
15 Obscure Words That Are Pure Fire
The world is heating up, and things are often on fire—literally. As we do what we can to squelch the flames, check out some old and obscure words people of the past used when they wanted to talk about all things fire.
2023-08-08 20:21

Apple to update iPhone 12 in France after fears over radiation
Apple will update the iPhone 12 in France after fears it was emitting too much radiation. The company will issue an update to users in the country that it said would address regulators’ concerns. It comes after officials ordered Apple to stop selling the phone, saying that testing showed that its radiation was over European Union Standards. Apple says that the iPhone 12 is safe and that it has successfully passed a range of tests in countries around the world. It has blamed the specific testing used by the French agency in charge, saying that the problems were “related to a specific testing protocol”. The French agency said the iPhone 12 recently failed one of two types of tests for electromagnetic waves capable of being absorbed by the body. On Tuesday, France’s government ordered a halt to sales of the iPhone 12 and told Apple to issue a software update to address the problem or face a recall. Apple said in a statement Friday that it “will issue a software update for users in France to accommodate the protocol used by French regulators.” It did not elaborate. The French ban could have extended to all 27 EU countries after three months if Apple had refused to issue updates and if no other government objected, European Commission spokesperson Sonya Gospodinova said Thursday. France’s digital affairs minister said the iPhone 12’s radiation levels are still much lower than what scientific studies consider potentially harmful to users, and the radiation agency acknowledged that its tests don’t reflect typical phone use. Cellphones have been labeled as possible carcinogens by the World Health Organization’s cancer research arm, putting them in the same category as coffee, diesel fumes and the pesticide DDT. The radiation produced by cellphones cannot directly damage DNA and is different from stronger types of radiation like X-rays or ultraviolet light. Experts have recommended that people concerned about their cellphone radiation exposure use earphones or switch to texting. Additional reporting by agencies Read More Warning over criminals using digital switchover to scam vulnerable people TikTok fined 345m euro by watchdog over use of children’s data Apple Store goes offline as Apple opens pre-orders for iPhone 15
2023-09-15 23:57
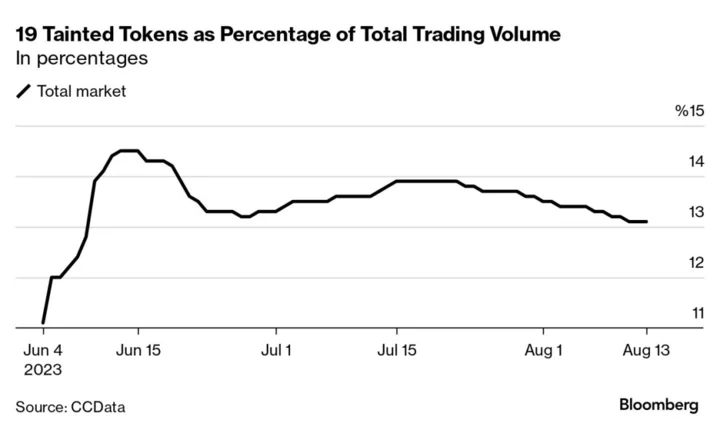
Cryptocurrencies Tainted by SEC Lawsuits Are Seeing an Increase in Trading
The impact of the SEC crackdown on crypto appears to be fading for the 19 tokens designated as
2023-08-15 18:19

10 of the best online web development courses you can take for free this week
TL;DR: A wide range of online web development courses are available for free on Udemy.
2023-05-18 12:26

Pre-Order the USB-C AirPods Pro at Best Buy, Save $50
Looking to upgrade your AirPods Pro? A new version with a USB-C charging case launches
2023-09-20 07:54

RAZ Mobility Launches Accessible and Innovative Smartphone for People Who Are Blind or Visually Impaired
CABIN JOHN, Md.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 1, 2023--
2023-08-01 19:51
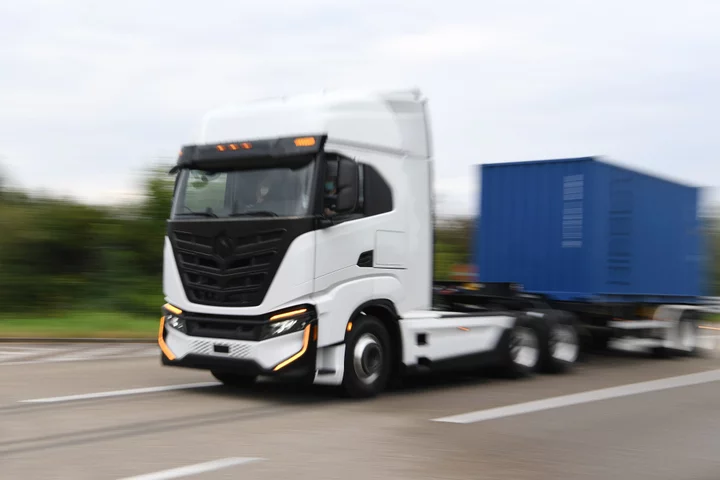

California Has an Electric Big Rig Mandate. Manufacturers Will Struggle to Meet It
California became the first state in the US to set emissions standards for trucks earlier this year. The
2023-10-18 21:57

