
India restricts laptop, PC imports to boost local manufacturing
India has placed restrictions on the import of computers and laptops in a surprise move from the government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi which has been trying to encourage domestic manufacturing in the tech sector.
2023-08-04 12:23

This new LG Gram laptop is on sale for $800
TL;DR: As of September 5, get a new open box LG Gram Laptop for just
2023-09-05 17:16

Code Avengers Review
The New Zealand-based Code Avengers remains an easy-to-use coding education service. Its built-in tools make
2023-08-03 06:29

Starmer Vows to Break ‘Class Ceiling’ in UK Workplaces
UK opposition leader Keir Starmer vowed to break the “class ceiling” stopping people from poorer backgrounds progressing in
2023-07-06 17:28

Save $300 on the roborock Q5+ at Amazon
Save $300: As of July 14, the roborock Q5+ is on sale at Amazon for
2023-07-15 02:18

Startup That Lets You Instantly Talk in Foreign Language Targets a Nasdaq IPO at $1 Billion Value
The maker of Japan’s most popular voice-and-camera translator is fighting to differentiate itself as it pursues a listing
2023-09-15 14:49
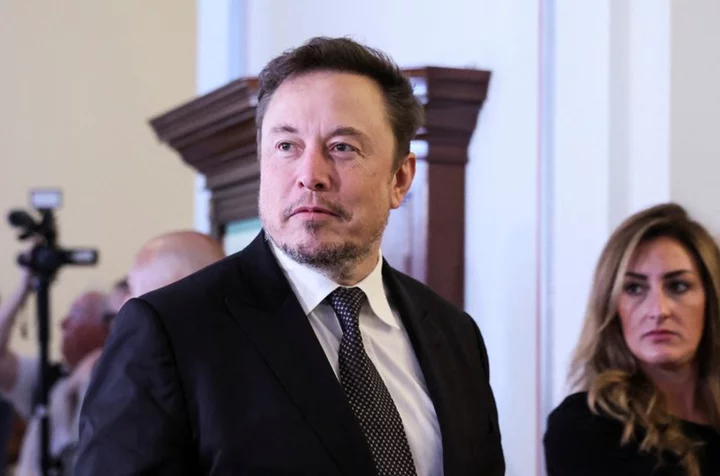

Elon Musk must face fraud lawsuit for disclosing Twitter stake late
By Jonathan Stempel NEW YORK Elon Musk was ordered by a U.S. judge to face most of a
2023-10-03 23:45
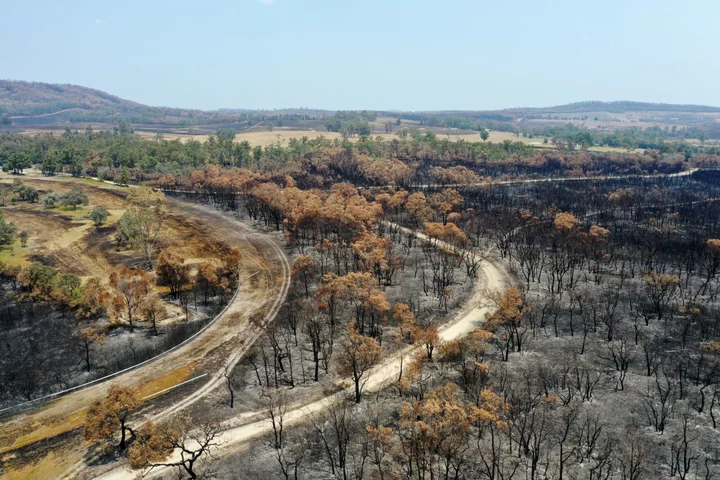

Australia Insurance Head Sounds Alert on Spiraling Climate Costs
Increasing numbers of Australians are abandoning their insurance policies as premiums surge in response to climate-linked natural disasters,
2023-11-23 14:24
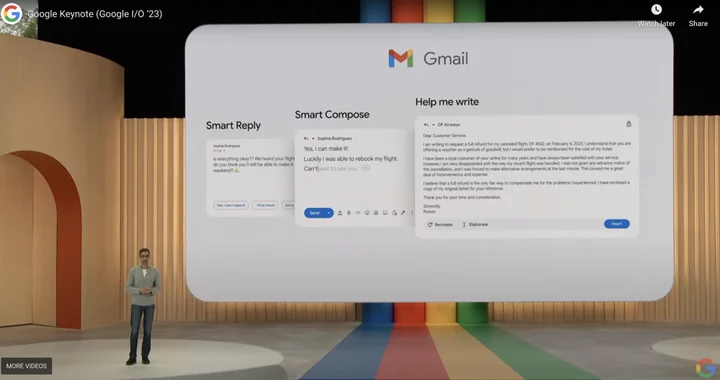
Gmail's new AI feature will soon write entire emails for you, Google announces
Gmail will soon have a feature that will write entire emails for you using AI,
2023-05-11 01:46

FPT Software Attains Triple Wins in 2023 International Business Awards®
HANOI, Vietnam--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 16, 2023--
2023-08-17 11:27

