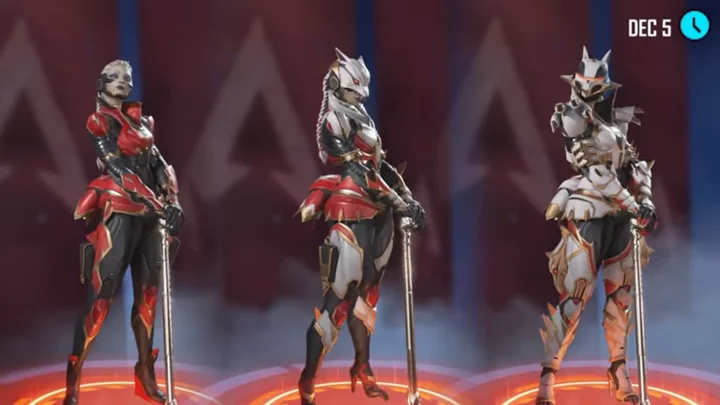

Apex Legends Uprising Collection Event: Skins, Release Date
The Apex Legends Uprising Collection Event features new skins for Valkyrie, Bangalore, and more, as well as the Loba Prestige skin, releasing on Dec. 5.
2023-11-28 01:22

DHL, Sasol Agree to Produce Sustainable Aviation Fuel in Germany
DHL Group, Sasol Ltd. and HH2E AG agreed to collaborate on producing sustainable, hydrogen-based aviation fuels in Germany
2023-09-25 18:53
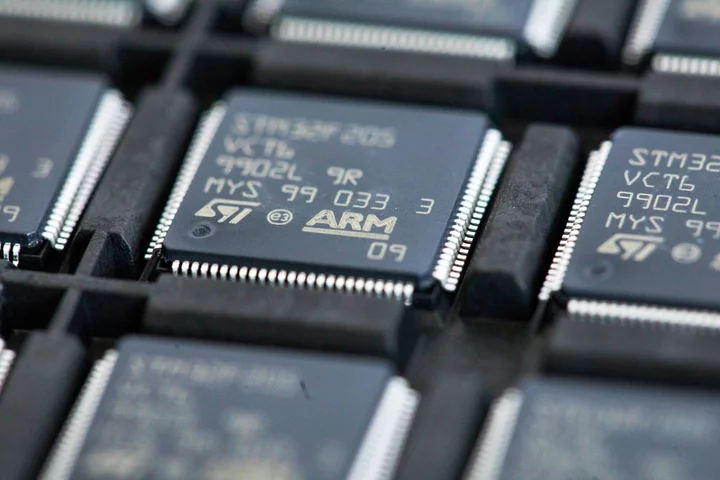
Amazon In Talks to Be Anchor Investor in Arm IPO, Reuters Says
Amazon.com Inc. is in talks to join other tech companies as an anchor investor in Arm Ltd.’s initial
2023-08-09 06:58
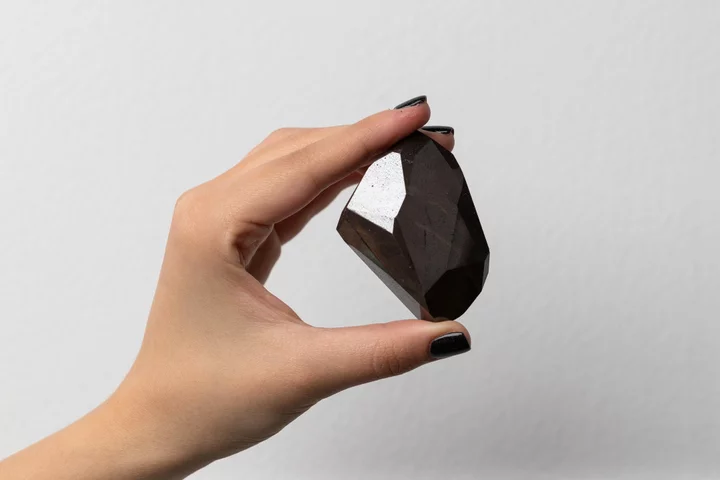

Huge Diamond Bought Illegally With Crypto Proceeds, SEC Alleges
The creator of crypto token Hex illegally used millions of dollars of investor funds to buy a 555-carat
2023-08-01 00:45

WiSA Technologies Announces 3-Channel Output Support for its WiSA E Receiver Module
BEAVERTON, Ore.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 21, 2023--
2023-09-21 19:27

Ex-Bethesda design director hints at The Elder Scrolls 6 being similar to Skyrim and Oblivion
Former Bethesda design director Bruce Nesmith is having his say on what he anticipates 'The Elder Scrolls 6' to be like.
2023-10-24 20:45

Score this mini body camera on sale for just $38
TL;DR: As of August 24, you can get the Mini Body Camera Video Recorder for
2023-08-24 17:51
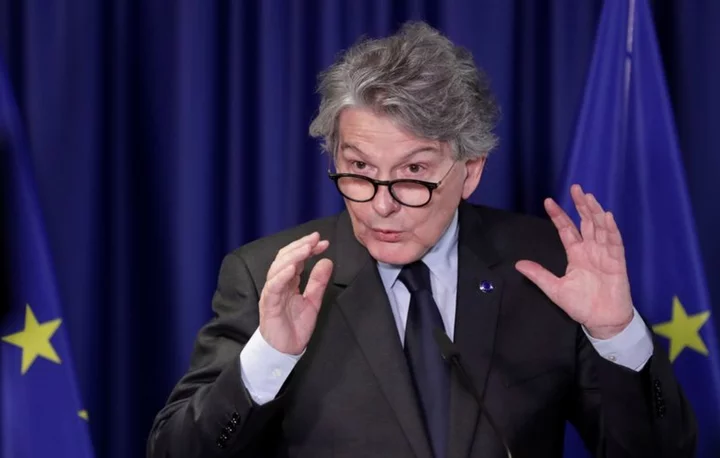

