
Who is Colleen Ballinger? YouTuber denies grooming allegations with song, says she's 'not a groomer, just a loser'
Colleen Ballinger faced grooming allegations after screenshots were shared from a group chat in which she sent inappropriate messages to minor fans
2023-06-29 17:49
Elon Musk's X to roll out audio, video calling feature
Social media platform X, formerly Twitter, plans to launch video and audio calls as owner Elon Musk races
2023-08-31 19:23

RAZ Mobility Launches Accessible and Innovative Smartphone for People Who Are Blind or Visually Impaired
CABIN JOHN, Md.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 1, 2023--
2023-08-01 19:51

Meta Fined Record €1.2 Billion in EU Over US Data Transfers
Facebook owner Meta Platforms Inc. was hit by a record €1.2 billion ($1.3 billion) European Union privacy fine
2023-05-22 17:20
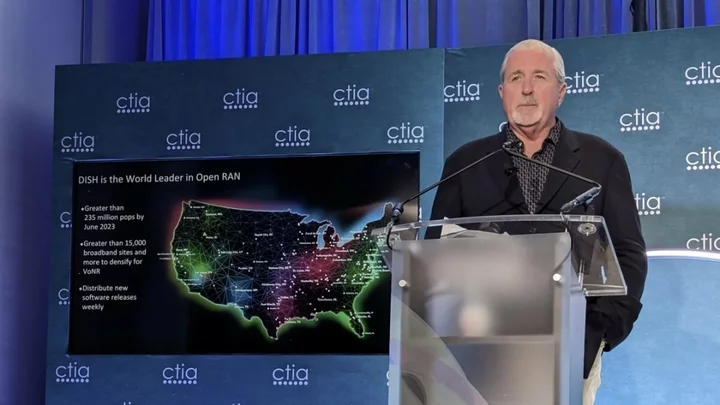

Dish Wireless: We’ll Meet June Deadline to Cover 70% of Americans With 5G
Dish remains on course to build the US’s first new nationwide wireless network in decades
2023-05-20 06:18

Ed Boon says Mortal Kombat's success is down to adding 'brand new' features
The co-creator of the popular fighting games has discussed why he thinks they continue to attract larger numbers after more than three decades.
2023-09-20 19:21
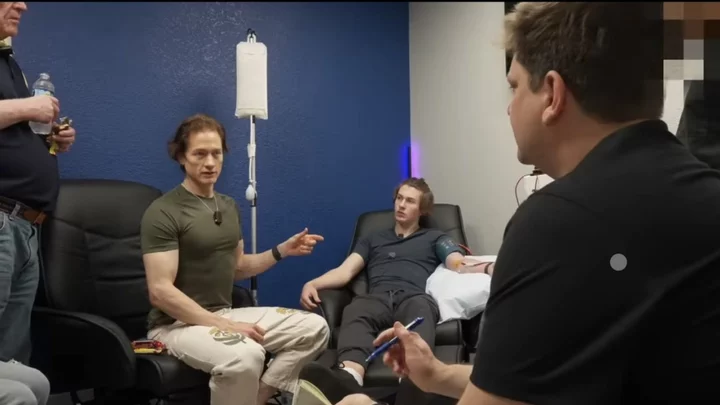

