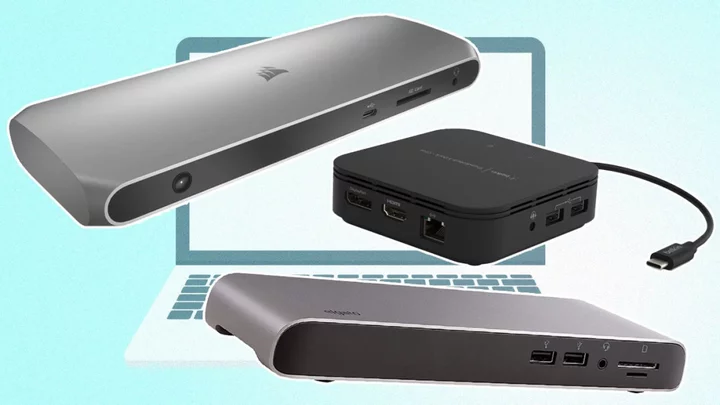

How to Choose the Best Laptop Docking Station
At your desk or on the go, are you forever unplugging devices from your laptop
2023-07-15 22:48
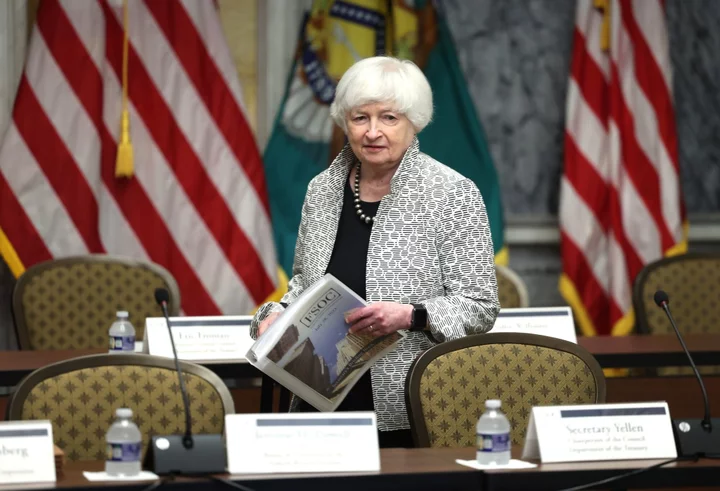

Yellen Pushes Treasury, World Bank to Fuller Climate Reckoning
Janet Yellen planted a flag during her confirmation hearing in January 2021. Climate change, she declared, was an
2023-09-20 05:53
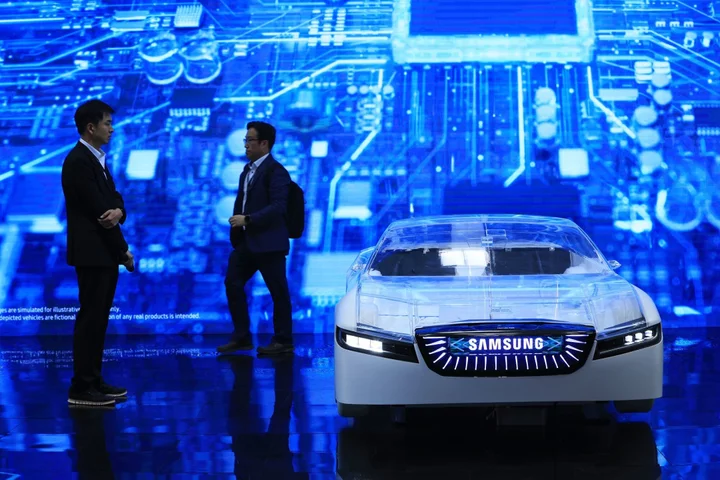

