
Zscaler Had a Good Quarter. Why Analysts Aren’t Worried About Its Stock Fall.
Zscaler stock is suffering despite Wall Street hailing the last quarter as evidence of its strong business. The security-software company’s caution about its guidance looks to have disappointed the market but analysts aren’t too concerned.
2023-11-28 19:50

Gensler Claims More Crypto Turf in Washington as Dissent Dithers
Gary Gensler’s Securities and Exchange Commission is filling the crypto regulatory void, and the industry and its backers
2023-07-11 18:28

Netflix Has Been Threatening to Crack Down on Password Sharing for Years—Now They're Finally Doing It
When it comes to password sharing, Netflix no longer has any chill.
2023-05-25 01:54

'Don't steal our voices': dubbing artists confront AI threat
Voice actors around the globe are mobilizing against the unregulated use of artificial intelligence (AI) to generate and clone human voices that they fear poses...
2023-06-21 10:30

Alphabet, Microsoft, Meta, Amazon, Boeing, and More Stocks to Watch This Week
Third-quarter earnings from Big Tech, auto makers, and more. Plus, a first look at GDP growth and the Federal Reserve's preferred inflation measure.
2023-10-23 02:16

Seasoned Analyst, Scott Devitt Joins Wedbush Securities as Managing Director, Equity Research, Internet: E-commerce and Online Travel
LOS ANGELES--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 20:17

GOP candidate's wife portrays rival's proposed pay raise for school personnel as unfeasible
The wife of Republican gubernatorial nominee Daniel Cameron has dismissed the Democratic governor’s proposal for an 11% pay raise for public school personnel as unfeasible
2023-09-15 05:24

Andrew Tate backs Twitter user's offensive opinion of women finding cheating partners appealing, Internet says 'as if you're different'
'You sure think you know a lot about women for someone who has never been in a successful relationship,' a criticizer remarked
2023-08-07 20:16

Global rules leave crypto firms with no place to hide, says G20 watchdog
By Huw Jones LONDON Globally agreed rules leave crypto firms with no option but to introduce basic safeguards
2023-07-17 15:28

DIC Graphics Releases Updated Version of DIC Digital Color Guide
TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 22:20

Cisco Gives Tepid Annual Forecast, Stoking Fears of Slowdown
Cisco Systems Inc., the largest maker of computer networking equipment, gave a lukewarm revenue forecast for the coming
2023-08-17 05:20
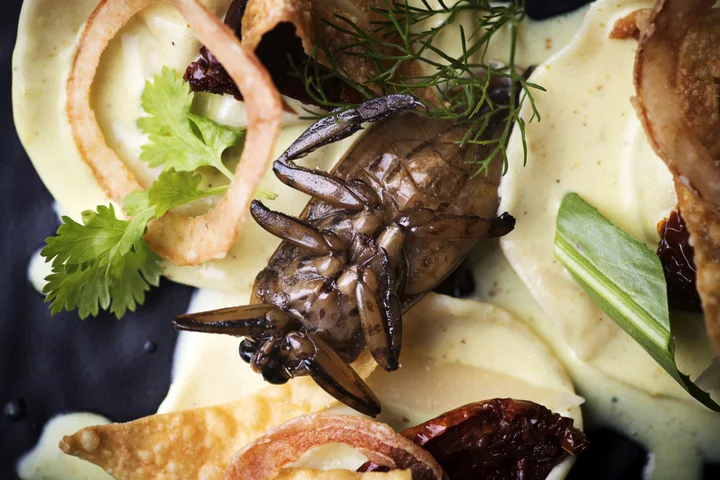

Edible Insects and Exotic Plants May Be the Future of Food
You may see lab-grown meat and insects on the menu in future decades, as the world grapples with
2023-10-19 11:28
You Might Like...

Britain will host AI summit at World War Two code-breaking centre

Amazon expands pay-by-palm service in US grocery stores
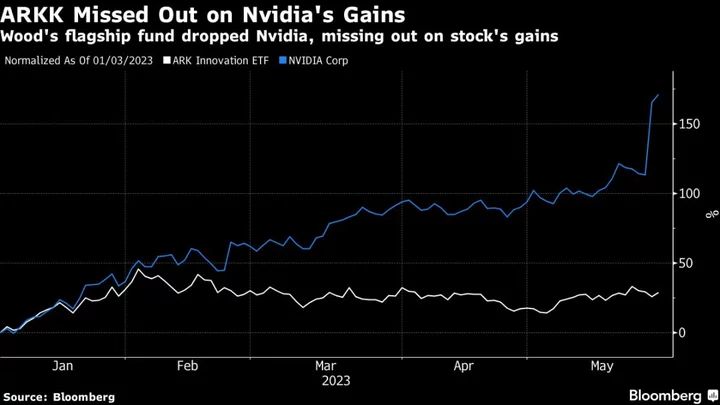
Cathie Wood Defends ARKK’s Decision to Dump Nvidia, Citing Chip-Cycle Risks

What you need to know about a glass cliff and why it could put Twitter's new CEO in danger

The iPad Air is on sale for its lowest price ever just in time for back to school

GIGABYTE’s AI Servers with Superchips Shine at COMPUTEX, Redefining a New Era of Computing

Google’s powerful ‘Bard’ AI chatbot can now get into your email

Hydro Venture Plans to Boost Madagascar Power Generation by 50%
