
Skyflow Launches On AWS Marketplace
PALO ALTO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 27, 2023--
2023-07-28 05:19

ExaGrid Wins 2 Industry Awards at the Storage Awards 2023
MARLBOROUGH, Mass.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-13 20:24

Fintech Company Ballerine Announces $5 Million Seed Funding to Deliver Open-Source Risk Decisioning Platform
TEL AVIV, Israel & NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 23, 2023--
2023-05-23 20:54

Olivia Dunne unveils the key to success in building an NIL and social media empire
On Instagram, Olivia Dunne has over 4 million followers, and on TikTok, she has 7.4 million and of all 520,000+ athletes out there, she is the biggest
2023-06-02 13:29
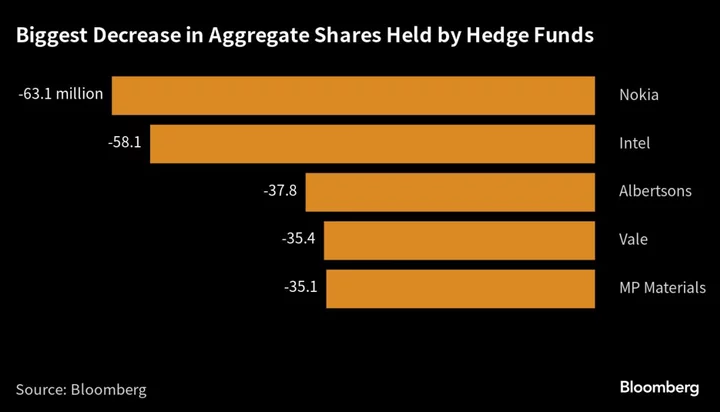
Hedge Funds Dump Intel While Snapping Up Rivals
While hedge funds were busy chasing the technology rally in the second quarter, there was one stock that
2023-08-16 19:15

NBA 2K24 Arcade Edition Release Date, Platforms
The NBA 2K24 Arcade Edition will likely release in October 2023 across all Apple platforms, including iPhones, iPads, Macs, and Apple TVs.
2023-09-29 23:17
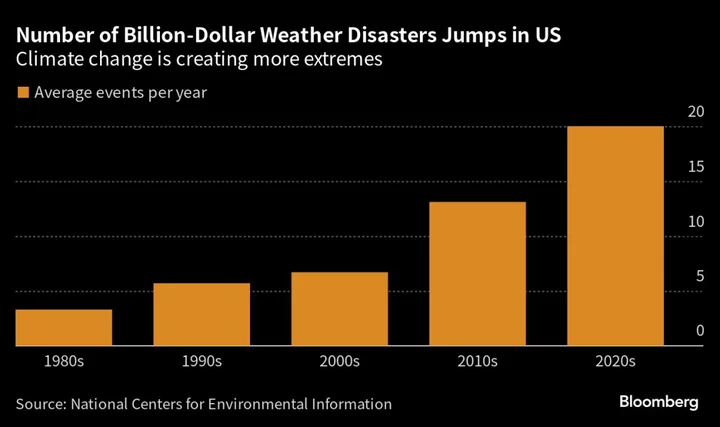
US Faced Record Number of Natural Disasters This Year With Losses Topping $1 Billion
There’s more than two months left in the year, but the US has already faced a record number
2023-10-11 01:50

The Best SSDs for Upgrading Your Laptop in 2023
Looking to upgrade your aging laptop? You can do only so much without a fabrication
2023-08-24 10:19

The solution to Twitter's downfall isn't five Twitter clones
It seems like every day, another self-described entrepreneur launches a Twitter without Elon (BlueSky); a
2023-06-23 17:58
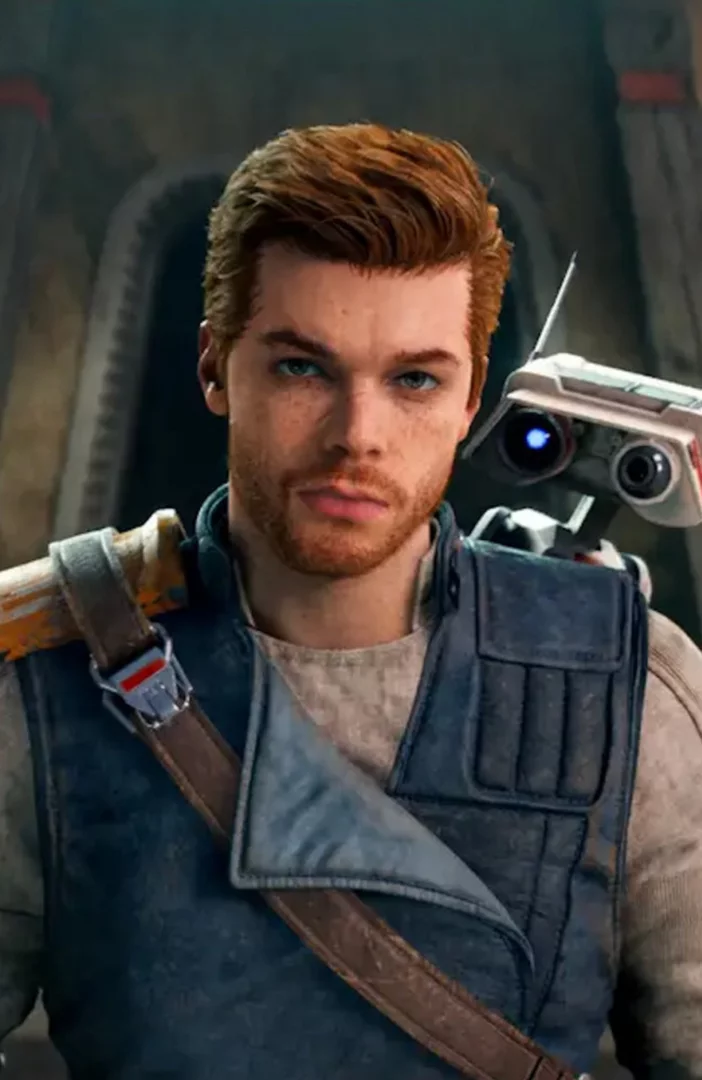