It's Done. The Future Is Battery-Powered Electric Cars
The rise of electric cars is staggering. Over the past decade, Teslas have gone from being the car
2023-10-05 13:23
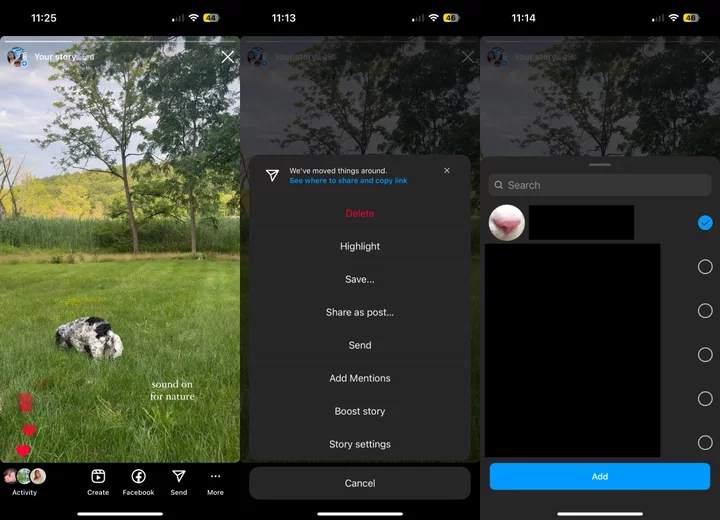
Forgot something? You can add mentions in an Instagram Story after it's posted
It's true: You can add mentions in an Instagram Story even after it's posted. And
2023-07-08 19:27

The Tesla Cybertruck is closer than ever - but people don’t seem impressed
When Tesla revealed its Cybertruck in 2019, it didn’t go so well. The supposedly bulletproof windows were smashed when hit by a metal ball, much to the embarrassment of chief executive Elon Musk. Now, the electric car company is nearing the point when it starts shipping the product – which it says is new and improved – but people still aren’t particularly impressed. Musk has said deliveries can be expected at the end of this year, with mass production set to begin in 2024. And during the firm’s latest earnings update this week, it gave a fresh sneak peak of the highly anticipated truck driving through a desert. But eagle eyed observers have already noticed a problem: the wiper doesn't cover the whole windscreen. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The Tesla Cybertruck Is Officially HERE! www.youtube.com In the video, the Cybertruck’s enormous glass windscreen has been covered in muddy water, some of which is pushed away by the long, singular wiper. But the passenger’s side is still completely covered in mud. For $40,000 dollars, which is the Cybertruck’s expected cost, it’s probably safe to say you’d be disappointed. Meanwhile, the wiper also rests upright on the side of the windscreen, unlike most cars where it sits horizontally next to the bonnet. Tesla’s design chief Franz von Holzhause also shared a picture of him standing in front of a dust-covered Cybertruck at a construction site in Texas earlier this year, and the top part of the passenger side was again untouched by the wiper. Watch the Tesla Cybertruck's Windows Get Smashed www.youtube.com People took to Twitter to criticise the design. One person said: “Am I the only one who thinks that Tesla Cybertruck Windshield Wiper needs to be better? They can put two wipers, one on each side, just like it is now or at the bottom like a traditional one.” “They can even put a pushing motion on the one they have to get more coverage.” Another person added: “I can only imagine the visibility from inside this tin can is horrible.” Even Musk is aware of the issue. He told Fox News earlier this year: “The wiper is what troubles me most.” And on Twitter, he said there's “no easy solution” to the massive windshield, saying: “Deployable wiper that stows in front trunk would be ideal, but complex.” That said, at least there’s a wiper now. The famous 2019 version didn’t even have one. Keep plugging away, Tesla galaxy brains. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-21 21:59
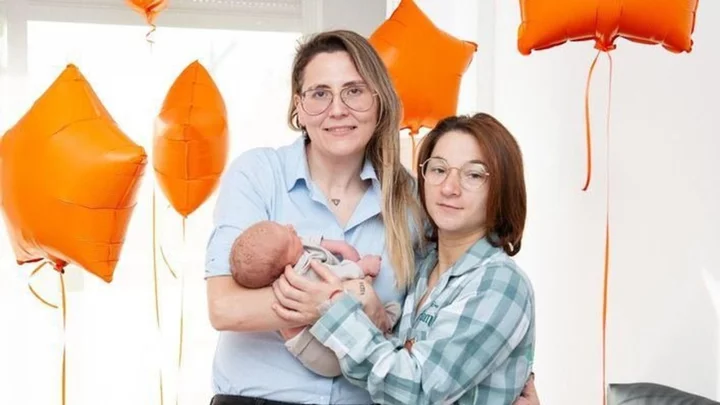

