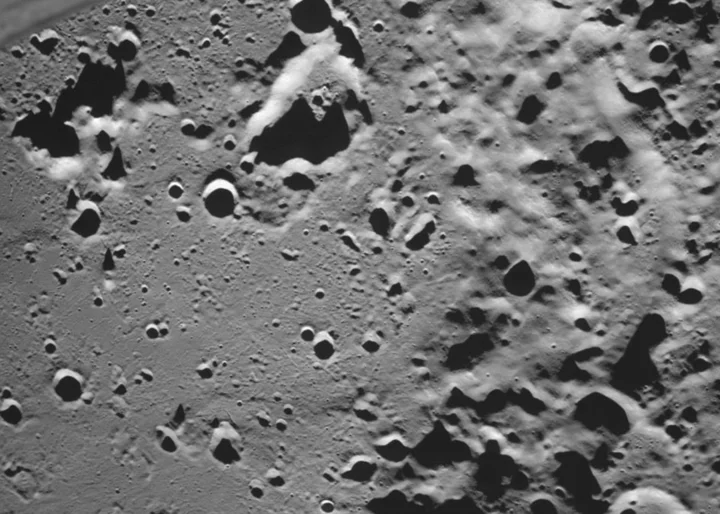

India's spacecraft snaps final photos before its nail-biter landing
India's robotic spacecraft has beamed back intriguing close-up views of the moon as it gets
2023-08-22 17:18
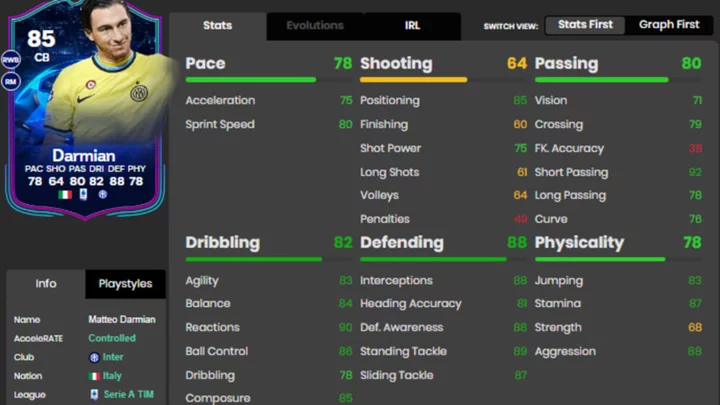
Matteo Darmain FC 24 Challenges: How to Complete the Road to the Knockouts Objective
Matteo Darmian FC 24 challenges detailed for the Road to the Knockouts objective set. Here's how to complete each objective.
2023-10-07 01:50

Indiana Jones game cancelled on PS5
Bethesda's 'Indian Jones' game will not be coming to the PS5.
2023-06-23 20:22

HR Practitioners Name Phenom a Leader for Talent Marketplace Platforms and Recruiting Automation Software in G2 Grid® Summer 2023 Reports
PHILADELPHIA--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 30, 2023--
2023-08-30 21:52

Child social media stars have few protections. Illinois aims to fix that
Illinois lawmakers aim to make their state what they say will be the first in the country to create protections for child social media influencers
2023-05-14 21:20
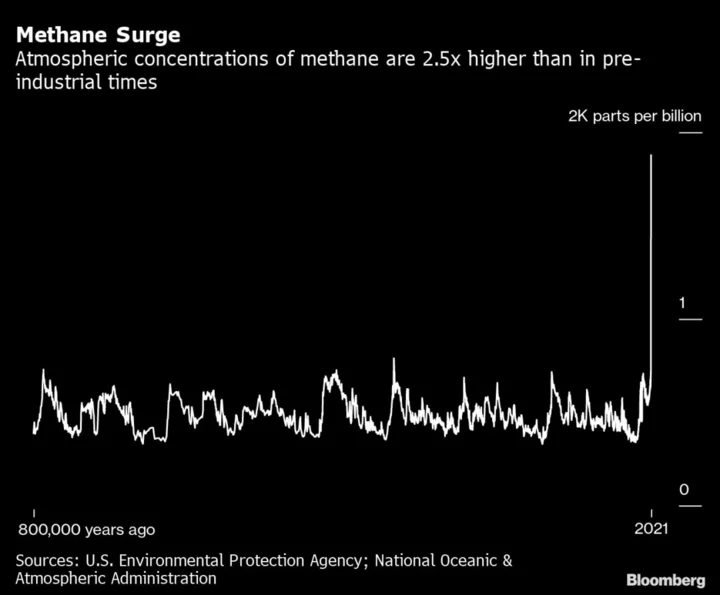
The $75 Billion Climate Solution That’s a Bargain
Halting methane releases is one of the most effective ways for the oil and gas industry to combat
2023-06-27 13:50

