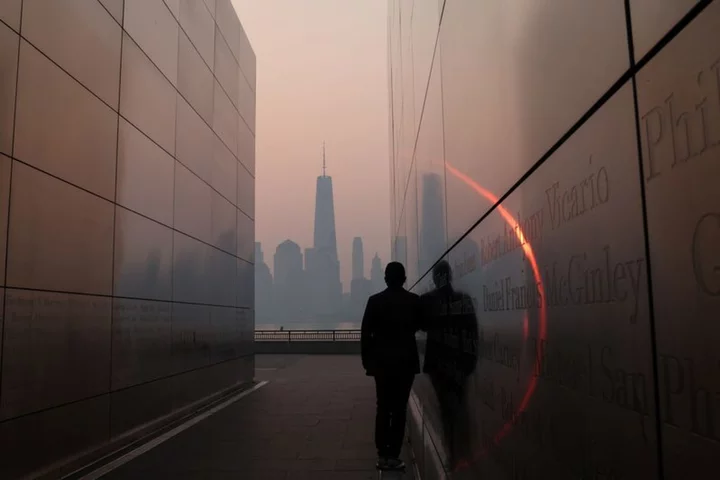

Smoke hangs over U.S. Midwest, East, hurting air quality
By Brendan O'Brien CHICAGO (Reuters) -Hazy, smoke-filled skies from raging Canadian wildfires hovered Wednesday over the U.S. Midwest and East,
2023-06-29 03:23

How to unblock websites and access restricted content
TL;DR: ExpressVPN is the best service for unblocking websites and accessing restricted content. A one-year
2023-08-09 12:25

How to Stream Games Without Hogging All the Wi-Fi Bandwidth
In an era where work from home and hybrid work scenarios are increasingly common, one
2023-07-29 11:28
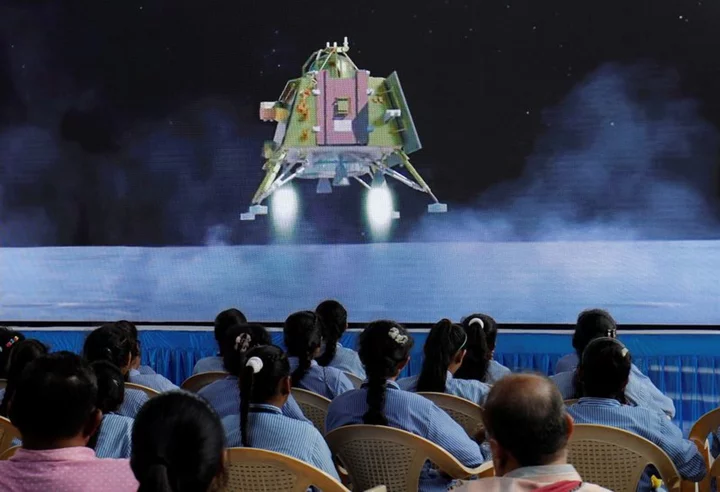

Chandrayaan-3 rover rolls onto moon's surface as ecstatic India celebrates
By YP Rajesh, Sakshi Dayal NEW DELHI (Reuters) -The moon rover of India's Chandrayaan-3 exited the spacecraft on Thursday to
2023-08-24 17:26
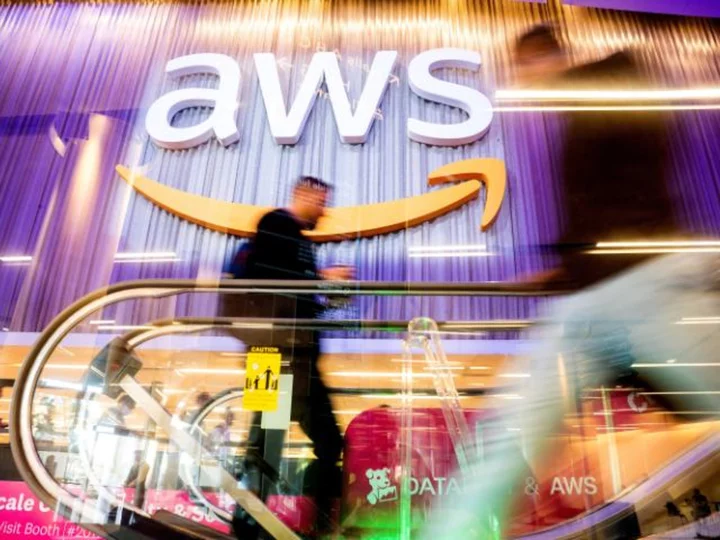

