
What happened to MrBeast's ex-editor Matt Turner? Here's what he is up to
Matt Turner started a custom rug shop and took part in a reality show after his stint with MrBeast
2023-06-04 16:45
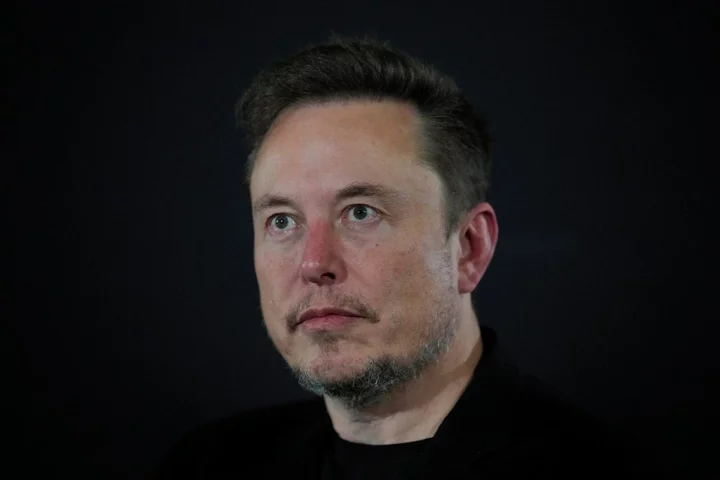

Musk mocked for trying to resurrect QAnon Pizzagate conspiracy following fake headline
Elon Musk has been criticised for seemingly attempting to resurrect the widely debunked QAnon conspiracy theory, “Pizzagate”. Pizzagate was an anti-Hillary Clinton conspiracy theory promoted on 4chan, Reddit, Twitter and other platforms in the final days before the 2016 US presidential election, and is seen as a precursor to the QAnon movement. Believers accused then presidential hopeful Ms Clinton and other senior Democrats of running a child sex trafficking ring out of the basement of a Washington DC pizza restaurant. The conspiracy theory led to a shooting at the restaurant – which turned out not to have a basement. On Tuesday the billionaire tech entrepreneur shared a meme from from the US television comedy The Office on his social media platform X on Tuesday, which accused the “experts” that had debunked the theory of themselves being paedophiles. The post, which was not labelled with a correctional “community note”, made reference to former ABC journalist James Gordon Meek who pleaded guilty to child sexual abuse image charges earlier this year. “Does seem at least a little bit suspicious,” Mr Musk wrote, also linking to an article about Meek’s guilty plea. Other X users suggested that Mr Musk had fallen for a fake New York Post headline which was circulated on the platform that associated Meek with the debunking of Pizzagate. The former journalist was not involved in the exposing of the conspiracy theory, according to a fact check by the Reuters news agency. “So... Community notes? He’s just wildly transparent,” wrote one user. Another added: “Man who controls Twitter/X and, while we’re on it, a majority of the earth’s satellites, among other things, sharing a *wildly* debunked conspiracy theory. “We don’t just have "experts" – we *know* it was invented on 4chan. This is flirting with some incredibly dangerous stuff.” Shayan Sardarizadeh, of the BBC Verify team, wrote in response: “The meme shared by Elon Musk about the pizzagate conspiracy theory is itself based on the completely false claim… “... that James Gordon Meek, a journalist who recently pleaded guilty to possessing child pornography, had debunked pizzagate. Meek never reported on pizzagate.” Another BBC disinformation journalist, Alistair Coleman added: “Your regular reminder that Pizzagate was created as a joke on a 4Chan message board, but spread because far too many people on social media aren’t particularly good at critical thinking. And here we are.” By Tuesday lunchtime Mr Musk had apparently deleted the tweet. It comes shortly after another online post by Mr Musk that attempted to link the founder of Media Matters – a left-leaning non-profit group that has accused X of promoting adverts from global companies alongside pro-Hitler content – to the owner of the Pizzagate restaurant. Earlier this month, a slew of big brands, including Disney and IBM, decided to stop advertising on X after a report by Media Matters said ads were appearing alongside pro-Nazi content and white nationalist posts. Mr Musk boosted a post rehashing the claims of links between the company and the restaurant owner by replying to it, with the one-word phrase: “Weird.” Self-described “free-speech absolutist” Mr Musk has also come under fire on multiple occasions recently over content promoting antisemitism on the site, sparking outrage over his own posts and comments which have promoted antisemitic content. On Wednesday November 15, Mr Musk described a post that said a post, had appeared to push the “great replacement” conspiracy theory on X, was “the actual truth”. The post claimed that Jewish communities “have been pushing the exact kind of dialectical hatred against whites that they claim to want people to stop using against them”. “You have said the actual truth,” Mr Musk wrote, a response which earned him praise from white nationalist Nick Fuentes – and accusations of antisemitism from dozens more, including the White House. He later responded to the accusations of antisemitism, insisting “nothing could be further from the truth”. Following the controversies, Mr Musk visited Israel on Monday, where he toured a kibbutz attacked by Hamas militants and held talks with top leaders. The billionaire met with Israeli President Isaac Herzog, who scolded him over content on his platform, and joined Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu for a tour of the Kfar Azza kibbutz, a rural village that Hamas militants stormed on 7 October in a deadly assault that launched the war. “The platforms you lead, unfortunately, have a huge reservoir of hatred, hatred of Jews and antisemitism,” Mr Herzog told him. Read More Elon Musk amplifies Pizzagate conspiracy theory Trump says Pence trying to ‘curry favour’ with DoJ over Jan 6: Live House has two days to respond to official motion to expel George Santos Trump says Pence trying to ‘curry favour’ with DoJ over Jan 6: Live House has two days to respond to official motion to expel George Santos Rosalynn Carter’s memorial service to be attended by Jimmy and fellow first ladies
2023-11-29 05:23
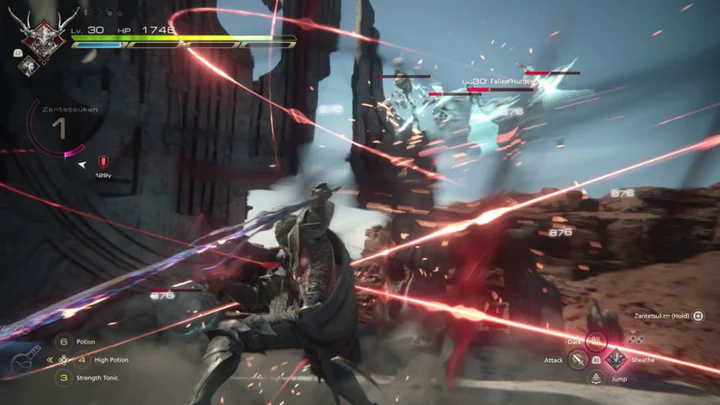