Same sex couple become first in Europe to have baby which they both carried
A lesbian couple have become the first in Europe and only the second in the world to have a baby they both carried. Little Derek Eloy came into the world weighing just over 7 lb 4 oz. Couple Estefanía, 30, and Azahara, 27, went to a fertility clinic in March to begin the process. A capsule of eggs and sperm was first placed into Estefania’s vagina. It was left for five days so the sperm could naturally fertilise the eggs in vivo. After the device was removed, the embryos were examined and selected before being transferred into Azahara’s uterus for further development. Azahara then carried Derek for nine months before giving birth to the healthy boy on 30 October. Derek’s birth in Palma, Majorca, was made possible thanks to an innovative fertility treatment called INVOcell. In total, the couple paid more than £4,400 (€5,000) for the treatment and the medication they had to take. A doctor from the team that made Derek’s birth possible explained: “The novelty in this process is that both could carry the embryo and share it for as long as needed.” Estefanía told local media: “It was a way for both of us to be able to carry him. “The idea that I could participate in this way and carry him in my womb was much more exciting.” Derek is the first European baby born via INVOcell. The technology has only been used once before - in 2018 by Texan couple Bliss and Ashleigh Coulter to allow them to carry their son, Stetson. Estefanía said: “Now, I look at him, my partner and I look at each other, and we feel that it’s something that has been within both of us, something we’ve done together.” Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-14 21:24

The best — and worst — social media apps in 2023 (so far)
For a bunch of people who supposedly hate social media, we sure do spend a
2023-06-02 17:57

Calendly Welcomes Former Salesforce Product Executive Stephen Hsu as CPO
ATLANTA--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 9, 2023--
2023-05-09 21:16
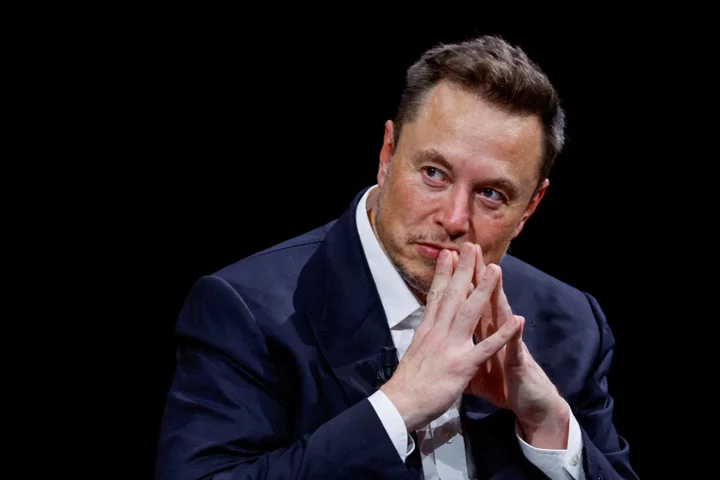