Amazon Web Services hit by wide-ranging outage, impacting major websites
Amazon Web Services was hit by a wide-ranging outage on Tuesday afternoon that impacted a large number of major websites, including the Boston Globe and New York City's Metropolitan Transit Authority.
2023-06-14 06:51
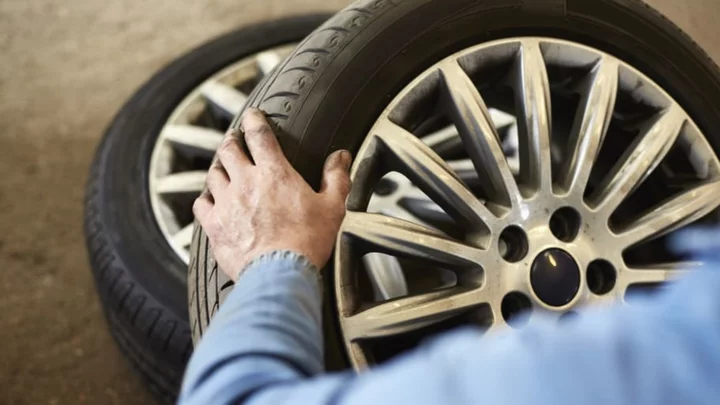

Hubcaps vs. Rims: What’s the Difference?
Get up to speed on your car lingo.
2023-08-05 05:59

Where did Casey DeSantis graduate from? First Lady of Florida's early life and career explored amid Mamas campaign debut
Casey DeSantis' Mamas for DeSantis campaign seeks to promote her husband Ron DeSantis as the face of the parents' rights movement
2023-07-09 21:00

Was Adept a 'crazy girlfriend'? Asmongold 'completely supports' xQc amid relationship drama: 'Sad, weird and awful'
Asmongold states, 'I mean, if you're talking about the stuff with Adept, I just think that... I think it's sad. It's just weird'
2023-06-16 18:54

How to unblock Pornhub videos for free
TL;DR: ExpressVPN is the top choice for unblocking leading porn sites. A one-year subscription to
2023-07-25 12:26

5 Ways to Get Yourself Banned in Apex Legends
Check out the 5 most common ways players get banned in Apex Legends so you can maintain your account ahead of Season 18 in August.
2023-07-12 01:48

Sleeping with your bedroom door closed is not a good idea according to experts
You might want to start leaving your door open at night, if new advice from sleep experts is anything to go by. New guidance might just change people’s choices when it comes to sleeping habits as we approach the warmer summer weather. While purchasing a fan is recommended for keeping cool when it comes to hotter temperatures, opening doors can do a lot when it comes to air circulation at night. “Surprisingly, only 60 per cent of adults sleep with their door closed meaning that 40 per cent sleep with their door open,” says Rex Isap, CEO and sleep expert at Happy Beds. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Explaining the implications of leaving doors open, Isep added [via Ideal Home]: “Firstly, a study found that those who slept with the bedroom door open reported a better and longer night’s sleep than those who slept with the door close. The reasoning behind this is that leaving the door open helped regulate the temperature in the room by making the temperature slightly lower, averaging 19 degrees Celsius.” Isap added: “Given that between 18 and 20 degrees Celsius is the ideal bedroom temperature, this naturally makes it easier for a person to fall asleep. It also makes it the ideal thing for a person to do if they suffer from night sweats, are going through menopause, or are generally overheating from the hot weather.” It’s not just a case of improving air flow and better maintaining temperatures either, as Sammy Margo at Dreams claims that leaving doors open also connects sleepers with the rest of their house and improves natural light in the mornings. Margo said: “Sleeping with an open door can also create a sense of openness and connection to the rest of your living space. It can alleviate feelings of isolation or confinement and promote a more positive and harmonious atmosphere in your home. It also opens the bedroom up to natural light from other areas of the house which can help in the morning!” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-01 00:48
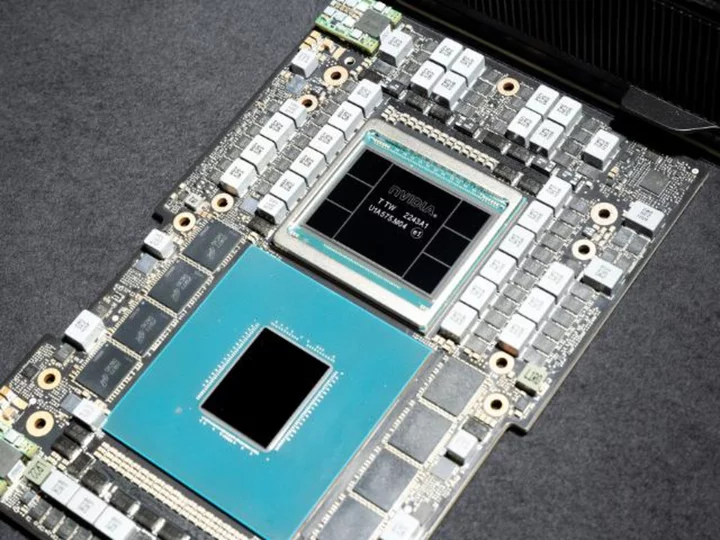
Nvidia set the market alight last quarter. Can it repeat the trick?
Artificial intelligence darling Nvidia's upcoming earnings report could be a boost or a drag on a market already mired in the summer doldrums.
2023-08-23 19:54
You Might Like...

