
AI pioneer warns UK is failing to protect against ‘existential threat’ of machines
One of the pioneers of artificial intelligence has warned the government is not safeguarding against the dangers posed by future super-intelligent machines. Professor Stuart Russell told The Times ministers were favouring a light touch on the burgeoning AI industry, despite warnings from civil servants it could create an existential threat. A former adviser to both Downing Street and the White House, Prof Russell is a co-author of the most widely used AI textbook and lectures on computer science at the University of California, Berkeley. He told The Times a system similar to ChatGPT – which has passed exams and can compose prose – could form part of a super-intelligence machine which could not be controlled. “How do you maintain power over entities more powerful than you – forever?” he asked. “If you don’t have an answer, then stop doing the research. It’s as simple as that. “The stakes couldn’t be higher: if we don’t control our own civilisation, we have no say in whether we continue to exist.” In March, he co-signed an open letter with Elon Musk and Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak warning of the “out-of-control race” going on at AI labs. The letter warned the labs were developing “ever more powerful digital minds that no one, not even their creators, can understand, predict or reliably control”. Prof Russell has worked for the UN on a system to monitor the nuclear test-ban treaty and was asked to work with the Government earlier this year. “The Foreign Office … talked to a lot of people and they concluded that loss of control was a plausible and extremely high-significance outcome,” he said. “And then the government came out with a regulatory approach that says: ‘Nothing to see here… we’ll welcome the AI industry as if we were talking about making cars or something like that’.” He said making changes to the technical foundations of AI to add necessary safeguards would take “time that we may not have”. “I think we got something wrong right at the beginning, where we were so enthralled by the notion of understanding and creating intelligence, we didn’t think about what that intelligence was going to be for,” he said. We've sort of got the message and we're scrambling around trying to figure out what to do Professor Stuart Russell “Unless its only purpose is to be a benefit to humans, you are actually creating a competitor – and that would be obviously a stupid thing to do. “We don’t want systems that imitate human behaviour… you’re basically training it to have human-like goals and to pursue those goals. “You can only imagine how disastrous it would be to have really capable systems that were pursuing those kinds of goals.” He said there were signs of politicians becoming aware of the risks. “We’ve sort of got the message and we’re scrambling around trying to figure out what to do,” he said. “That’s what it feels like right now.” The government has launched the AI Foundation Model Taskforce which it says will “lay the foundations for the safe use of foundation models across the economy and ensure the UK is at the forefront of this pivotal AI technology”. Read More ChatGPT creators try to use artificial intelligence to explain itself – and come across major problems Artificial intelligence could ‘transform’ heart attack diagnosis, scientists say Hackers aim to find flaws in AI - with White House help ChatGPT user in China detained for creating and spreading fake news, police say Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-05-13 21:51