Star Wars Jedi: Survivor had 'millions' of players in first two weeks
'Star Wars Jedi: Survivor' is "pacing very strongly against" 'Jedi: Fallen Order'.
2023-05-11 19:23

How to unblock Kayo Sports for free
TL;DR: ExpressVPN is the best service for unblocking streaming services from around the world, including
2023-09-19 12:56
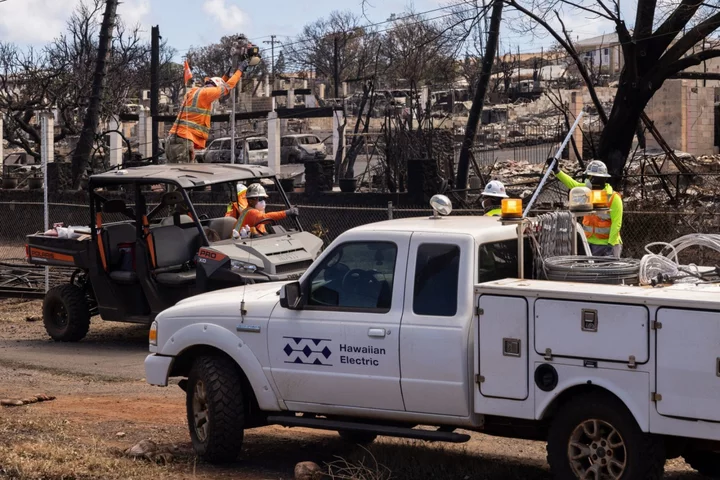

Hawaiian Electric Names Moelis Banker Scott DeGhetto as CFO
Hawaiian Electric Industries Inc. said it has named Scott DeGhetto of investment banking firm Moelis & Company as
2023-09-19 09:18
You Might Like...
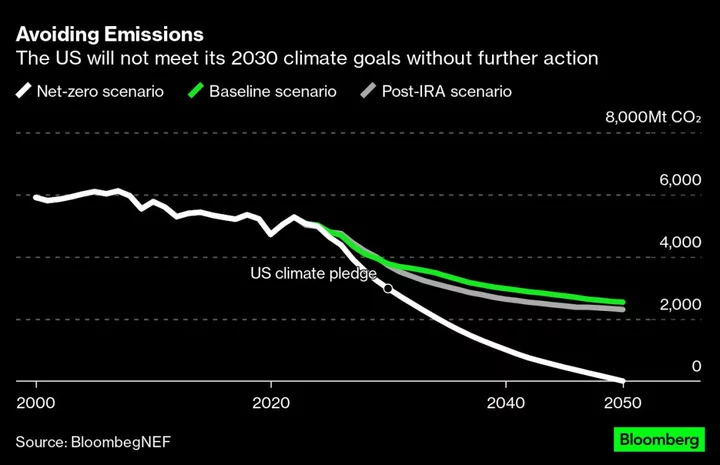
Biden's Climate Law Only Halves US Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050: Study

Put Down the Phone: How to Unplug With Google's Digital Wellbeing for Android

AI-altered political ads must now be disclosed on Google and YouTube

Uprite Services Achieves SOC 2® Type 1 Certification With Assure Professional

Bitcoin hits its highest level in a year

Xi Says China to Decide Its Own Path to Reduce Carbon Emissions

Ohmium Appoints Duncan Palmer as Independent Board Director

These Stocks Are Moving the Most Today: Paramount, Warner Bros. Discovery, Amazon, Instacart, and More