EU's Breton urges Big Tech to use new online content rules to restore trust
By Foo Yun Chee BRUSSELS Alphabet's Google, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, Twitter, TikTok and other tech giants should use
2023-08-24 04:59
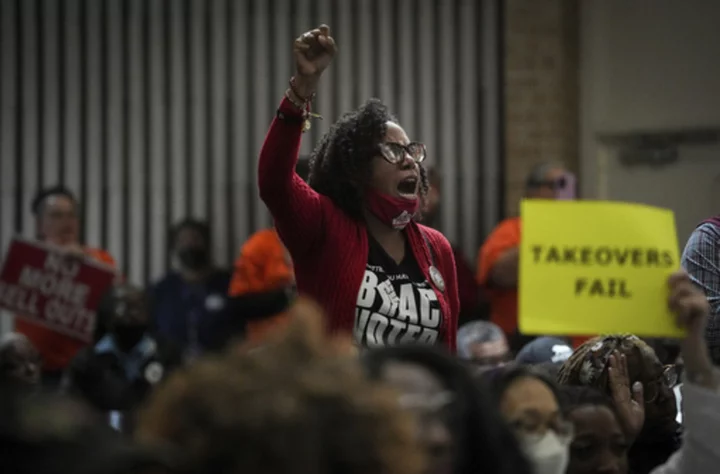
Texas takeover raises back-to-school anxiety for Houston students, parents and teachers
The largest school district in Texas is opening a new chapter as it begins the school year
2023-08-28 12:46

The best VPNs for Chrome
Google Chrome is the most popular web browser in the world, and it's already highly
2023-08-07 18:16

Mizkif slams Twitch after Alinity’s twerk ban; pro gamer bombarded with streaming offers
Popular streamer Mizkif criticized Twitch's ban regulations after Alinity received a three-day suspension for 'sexually suggestive' content
2023-06-01 13:56
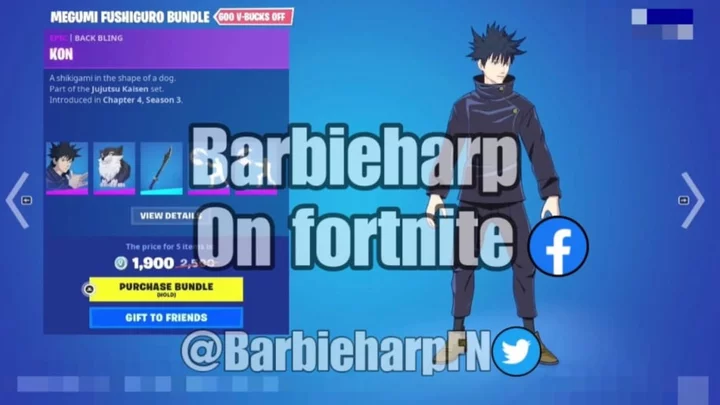
LEAK: Fortnite x Jujutsu Kaisen Skins Coming
Fortnite Jujutsu Kaisen skins have been leaked for Megumi Fushiguro, Nobara Kugisaki and Satoru Gojo.
2023-08-01 03:17
You Might Like...

Tristan Tate expresses admiration for Dillon Danis while mocking Logan Paul's fiancee Nina Agdal, Internet says 'he made it personal'

Diablo 4 Season 1: What We Know so Far

SmartSoda® Expands Distribution Reach Through Partnership with Consolidated Services Group, LLC

7 Fascinating Facts About Jhumpa Lahiri

Biden Blocks Activist Bid to Slash Oil Output From Federal Lands
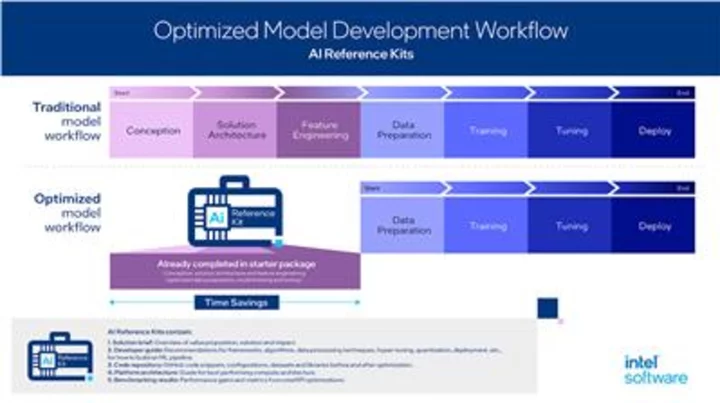
Intel Accelerates AI Development with Reference Kits

California Water Reservoirs Are Still Brimming as El Niño Looms

Apex Legends Promo Codes October 2023: How to Redeem
