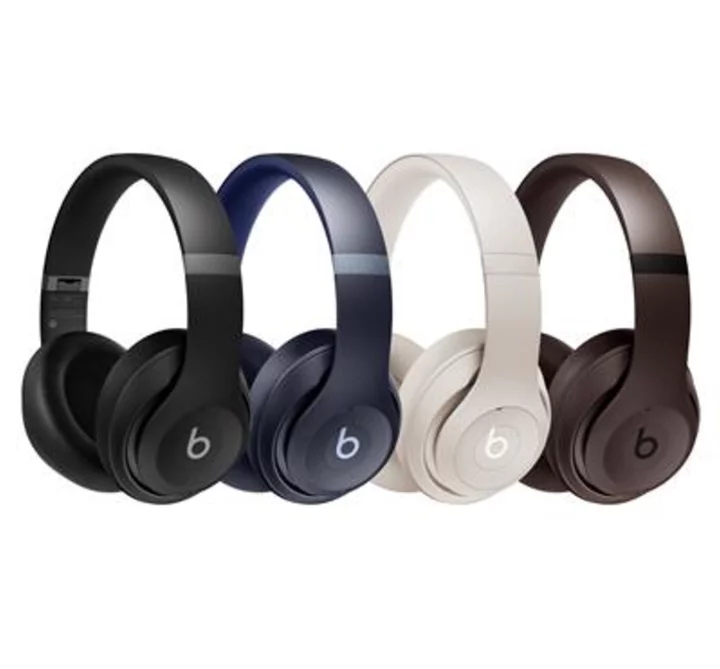

Introducing Beats Studio Pro: The Cultural Icon Reengineered
CULVER CITY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 19, 2023--
2023-07-19 22:15
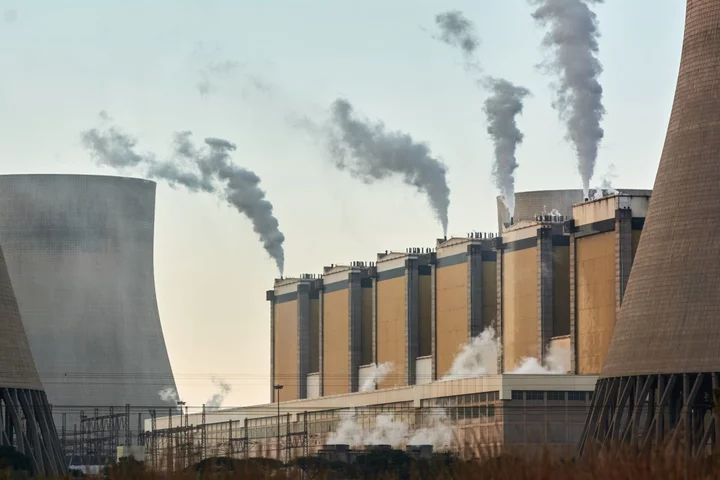

Germany Will Lend South Africa €500 Million for Energy Switch
Germany, through its KfW development bank, will as soon as Friday sign an agreement to lend South Africa
2023-11-17 17:53

LexFusion Deepens Bench of Legal Technology Talent to Focus on Corporate Legal Operations, Commercial Transactions, and Knowledge Management
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 12, 2023--
2023-09-12 22:45
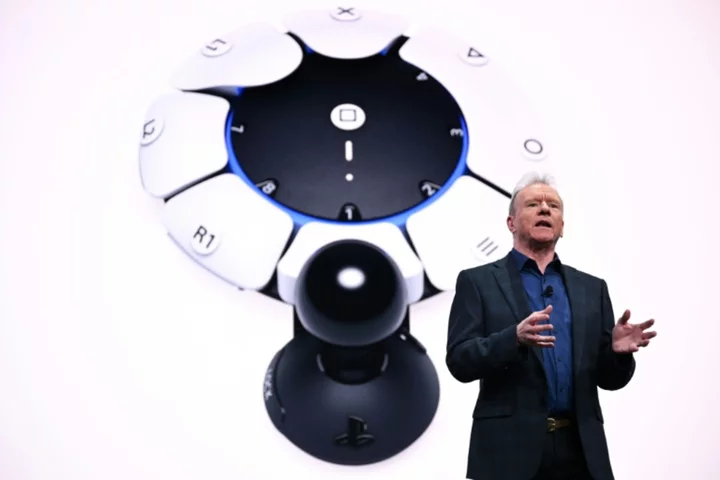

Sony PlayStation CEO Ryan to retire
Sony said Thursday that the chief executive of its PlayStation unit Jim Ryan will retire next March after almost 30...
2023-09-28 09:52
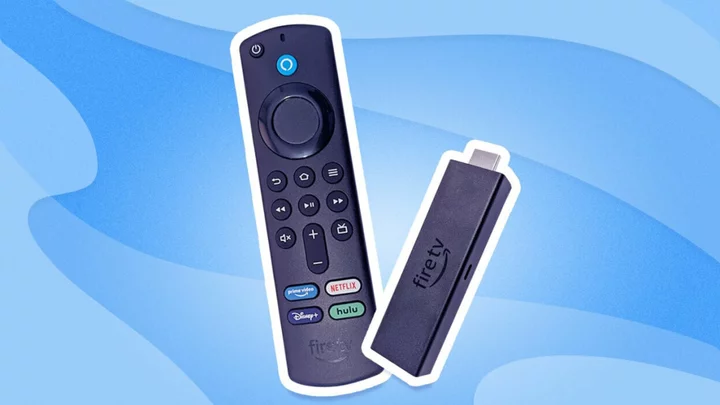