ZEDEDA Launches Industry-First Application Services Suite, Revolutionizing Edge Computing

HyperX Announces VALORANT Champions Tour-Inspired Keycap in Collaboration with Riot Games

'This is crazy': Adin Ross expresses frustration over invasive stream sniper during live IRL stream
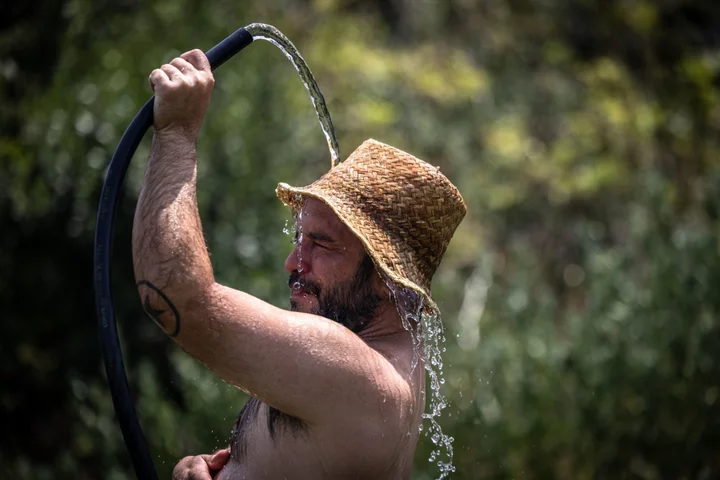

Spain Braces for Next Blast of Heat as Northern Europe Stays Cool

Pick up a refurbished MacBook Air for $345.99

Hithium Exhibits at RE+ in Las Vegas, Launching First 5 MWh Container Product

EA Sports FC 24 Cover Star Leaked, Reveal Date
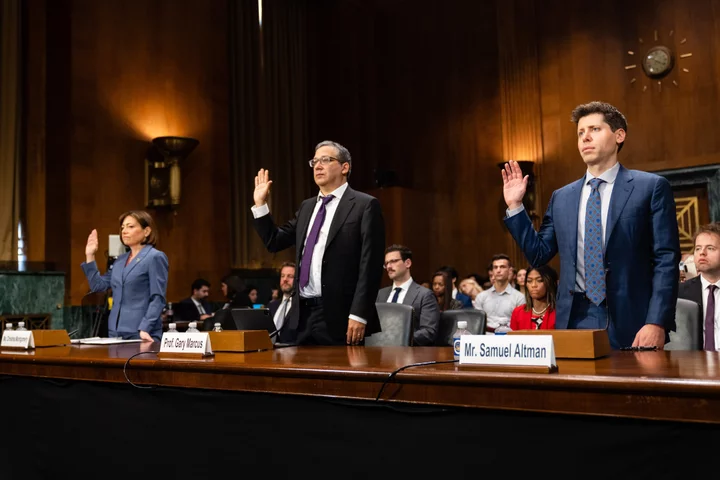

Shocking: Congress seemed to actually understand AI's potential risks during hearing