How to Find The Breaker of Worlds in FF16
Here's how to find The Breaker of Worlds in Final Fantasy 16 and the rewards players will get for taking out the S-rank Hunt.
2023-07-07 05:53

How much are 'TikTok challenges' to blame for recent tragedies?
The nefarious potential of digital technology has never been of greater concern. Artificial intelligence is already outsmarting us, and doxxing and deepfake are now firmly part of the common lexicon, so it’s no wonder we live in fear of what lies ahead for our kids. We already lament that young people live their lives as much on social media as they do in the real world, but to what extent can we blame these platforms for everyday mistakes and, even, tragedies? To answer that question, we must turn to two words which strike fear in the hearts of parents around the world. They are: “TikTok” and “challenge”. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter To the uninitiated, trends and challenges are the lifeblood of the video-sharing app. What began as a lighthearted stage for lip-syncing and dance routines (originally called Musical.ly), is now a hive of endless hashtags, each one encouraging a new stunt or craze. TikTok’s algorithm is a formidable and unpredictable beast, with the power to propel content creators to global stardom and seven-figure earnings and churn out entire new brands. But while most of us can forgive the platform for inviting pink sauce and Charli d’Amelio into our homes, we will not forget its more sinister capabilities. Indeed, mums and dads not only have to contend with the influence of certain notorious brainwashers, but they also face the prospect of losing their child to a dangerous prank – all for the sake of a few likes and the fleeting respect of their peers. A number of serious injuries and deaths have now been attributed to misguided attempts at “trends” on the app, with the so-called “blackout challenge” alone deemed culpable for the deaths of at least 20 children aged 14 or under in the past two years, a Bloomberg Businessweek investigation found. Archie Battersbee, 12, was widely reported to have taken part in the self-choking craze before he was found unconscious by his mother back in 2022. He’d suffered a catastrophic brain injury and died four months later. Then, in April this year, 13-year-old Jacob Stevens passed away in hospital six days after taking on the “Benedryl challenge,” according to his grieving dad. And less than a month ago, 16-year-old Mason Dark was left “unrecognisable” with burns after creating a makeshift blowtorch as part of an alleged TikTok stunt. Yet, there is scant, if any, proof that the platform had any part in fuelling the tragedies suffered by each of these particular kids. In the case of Archie, an inquest found that there was “no evidence” to back up his mum’s fear that he’d been doing the blackout challenge. A police report concluded that the 12-year-old had accessed TikTok on his mobile phone on the day of his fatal accident, but officers had been unable to pinpoint exactly what he’d been watching. However, photos and videos downloaded from the device offered no indication that he’d expressed interest in any auto-asphyxiation material. Similarly, TikTok took centre stage in reports on Jacob’s death, but a spokesperson for the company told indy100: "We have never seen this type of content (meaning the Benadryl challenge) trend on our platform and have blocked searches for years to help discourage copycat behaviour.” And although it was almost universally reported that a "TikTok challenge" had inspired Mason to created his near-lethal flamethrower, no outlets were able to provide any details on this. Could it be that he got the idea from another source or platform? Indeed, YouTube hosts numerous make-your-own blowtorch videos, some of which date back a number of years –meaning many of these fad projects were around before TikTok even existed. Still, although TikTok claims that it carefully monitors hashtags so that it can block potentially damaging content, a quick search of “flamethrower challenge” by indy100 yielded at least five examples of creators brandishing dangerous homemade devices. Admittedly one of these was captioned: “Don’t try this at home,” but doesn’t that sound like a challenge in itself? Social media companies are