The best Fire TV Stick deals this Prime Day
TL;DR: Use your voice to search and launch programmes from across different apps with a
2023-07-10 19:48
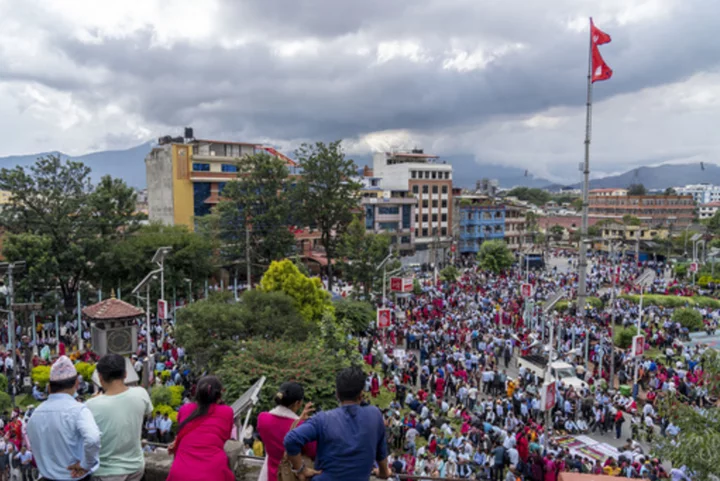

Thousands of teachers protest in Nepal against education bill, shutting schools across the country
Schools for millions of students in Nepal are closed as tens of thousands of teachers protest in the capital against an education reform bill in parliament
2023-09-22 20:53

New Twitter boss says ‘game on’ over Instagram clone rumours
The incoming head of Twitter has said she is ready to take on Instagram’s rumoured rival to the text-based app. Linda Yaccarino, who is set to take over as chief executive of the social media platform at the end of June, shared her reaction to the anticipated Twitter clone, tweeting: “Game on!” Instagram’s parent company Meta reportedly shared details about its plan for a microblogging app with creators last week, claiming that it would be partially integrated with Instagram. Leaked details suggest the as-yet unnamed app, codenamed P92 or Barcelona, will be decentralised and could work with Twitter’s rival Mastodon. “We’re exploring a standalone decentralised social network for sharing text updates,” Meta said in a statement to Money Control. “We believe there’s an opportunity for a separate space where creators and public figures can share timely updates about their interests.” Social media consultant Matt Navarra claimed that it would launch this summer, and that Instagram’s billion-plus users around the world would be able to keep their username, followers, and verification on the new app. He added that Meta is targetting “film and television actors, producers, writers, directors, showrunners, athletes, and comedians” to join the new platform. Elon Musk revealed Ms Yaccarino as his successor earlier this month, saying that she will focus primarily on business operations, while he continues to oversee “product design and new technology”. Together, they plan to transform Twitter into “the everything app”, which is expected to have similar functionality to China’s WeChat. Stretching beyond social media, Mr Musk’s X app could support shopping, news, mobile payments, and other services like booking restaurants and ordering taxis. “WeChat has a lot of functionality that Twitter should have,” he said during a Twitter Spaces session last year, just one month after acquiring the company in a deal worth $44 billion. The tech billionaire has also committed to making Twitter the “digital town square”, while acting as “an accelerant” to the X app. Read More Linda Yaccarino: How Elon Musk may have hired his biggest critic to head Twitter Google to delete Gmail and Photos accounts in huge purge Elon Musk calls working from home ‘morally wrong’ Sky Mobile hit by massive outage
2023-05-22 19:15

ZPMC Unveiled at the 2023 European TOC
SHANGHAI--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 25, 2023--
2023-06-25 14:47

Big Tech braces for roll-out of EU's Digital Services Act
By Martin Coulter LONDON More than a dozen of the world's biggest tech companies face unprecedented legal scrutiny,
2023-08-24 11:15

Kenyan court orders mediation in Meta labour dispute
NAIROBI (Reuters) -A Kenyan court has given Facebook's parent company Meta and content moderators suing it for unfair dismissal 21
2023-08-24 01:26

Enjoy unlimited premium web hosting, for life, for only $80
TL;DR: As of July 18, get a lifetime subscription to iBrave Cloud Web Hosting for
2023-07-18 17:49

Fortnite Chapter 5 Countdown
Here's the Fortnite Chapter 5 countdown to see how many more days until the next Fortnite Chapter drops on Sunday, Dec. 3, 2023.
2023-12-01 04:45
You Might Like...

Nintendo Embraces Passwordless Sign-Ins With Passkey Support

Stellantis invests 100 million euros in startups, mobility fund

UAE's Technology Innovation Institute Launches Open-Source "Falcon 40B" Large Language Model for Research & Commercial Utilization

Did Adin Ross get scammed? Kick streamer's swindler found on-stream, trolls say 'finally getting the karma he deserves'

10 of the best Python courses you can take online for free

Is The Haunting Coming Back to Warzone in 2023?
Big Tech Suppliers Need to Cut Emissions Faster, Greenpeace Says

Analysis-US SEC crackdown on Coinbase, Binance puts crypto exchanges on notice
