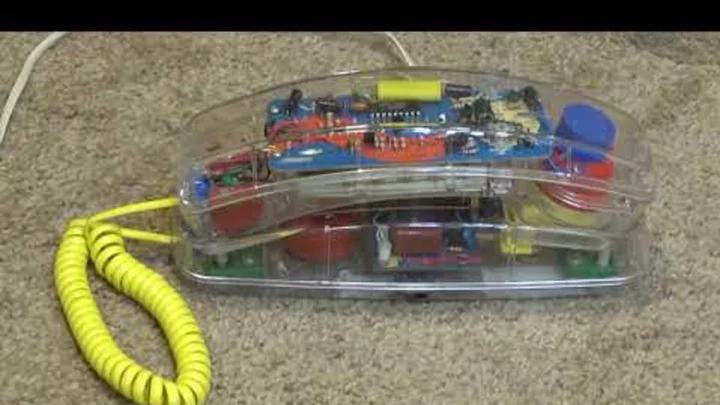

Loud and Clear: When See-Through Telephones Ruled the ‘90s
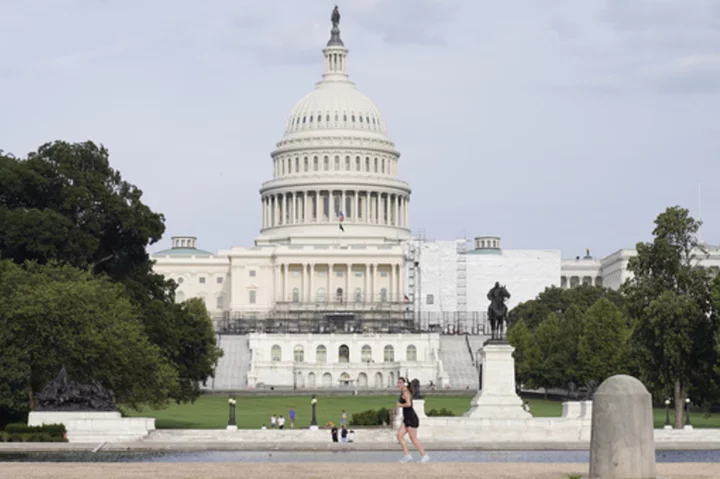

Prosecutors in all 50 states urge Congress to strengthen tools to fight AI child sexual abuse images

MTG Lord of the Rings: Tales of Middle Earth Pre-Release Dates

Adin Ross: Broadcaster's statement about streaming leaves NBA pro Dennis Schroder baffled