Elon Musk vows to sue ADL for calling him antisemitic after he promoted antisemitic campaign on X
Elon Musk has threatened to sue the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) for billions of dollars after quixotically blaming the Jewish rights organisation for spreading antisemitism on his social media platform X. The self-proclaimed “free speech absolutist”, who has amplified and reinstated neo-Nazi and far-right accounts since acquiring X, formerly known as Twitter, for $44bn last year blamed the ADL for “destroying” $22bn in the company’s value in a series of posts on Monday. “Since the acquisition, The ADL has been trying to kill this platform by falsely accusing it & me of being anti-Semitic,” Mr Musk wrote. He claimed that the site’s United States advertising revenue was down 60 per cent “primarily due to pressure on advertisers by ADL”. “If this continues, we will have no choice but to file a defamation suit against, ironically, the ‘Anti-Defamation’ League.” An ADL spokesperson told The Independent in a statement that it did not comment on legal threats, but added that Mr Musk was helping to boost a coordinated “Ban the ADL” campaign being waged by self-declared antisemites. “ADL is unsurprised yet undeterred that antisemites, white supremacists, conspiracy theorists and other trolls have launched a coordinated attack on our organisation. This type of thing is nothing new,” the ADL spokesperson said. “Such insidious efforts don’t daunt us. Instead, they drive us to be unflinching in our commitment to fight hate in all its forms and ensure the safety of Jewish communities and other marginalised groups.” Mr Musk’s threats to sue the ADL, a century-old NGO that describes itself as the “leading anti-hate organisation in the world”, were met with anger and disbelief from some commentators on X. “In his pursuit of some kind of utopian free speech universe, Elon Musk has turned Twitter / X into a free-for-all for Neo Nazis and White Extremists to unleash a torrent of unprecedented antisemitism and Jew hatred,” wrote Israeli human rights lawyer Arsen Ostrovsky. NYU professor Ruth Ben-Ghiat posted: “So it's the Jews manipulating others. Elon Musk that is so original!” Since Mr Musk’s takeover, advertisers have fled the platform or reduced their ad spend as hateful content was allowed to spread unchecked. Mr Musk, the world’s richest person with an estimated net wealth of $248bn, fired an estimated 80 per cent of its workforce, including most of its content moderators, and reinstated previously banned accounts. X’s US advertising revenue over a five-week period from April to May this year came to $88m, a 59 percent decrease from one year ago, according to the New York Times. In August, X filed a lawsuit against the Center for Countering Digital Hate (CCDH) after it published a report showing that moderators had failed to take action on 99 out of 100 examples of harmful content by verified “blue check” users that the organisation had flagged. “Musk is trying to ‘shoot the messenger’ who highlights the toxic content on his platform rather than deal with the toxic environment he’s created,” CEO Imran Ahmed said in a statement. “CCDH has no intention of stopping our independent research – Musk will not bully us into silence.” The Independent attempted to reach Mr Musk through X, Tesla and via a personal email address but did not hear back. Read More Elon Musk calls Burning Man ‘best art on Earth’ amid chaos that saw thousands stranded and one dead Elon Musk promotes transphobic content as hate speech surges on his far-right platform X threatens to sue researchers who accused Twitter of allowing ‘hate to prosper’ on platform
2023-09-06 00:45

Why doesn't Christine Brown share pics with Paedon? Internet speculates 'Sister Wives' star's relationship with son turned sour
'Sister Wives' star Christine Brown has always been seen posting about her daughters, but nver her son
2023-08-04 09:29
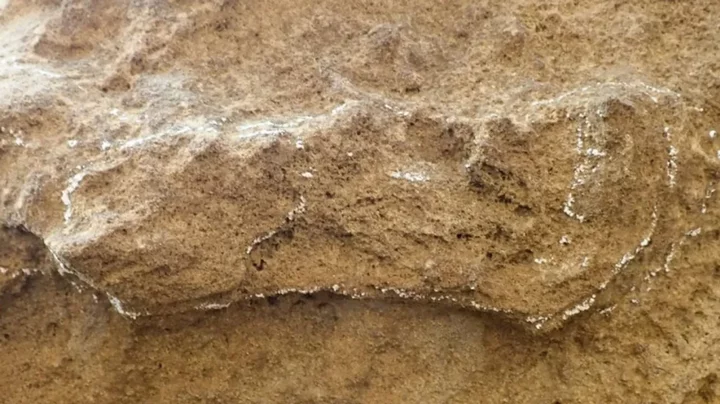