Ford Hands Tesla a Big Win in VHS Versus Betamax-Like Battle
Hours before Tesla Inc. and Ford Motor Co. announced their surprise charging partnership, Ford’s chief executive officer offered
2023-05-30 23:50
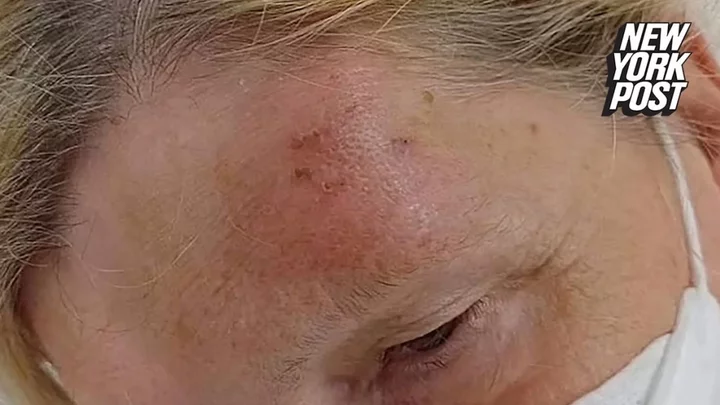
Pets pose a serious health threat that we've all been overlooking
While millions of people own cats and dogs and wouldn’t dream of getting rid of them, pets pose a health risk to humans that is massively overlooked, according to a new study. Since the Covid-19 pandemic swept the world with devastating impact, it has become evident how much of a risk new viruses can pose to our well-being. However, experts are warning that it is not just the wildlife trade or exotic animals that we should be concerned about, as pets could also be sources of zoonotic diseases (which jump from animals to humans). Back garden pets, house pets, working animals and even rodents and pests could host new viruses that could affect humans, according to a new study. It warns that the urbanisation of our habitats and climate change will have an impact on diseases and their dynamics. The study was shared in Science Translational Medicine and penned by disease ecologist Amandine Gamble along with a group of colleagues, who gave examples of how companion animals (aka pets) and stray animals carried a risk of zoonotic spillover. While the risk is thought to be small, experts warn it is significantly underappreciated, especially given the frequent proximity human beings have to pets and strays. The study said: “These animals can play critical roles in zoonotic spillover by enabling the maintenance of a zoonotic pathogen, facilitating its spatial spread, acting as a bridge between otherwise unconnected species, or providing particular opportunities for its evolution.” While the zoonotic spillover that caused Covid-19 sparked a global pandemic, any instance of infection that jumps from animal to human is known as a zoonotic, regardless of the numbers affected. Pet parrots are a known transmitter of the Chlamydia psittaci bacterium to humans. Elsewhere, bats and horses are also known sources of zoonotic diseases. In terms of common household pets, cats can act as a link to a number of fatal diseases. The experts explained: “Numbers of infections are low, but plague is endemic in 17 western U.S. states, and many of the small mammals on which cats prey carry Y. pestis. “Consequently, outdoor cats and cats with incomplete veterinary care, combined with human interaction, suggest that cat-transmitted plague can be considered an increasing public health risk.” They conclude that “it is critical to implement surveillance programs allowing us to track changes in pathogen dynamics”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-19 17:21

Google Veteran Steps Down as Manager in Cloud Shakeup
One of Google’s earliest employees will step back from an executive management role, having held a senior position
2023-07-12 16:25

'Diablo 4': Bella Poarch joins Simu Liu and Valkyrae for livestream
Bella Poarch is not alone and many streamers were insterested in playing the fourth installment in the 'Diablo' series
2023-06-12 20:29

Hands On: Dragon's Dogma 2 Delivers Hard-Hitting Action In a Dark Fantasy World
Capcom has had several excellent video game releases this year, and there are more hot
2023-10-27 02:45

TXOne Networks’ New Edge V2 Engine for OT Cybersecurity Delivers Industry’s First Capability for Automatic Rule Generation, Enabling Effortless Network Segmentation
IRVING, Texas, & TAIPEI, Taiwan--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 5, 2023--
2023-09-05 22:21
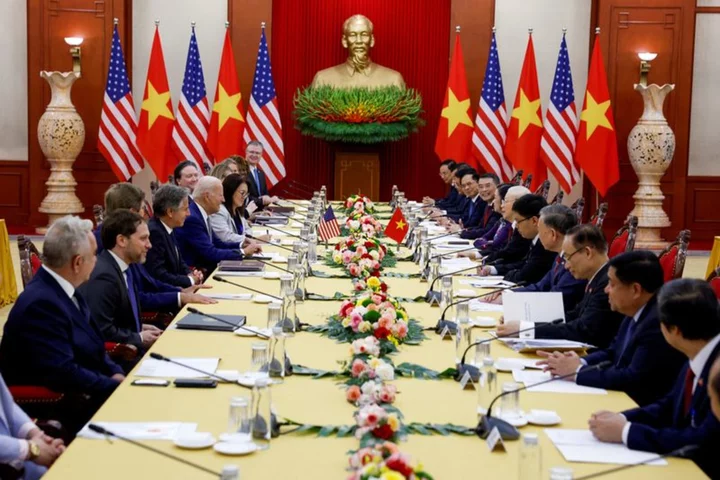