under mounting pressure to protect their young users from online harms and to better enforce age restrictions. And yet, even with the employment of increasingly sophisticated AI and tens of thousands of human moderators, they seem to constantly fall short in their duties. Yet, just look at recent headlines and it’s clear that TikTok seems to be shouldering most of the blame. Perhaps this is because it is the platform of choice among the very young and impressionable – it’s the most popular app in the US, used by almost 70 per cent of 13 to 17-year-olds, according to one survey. But perhaps it’s also because TikTok’s biggest rival launched a major campaign to tarnish its reputation last year, and it's still suffering the repercussions. Meta hired one of the most influential Republican consulting firms in the US to turn the public against the platform, driving home the idea that the app was a danger to American kids and society. The firm, Targeted Victory, used a nationwide media and lobbying push to spread the message that TikTok was a “threat”, according to leaked emails seen by the Washington Post. Among its tactics was to promote dubious stories about alleged “TikTok trends” that, in fact, originated on Facebook, the paper noted. In another email, a staffer for Targeted Victory asked one of the company’s partners: “Any local examples of bad TikTok trends/stories in your markets? [The] dream would be to get stories with headlines like ‘From dances to danger: how TikTok has become the most harmful social media space for kids’”. Following the Post’s investigation, Meta spokesperson Andy Stone defended the campaign saying: “We believe all platforms, including TikTok, should face a level of scrutiny consistent with their growing success.” TikTok responded by saying it was “deeply concerned” about “the stoking of local media reports on alleged trends that have not been found on the platform.” And yet, for all its protestations of innocence when it comes to the housing of high-risk content, TikTok was essentially the architect of its own problems. Back in 2016, Alex Zhu – the co-founder of what was then Musical.ly – boasted that his app was different to its competitors thanks to its promotion of "daily challenges". Every day, the company set users a new task – whether that be a dance routine or a weight-lifting mission – each of which typically spawned more than one million videos, according to Bloomberg. When Musical.ly was bought by Bejing-based platform ByteDance in 2017, and the two merged to become TikTok, the challenges came with it. These trends struck a particular chord with teens stuck at home during the first wave of the Covid pandemic, and so TikTok staff did everything they could to boost interest, for example, by getting influencers to encourage involvement. When more and more dangerous crazes started to crop up (remember the “milk crate challenge”?), TikTok established a “harm spectrum” to help its moderators decide what should be removed, Eric Han, the company’s US head of safety told Bloomberg. Nevertheless, children may be naive but they’re not stupid, and they soon found ways to circumvent the filters and restrictions. Participants adopted new names and hashtags for the dares, in some cases using deliberate typos or code names to signpost their content. The challenges were also carried over to different platforms, infesting social media as a whole with the weird, whacky and outright life-threatening. And so, we come back to our original question: to what extent can we blame these platforms – and, more specifically, TikTok – for the mistakes, injuries and even deaths of the young? The answer is, this shouldn't be about apportioning blame but about taking responsibility and collectively doing everything we can to protect our children. The likes of Facebook, Instagram and, yes, TikTok, too, all need to do more to impose age limits and remove harmful content, and stop putting growth over the safety of their young users. However, we must also accept that kids will always find ways to break the rules, and it's up to us as family members and friends, to remind them that a cheap thrill in your social life isn’t worth losing your whole life over. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-20 14:28
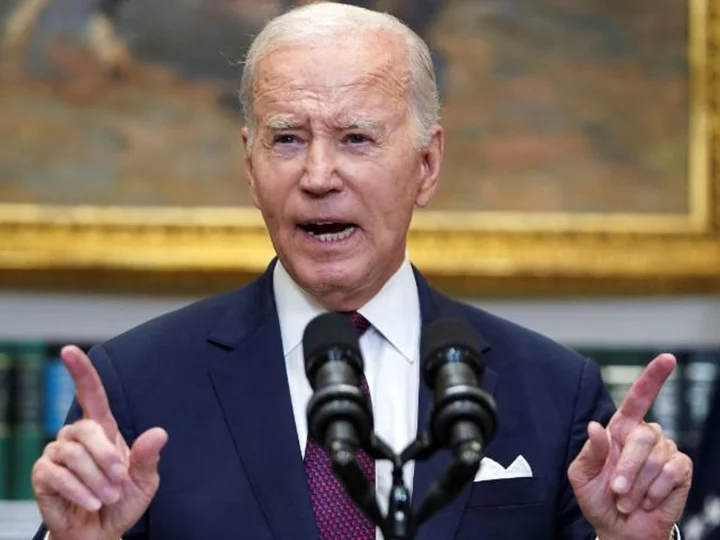