Study of oldest footprint ever may change the entire history of humanity
It’s not often that a single scientific discovery manages to change the way we think about the entire history of humanity. An ancient footprint has been newly uncovered, and it turns out that humans were walking around 30,000 years earlier than we previously thought. Two-legged homo sapiens were living in South Africa, it’s been proven, following the discovery of a 153,000 year old track. It was found in the Garden Route National Park near the coastal town of Knysna on the Cape South Coast. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The footmarks outdate the oldest previous discoveries, with the previous oldest found in nearby areas dated at 124,000 years old. The discoveries were made possible thanks to the optically-stimulated luminescence dating method, which analyses how long it’s been since a grain of sand has been exposed to sunlight. Researchers Charles Helm of Nelson Mandela University and the University of Leicester's Andrew Carr wrote in the Conversation: "In 2023, the situation is very different. It appears that people were not looking hard enough or were not looking in the right places. "Today, the African tally for dated hominin ichnosites (a term that includes both tracks and other traces) older than 50,000 years stands at 14. "Given that relatively few skeletal hominin remains have been found on the Cape coast, the traces left by our human ancestors as they moved about ancient landscapes are a useful way to complement and enhance our understanding of ancient hominins in Africa." The scientists involved believe that the area could be home to many illuminating discoveries given the makeup of the soil. They wrote: "We suspect that further hominin ichnosites are waiting to be discovered on the Cape South Coast and elsewhere on the coast. "The search also needs to be extended to older deposits in the region, ranging in age from 400,000 years to more than 2 million years. "A decade from now, we expect the list of ancient hominin ichnosites to be a lot longer than it is at present – and that scientists will be able to learn a great deal more about our ancient ancestors and the landscapes they occupied." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-16 21:26
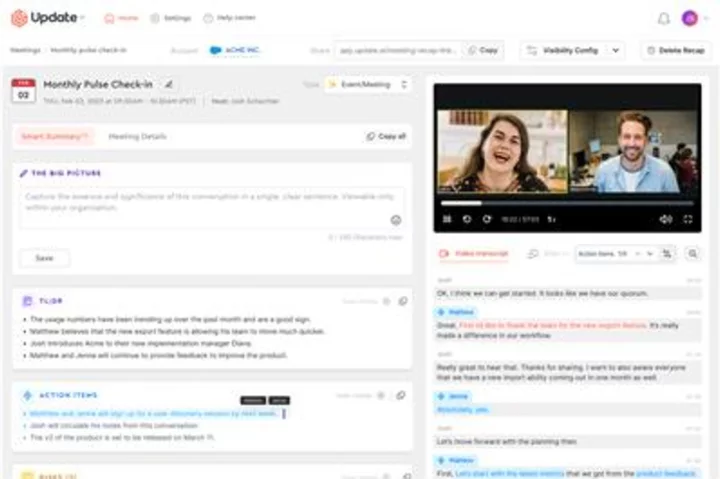
UpdateAI Lands $2.3M to Ignite Customer Success with Cutting-Edge AI Technology
PASADENA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-01 21:18
You Might Like...
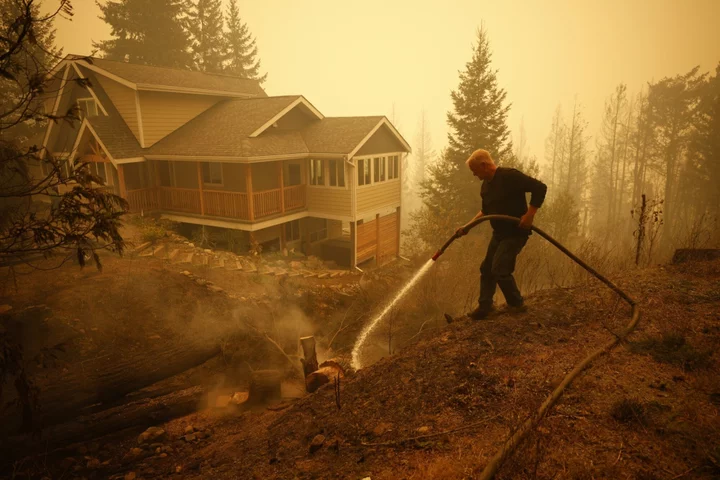

Trudeau Slams Facebook for Blocking News With Wildfires Raging in Canada

Nvidia Still Leads AMD, Intel In the AI Chips Race. How It Plans to Stay Ahead.