US, Vietnam firms hold business summit during Biden visit; AI deals unveiled
By Phuong Nguyen and Francesco Guarascio HANOI (Reuters) -Executives at top U.S. and Vietnamese firms in the semiconductor, tech and
2023-09-11 14:29

SoftBank seen returning to profit as tech stocks gain
By Anton Bridge TOKYO Japan's SoftBank Group is likely to report a return to profit when it announces
2023-08-07 08:25

China was reducing Micron chip purchases years before ban
By Eduardo Baptista BEIJING In the years before China declared U.S. firm Micron Technology's products a national security
2023-05-24 17:18

Belgium urges Apple to update iPhone 12 software across EU- minister
PARIS Belgium's state secretary for digitalisation said on Friday he had asked Apple to upgrade the iPhone 12
2023-09-15 22:25
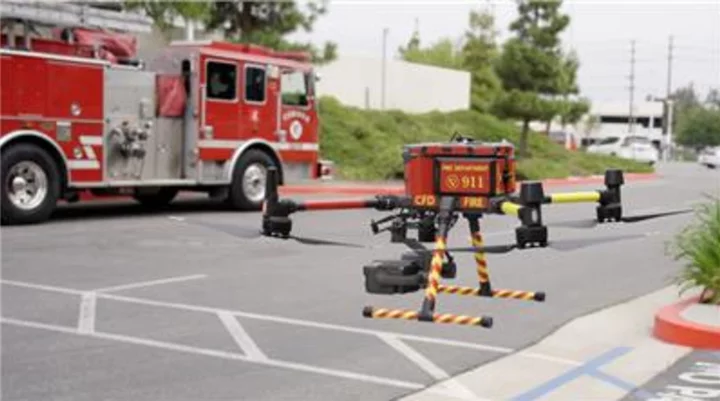

Fire Chiefs Gain Critical Access to Drone Tech and Streamlined Procurement with Cooperative Purchasing
KANSAS CITY, Mo.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 14, 2023--
2023-08-14 21:20
You Might Like...

Microsoft, Activision Weigh Sale of Some UK Cloud-Gaming Rights

China's SMIC sees lower Q4 gross margin, lifts annual capex forecast

Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 5 Battle Pass: What We Know So Far

Virginia finalizes guidance on transgender students, including rolling back some accommodations
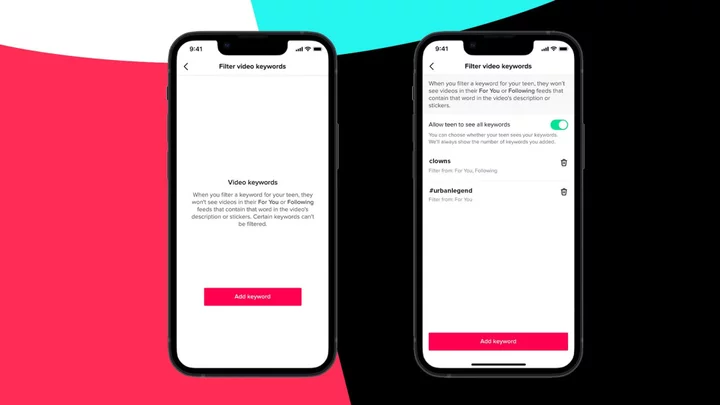
TikTok updates Family Pairing with new content filtering options

Tesla shares jump after Morgan Stanley predicts Dojo supercomputer could add $500 billion in market value

UK Needs Lower Energy Bills for Net Zero to Work, Says Ovo CEO

Sonic the Hedgehog’s US Workers Vote to Join Union