ECM Wins 4 SaaS Awards for its PrintStator Electric Motor CAD Platform
NEEDHAM, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 19, 2023--
2023-09-19 21:54

Google should break up digital ad business over competition concerns, European regulators say
European Union regulators have hit Google with fresh antitrust charges, saying the only way to satisfy competition concerns about its lucrative digital ad business is by selling off parts of the tech giant’s main moneymaker
2023-06-14 23:53

Soccer giants FC Barcelona create Barca Games
FC Barcelona President Joan Laporta has hailed the creation of Barca Games.
2023-11-09 22:27

Black holes could contain 'hidden spacetime structures'
Black holes are the most confusing things out there in the universe and no-one really knows what they are – at least, that’s our very basic grasp of it. Now, though, a new study has posited a theory that black holes are structures created by unseen cosmic dimensions - or topological stars. And just to make it a little more confusing, these topological stars exist purely in the hypothetical realms of mathematics. Researchers at Johns Hopkins University have been exploring string theory, which posits that particles in the universe are actually tied to extra (hidden) dimensions through vibrating strings. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter According to their findings, hypothetical topological stars could exist for real in the universe and they’re essentially formations of nothing which could appear in space. The study finds that topological stars would appear “remarkably similar to black holes in apparent size and scattering properties, while being smooth and horizonless”. The study, which was published in Physical Review D, found that these stars which until now have only existed in hypothetical form, look an awful lot like the black holes out in the universe. “String theory is a theory that reconciles quantum physics and gravity into a quantum gravity theory,” study leader Pierre Heidmann said. Speaking to Motherboard, he said: “Usually when you have a new theory like that, you have new degrees of freedom that come with it, and you can try to see what new fundamental objects can arise from that.” Co-author of the study Ibrahima Bah added: “It’s an interesting question to ask: Are there things other than a black hole [that] will give you a hint about what new physics could look like?” “But before you get there, you need to know how to tell whether you have a black hole or not, and to do that you have some prototype examples of things that are not black holes to be able to compare." As ever, black holes remain the most mysterious, and the most fascinating things out there. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-24 20:20

Best Buy is reviving its 'Black Friday in July' sale to give Prime Day a big run for its money
It was a matter of when, not if, Best Buy announced some conveniently scheduled counter-programming
2023-06-24 01:29
You Might Like...

ChatGPT makes its debut as a smartphone app on iPhones

US SEC sues Coinbase, one day after suing Binance
Can't Stand a Certain App's New Icon? Your iPhone Will Let You Customize It
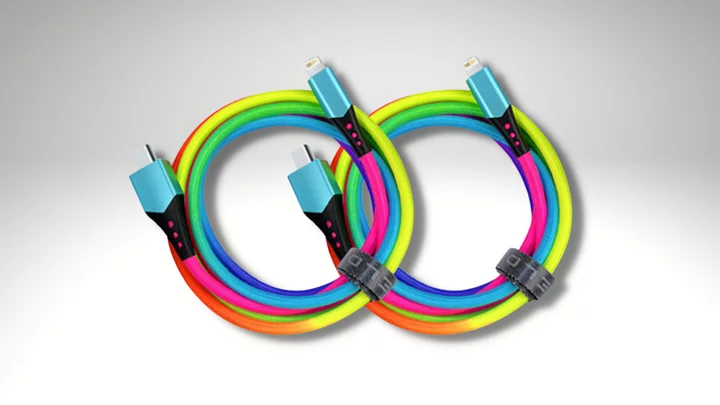

Grab two technicolored charging cables for under $40

Mega-cap firm valuations fall amid rising rates, tech earnings concerns

Head of US cybersecurity agency sees progress on election security, with more work needed for 2024
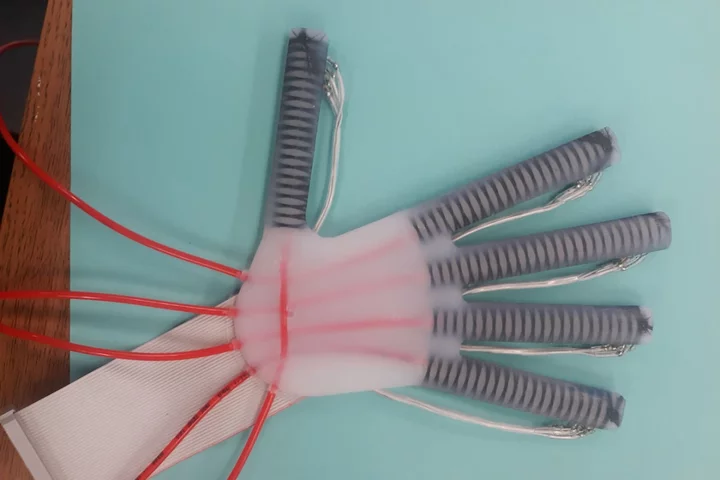
Smart gloves ‘could allow stroke patients to relearn to play the piano’

The Standard Names Dave Friesen Second Vice President of Enterprise Data and Analytics