How the White House prepared for the Supreme Court's affirmative action ruling
The White House has been preparing for months for a potential Supreme Court ruling gutting affirmative action, even as President Joe Biden expressed optimism late last year that the court would uphold consideration of race in college admissions.
2023-06-30 02:56

X removes hundreds of Hamas-affiliated accounts since attack, CEO says
The X social media platform has removed hundreds of Hamas-affiliated accounts and taken action to remove or label
2023-10-12 19:23

Uber Eats Pledges to Slash Takeout Emissions and Plastic Waste
Uber Technologies Inc. pledged to eliminate carbon emissions and “unnecessary” plastic waste from its growing delivery business by
2023-06-08 16:48

15 Dutch Slang Terms You Should Know
Knowing a bit of Dutch slang will not just help you find your bearings when you visit Amsterdam and its surroundings, but also earn you respect from the locals—who, despite being great at English, have a strong connection to their mother tongue.
2023-07-31 20:23
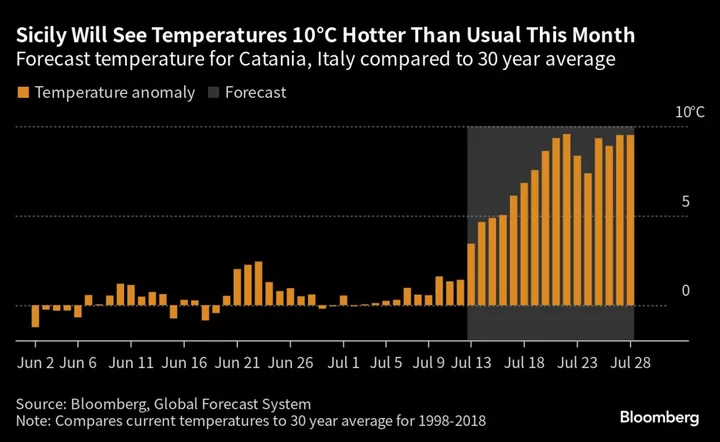
Italy Issues Emergency Warnings as Cerberus Heat Grips Europe
Extreme heat from a high-pressure system named Cerberus — after the three-headed hound from Dante’s inferno — is
2023-07-13 17:27

