
Supreme Court strikes down affirmative action in college admissions, and Biden 'strongly' disagrees
President Joe Biden says he “strongly, strongly” disagrees with the Supreme Court’s decision to strike down the use of affirmation action in college admissions
2023-06-30 01:18

PewDiePie: Twitch unbans YouTuber after 3-day ban without even streaming
PewDiePie hasn't been active on Twitch for a long time now
2023-05-13 12:50
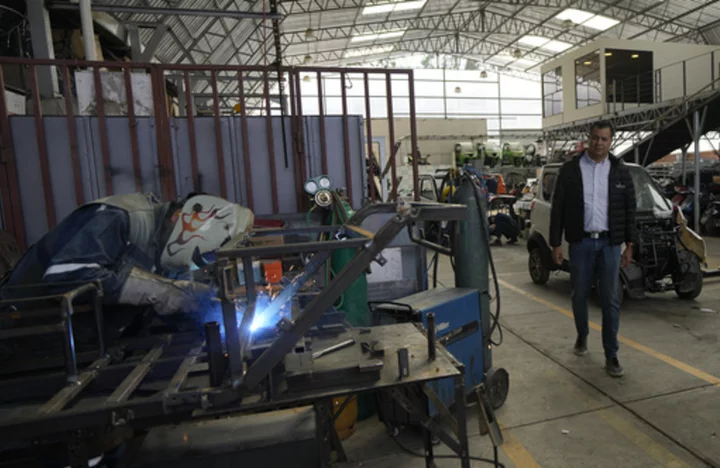

Bolivian EV startup hopes tiny car will make it big in lithium-rich country
The municipality of La Paz, Bolivia, is using a small fleet of tiny electric cars to bring doctors to patients' homes living in the suburbs of the capital city
2023-05-14 22:53

TXOne Networks’ New Edge V2 Engine for OT Cybersecurity Delivers Industry’s First Capability for Automatic Rule Generation, Enabling Effortless Network Segmentation
IRVING, Texas, & TAIPEI, Taiwan--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 5, 2023--
2023-09-05 22:21
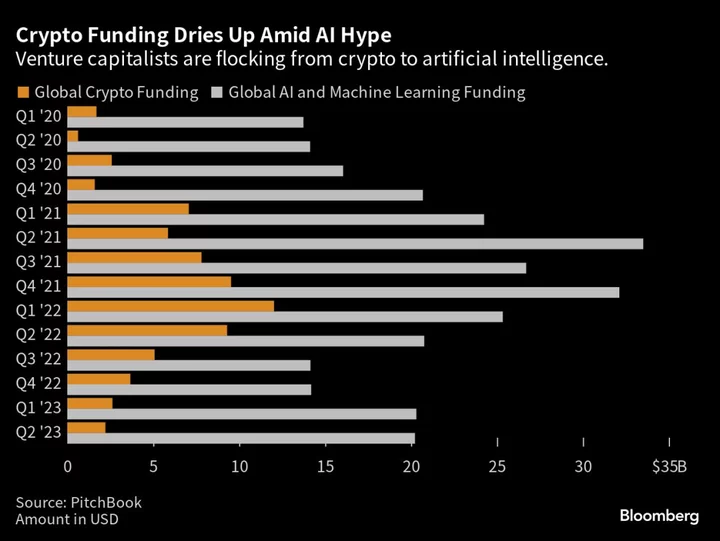
Tech Investors Bet on AI, Leave Crypto Behind
Silicon Valley venture capitalists are racing to get into artificial intelligence companies — including investors who once bet
2023-07-12 02:28

TSMC Sales Ride AI Demand Boost to Beat Estimates
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. reported better-than-expected sales on a boom in artificial intelligence applications demanding more of the
2023-07-10 13:59

TikTok Shop launches in the U.S. as the company bets big on e-commerce
After months of testing, TikTok is fully launching its e-commerce product in the U.S., in an effort to translate the app’s cultural relevance among young consumers to sales
2023-09-12 22:19

OPEC Defends ‘Vilified’ Oil Industry on Eve of Climate Meeting
OPEC issued a strongly worded defense of the oil-and-gas industry days before the start of the biggest ever
2023-11-28 12:25

Starfield Isn't Coming to PS5 Anytime Soon
Starfield will only be available for PC and Xbox gamers at launch, and it doesn't seem like it'll make its way to PlayStation anytime soon.
2023-08-08 04:51

Canada’s Supreme Court Voids Most of Trudeau Environment Law
A law passed by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s government to review major resource and infrastructure projects was largely
2023-10-14 01:48

EY in Talks to Close London Bridge Headquarters as Staff WFH
Ernst & Young LLP is considering moving out of its London headquarters as staff increasingly work from home
2023-11-21 02:27

Fortescue Buoyant on China Iron Ore as It Advances Green Pivot
Chinese demand for Australian iron ore will remain strong despite the nation’s disappointing post-pandemic recovery, according to Fortescue
2023-10-31 11:19
You Might Like...

Intelinair, Solvi Collaborate to Streamline Corn, Soybean Stand Assessments with AI-Powered Plant Counts

Is xQc living at Poke's house? Kick streamer explains housing situation amid ongoing relationship drama: 'I had no options'

Twitter now publicly shows who you're paying to subscribe to via Subscriptions

Billionaire Kretinsky Says He Won’t Boost Eviden Stake After French Concerns

Nintendo Direct June 21: How to Watch, Start Time

Screen sharing might be coming to WhatsApp for Android

ElectroNeek Among Top 10% of Companies on 2023 Inc. 5000 List
Windows 11 Test Feature Can Reduce Resources for Multi-Monitor Setups