Tech bro millionaire injects himself with son's blood in attempt to de-age himself
Bryan Johnson, the multimillionaire tech and science entrepreneur who is trying to reverse his biological age, has taken the next odd step in his attempt to achieve this. Johnson, who has already spent millions of dollars every year trying to turn back the clock, has now revealed that he’s injected himself with his teenage son’s blood. The multimillionaire recruited his 17-year-old son, Talmage, and his 70-year-old father, Richard, for a trigenerational blood transfusion. The family travelled to a clinic in Dallas, where Talmage and Richard gave a litre of their blood for it to be converted into a batch of plasma. Bryan then donated a litre of his blood to Richard. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Claims that plasma from younger bodies can benefit older people’s health have been around for a while. Previously there have been studies carried out on mice, however experts say the results are inconclusive. The FDA does not recommend the blood infusions Bryan has done. "We have not learned enough to suggest this is a viable human treatment for anything." said Charles Brenner, a biochemist at City of Hope National Medical Centre in Los Angeles. The 45-year-old has previously spoken about his lifestyle, and told the BBC that there have been improvements in different parts of his body. "my left ear is 64, my fitness tests say I’m 18, my heart is 37, my diaphragm strength is 18," he said. Bryan’s mission to reverse the ageing process has been titled ‘Project Blueprint,’ and involves following a strict diet, sleep, and exercise routine. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-23 19:51
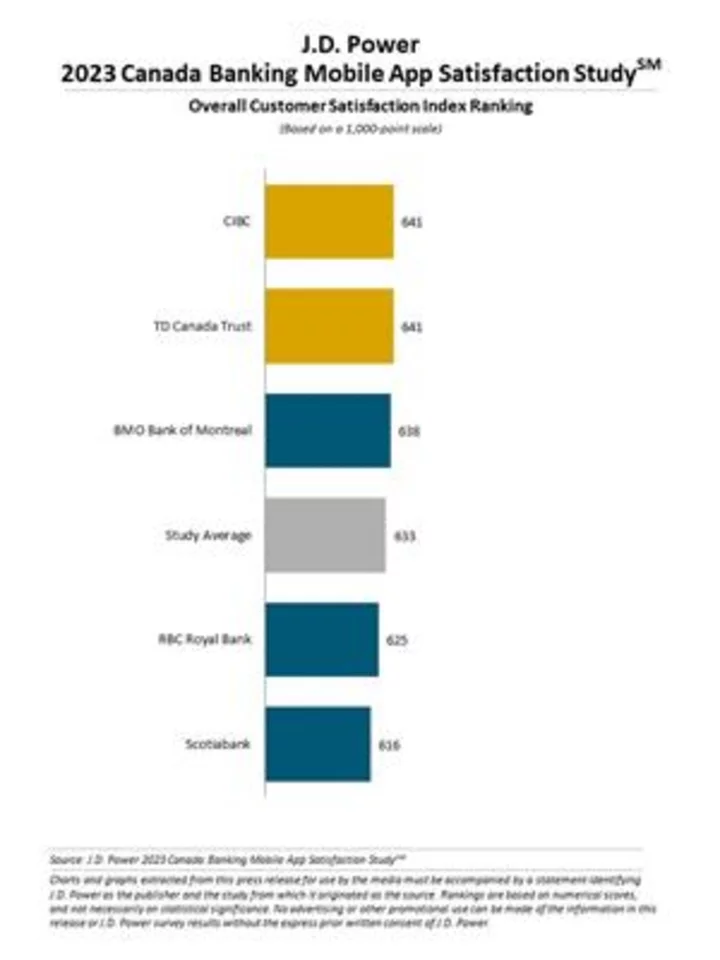
Canadian Bank and Credit Card Apps Slow to Include Personal Financial Management Tools, J.D. Power Finds
TORONTO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 8, 2023--
2023-06-08 18:20

Wells Fargo Ousted From Texas Muni Deal Over Energy Policy Probe
Wells Fargo & Co. has been dropped from underwriting a school district bond deal in Texas, the latest
2023-10-24 01:23
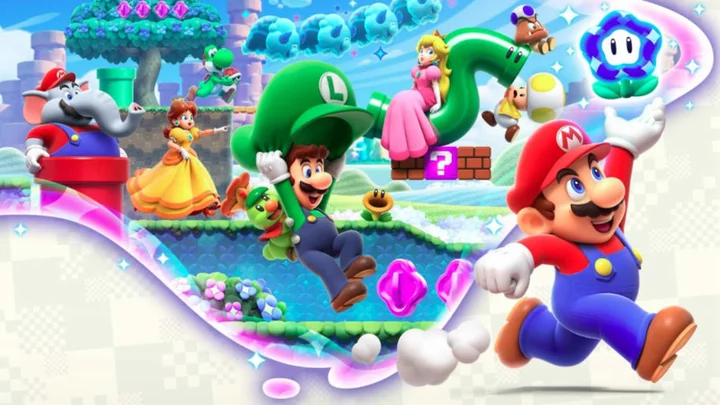