Has Logan Paul renewed contract with WWE? Fans say 'you gotta be trolling us'
A user wrote, 'It wasn’t photoshopped Logan, that was obviously AI'
2023-06-19 13:19
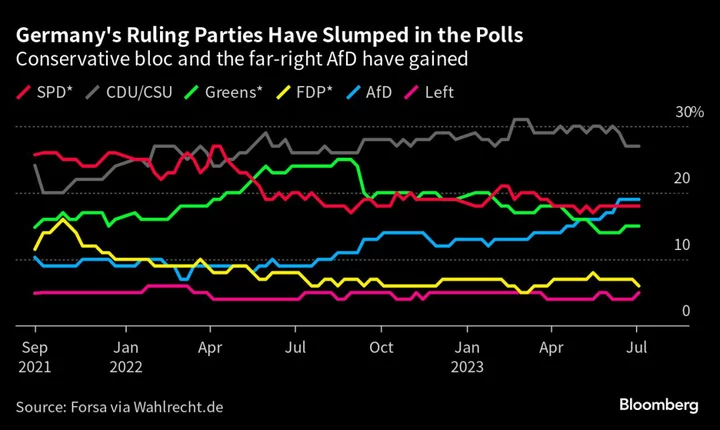
Scholz’s Stumbling Coalition Hit With Fresh Blow by Court Rebuke
After a bruising few months, Chancellor Olaf Scholz and senior members of his ruling coalition were relaxing at
2023-07-06 21:16

Twitter sues hate-speech watchdog, following through on its litigation threat
Twitter has sued the Center for Countering Digital Hate (CCDH), a nonprofit group that has criticized the company's handling of hate speech, following through on a litigation threat that had been publicly revealed just hours before.
2023-08-01 19:45
You Might Like...
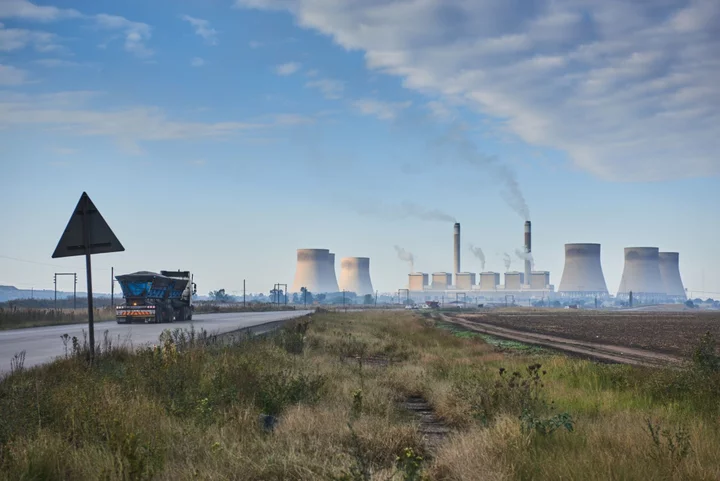

South African Coal Heartland Is Ill-Prepared for Energy Transition
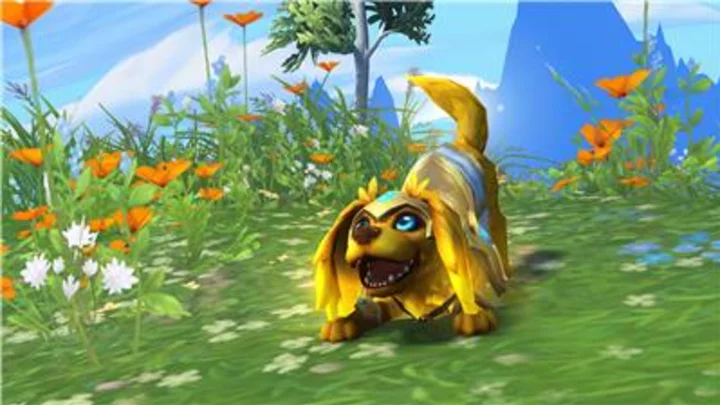