Cantaloupe Unveils New Seed Pick Easy Solution at NAMA
MALVERN, Pa.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-11 03:17
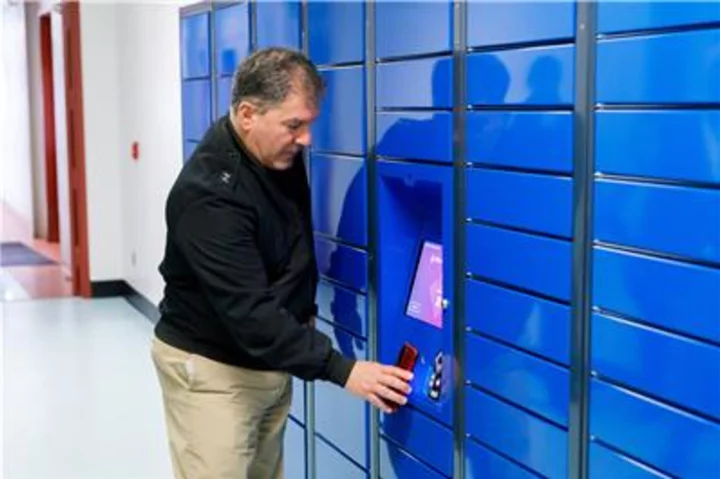

US Navy Chooses Pitney Bowes to Assist in Package Distribution Worldwide
STAMFORD, Conn.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 31, 2023--
2023-05-31 21:26
You Might Like...
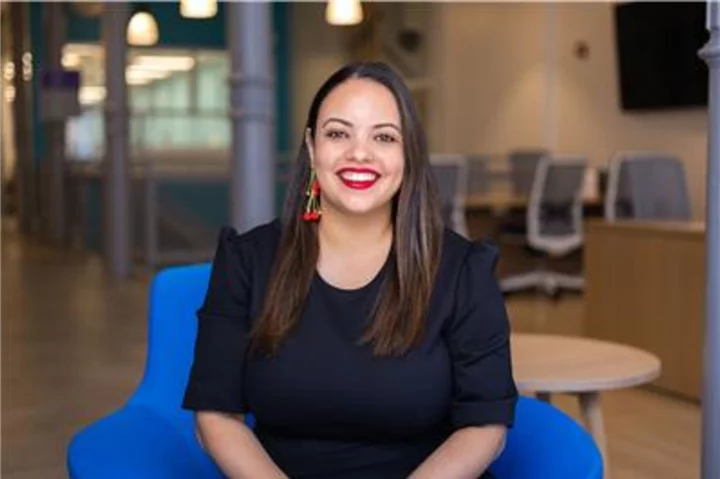

The Kaplan Educational Foundation Comments on the U.S. Supreme Court Decision on Affirmative Action

Gravity Officially Launches Mobile Idle Relaxing Game ‘WITH: Whale In The High’ for the Global Region!
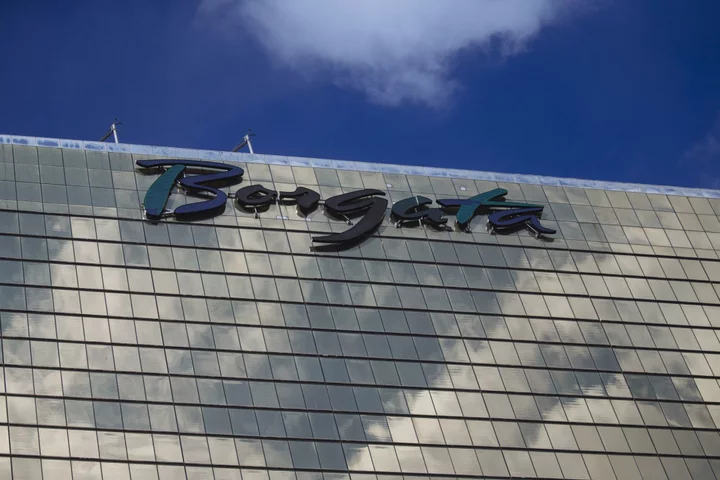

MGM Websites Remain Down After Cyberattack Hits Casinos and Hotels
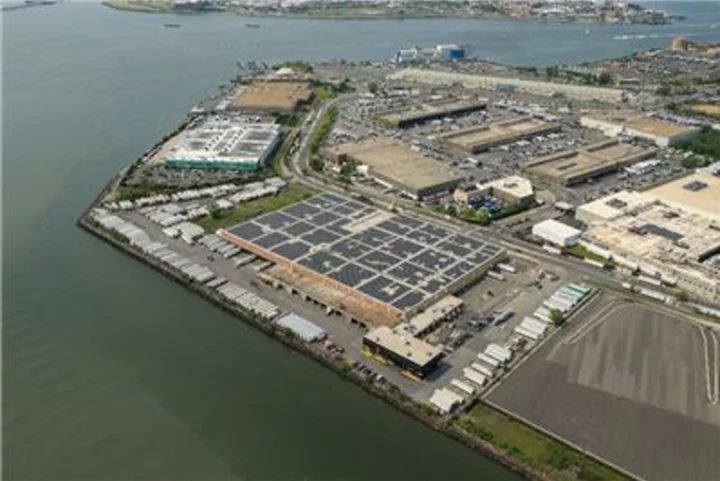

Krasdale Foods and PowerFlex Launch the Largest Solar System in the Bronx

Get a refurbished touchscreen Chromebook for under $90

Trump news – live: Trump suggests White House concealing security footage over cocaine scandal as Don Jr branded ‘big baby’

AMD Preps GPU to Challenge Nvidia's Grip on the Generative AI Market

EU, US ready common code of conduct on artificial intelligence