Super Mario Bros. Wonder Nintendo Direct: Everything We Know
The latest Nintendo Direct had tons of new information about Super Mario Bros. Wonder. Here's what you need to know about the upcoming title.
2023-09-02 04:53
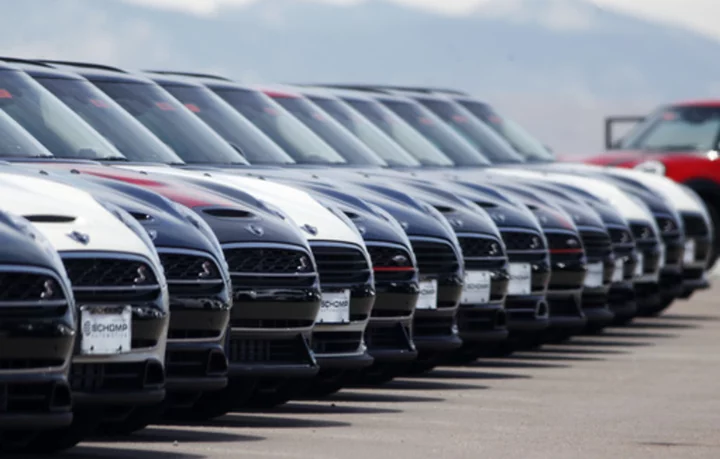

Ford decides to keep AM radio on 2024 models, will restore AM on two electric vehicles from 2023
Owners of new Ford vehicles will be able to tune in to AM radio in their cars, trucks and SUVs after all
2023-05-23 23:25

Google Wants to Let You Search for a Song by Humming It
Soon you might be able to hum a few lines from that song you can’t
2023-08-27 01:23
You Might Like...

Microsoft in talks to extend deal contract with Activision -source

The Vive XR Elite VR headset conforms to you

Binance plans to swap 750 million of token pairs to ensure liquidity
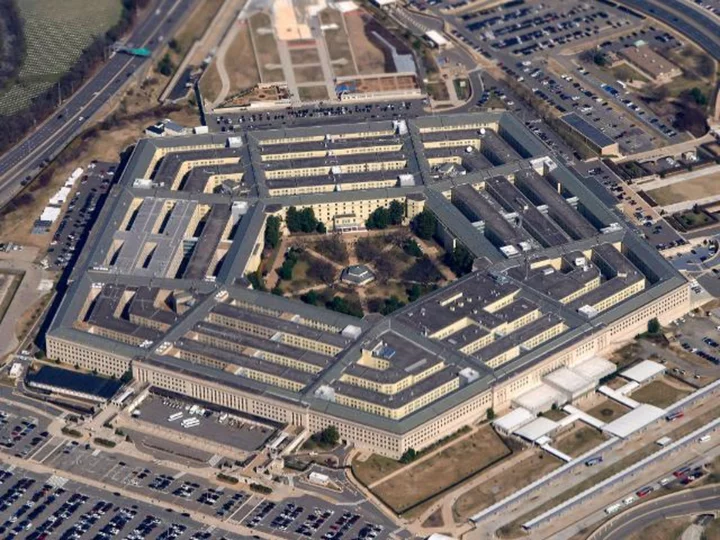

Common typo causes millions of emails intended for members of the US military to be sent to accounts in Mali

AT&T Says Less Than 10% of Its Network Has Lead Covered Cables

Planning an EV Road Trip? Good Luck Finding a Hotel With a Charger

Viral Nation_Talent Expands 360 Creator Services and Welcomes Bianca Serafini to Lead Launch of New OTT Distribution Division

Quantum-Si Appoints Biotech Executive and Entrepreneur, Amir Jafri, to its Board of Directors