Blizzard Entertainment Teams up with Mila Kunis for the World of Warcraft® Charity Pet Pack in Support of BlueCheck Ukraine

Circle Criticizes Crypto Firms That ‘Counterfeit US Dollars’
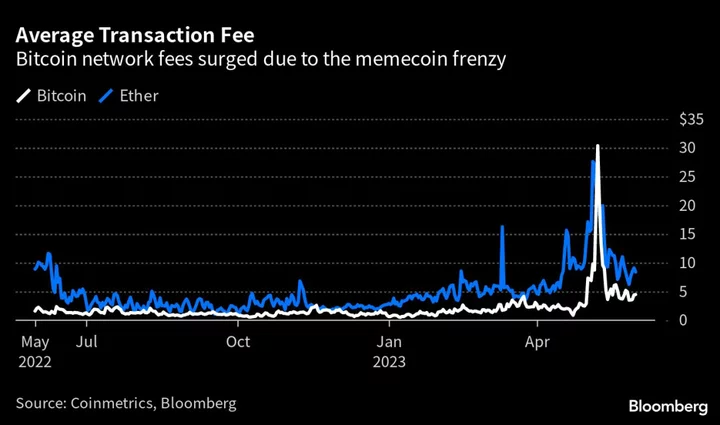
Bitcoin Coders Feud Over Whether to Crush $1 Billion Frenzy for Memecoins

Does Pokimane want to have a baby? Twitch queen reacts to Mizkif's reservations about having children as a streamer
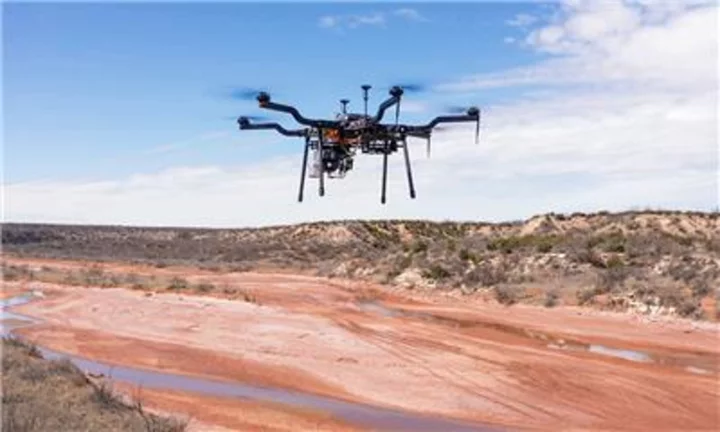

Valmont Records Longest BVLOS Drone Flight on the Wings of T-Mobile 5G
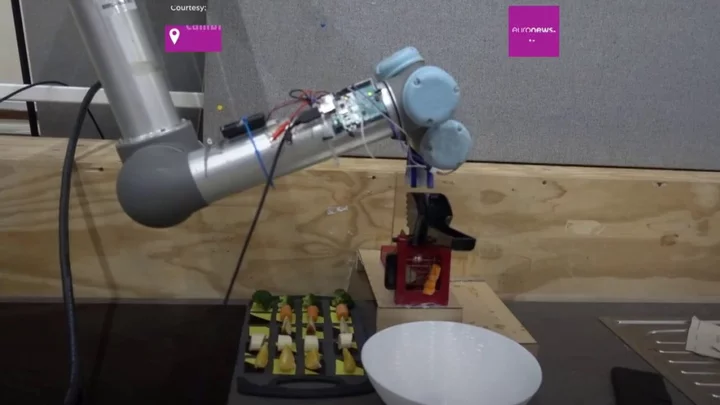
Scientists invent world's first ‘breathing, sweating, shivering’ robot

Get lifetime access to 10TB of cloud storage for under £70