What is Only Up? The game which is taking players hours or seconds to complete
The online gaming world has a new obsession, with a game called Only Up where you simply have to keep climbing up a series of random objects until you reach space. The game sounds relatively straightforward as anyone who has even the most basic concept of videogames knows how to climb up various structures. However, Only Up does not make the game easy for players as the seemingly infinite amount of objects range from pipes, bridges and trampolines but even the slightest of mistakes can end in disaster sending the players plummeting all the way back to the start of the game. Only Up was developed by SCKR Games and released in May 2023. It is available to play on Steam for the price of £8.50 ($10.80). Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The game has gone viral thanks to high-profile streamers such as Adin Ross, Hasan Piker and iShowSpeed playing the game on their respective streams. iShowSpeed, who has 17 million followers on YouTube, attempts to play the game have proved to be particularly entertaining. At one point he lost 8 hours of progress. Thankfully, while playing the game on Tuesday the 18-year-old was able to complete the game in just under 5 hours. The most impressive run on the game so far has come from streamer Shade managed to find a glitch which allowed him to complete it in just 33 seconds. Whether you want to complete the game properly or use the glitch is your call but have fun regardless. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-28 17:46
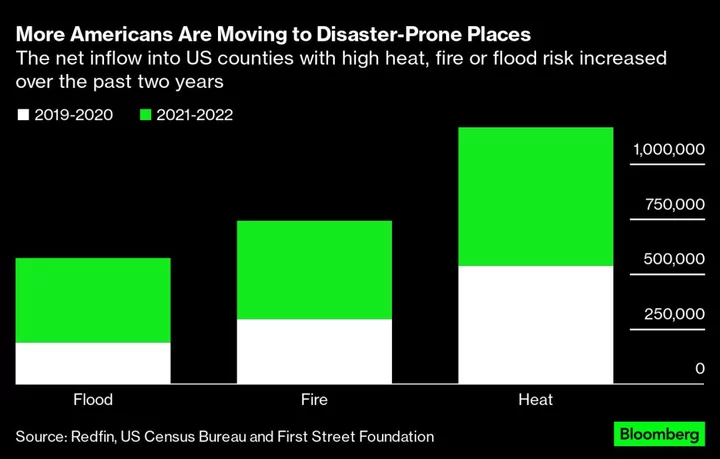
Americans Are Moving Toward Climate Danger in Search of Cheaper Homes
A midsummer quiz: Let’s say you read about an area experiencing blistering heat for weeks on end. Heat
2023-07-24 19:17

Kendall Jenner posts video of grand fireworks display from romantic Monaco vacation with Bad Bunny
Kendall Jenner and Bad Bunny spent the weekend with his friends on a yacht in the popular holiday destination
2023-05-30 23:15

Xsolla Appoints Chris Hewish as Interim CEO to Continue Its Global Expansion and Employee Growth
LOS ANGELES--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 25, 2023--
2023-05-25 23:23

The long wait is over: New 'Zelda' hits shelves
A six-year wait came to an end for "Zelda" fans across the world on Friday as Nintendo released the long-awaited next instalment...
2023-05-12 09:55

TikTok defends app following Welsh and UK government ban
The UK and Welsh government have banned the app from staff phones over security concerns.
2023-05-11 00:45
You Might Like...

SoftBank backs new autonomous trucking startup from founders of defunct Argo AI

How to Get Every Alternate Spider-Man 2 Suits

Here's When Call of Duty Games Are Likely Coming to Xbox Game Pass

Break The Web Tech Co. Launches Real-time, Machine-powered Internet Virality Scoreboard Enabled by Unique A.I. Partner Technology
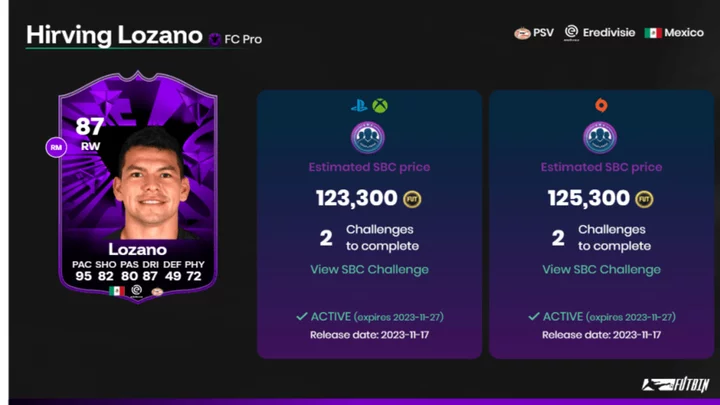
Hirving Lozano FC 24: How to Complete the FC Pro Live SBC

How much does Kylie Jenner charge per post on Instagram? Reality TV star pushed to second place by Cristiano Ronaldo who earns $2.40M per post
Grindr Launches Grindr Web Beta Increasing Accessibility and Ease of Use from Any Browser Anywhere
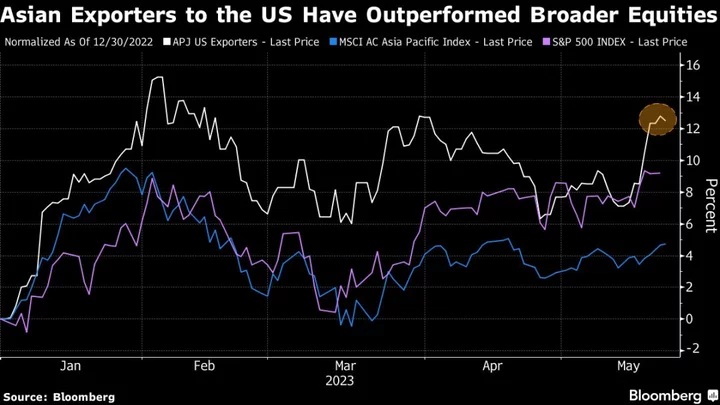
AI Frenzy Helps Asia Tech Exporters’ Shares Beat US Growth Woes