Tech companies try to take AI image generators mainstream with better protections against misuse

German Banking Regulator BaFin’s Website Hit by Cyber Attack
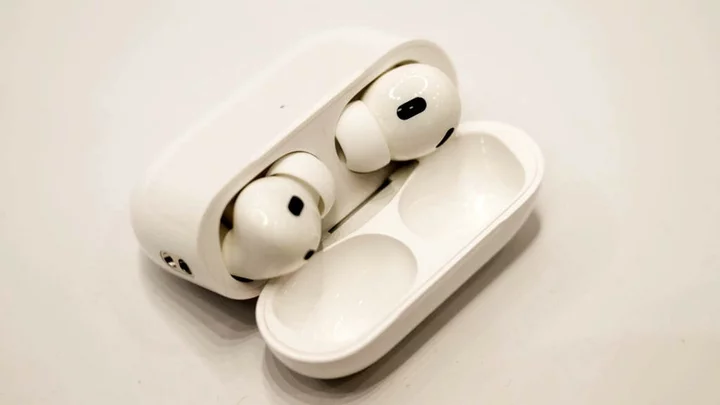

How to pair Apple AirPods with an Android device
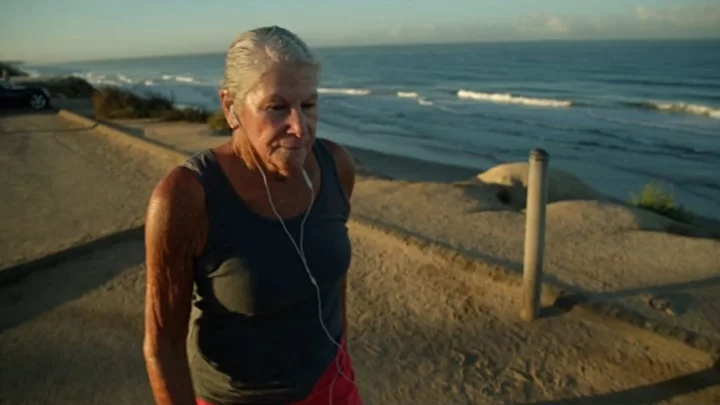

This is why time ‘speeds up’ when we get older, according to scientists
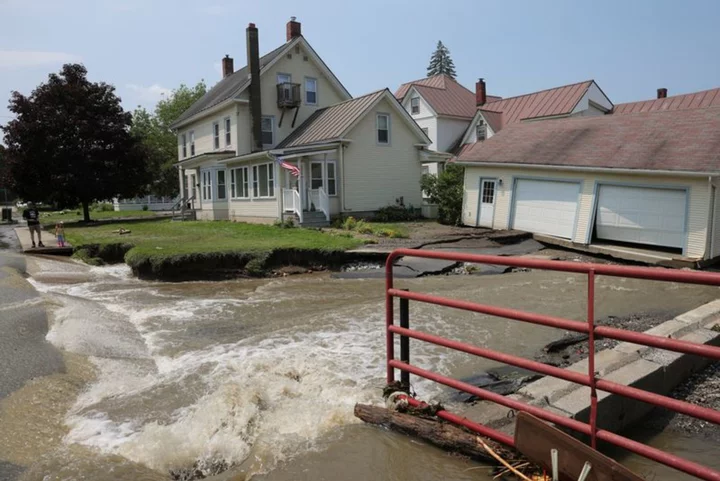

Vermont reservoir threatens to bring more flooding to state capital
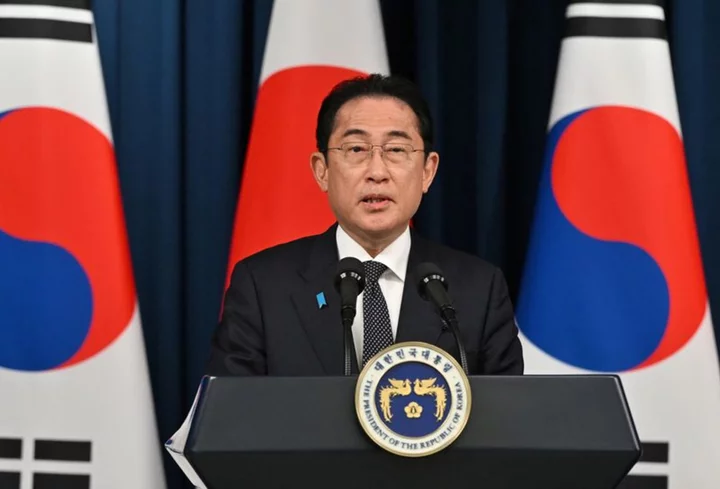

In symbolic Hiroshima, U.S. allies size up an ascendant China and unpredictable Russia
