
10 Ancient Kings Who Were Too Dramatic For Your History Books
You probably didn't learn about these ancient kings in history class.
2023-07-29 06:26

Voices: The real reason companies are warning that AI is as bad as nuclear war
They are 22 words that could terrify those who read them, as brutal in their simplicity as they are general in their meaning: “Mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority alongside other societal-scale risks such as pandemics and nuclear war.” That is the statement from San Francisco-based non-profit the Center for AI Safety, and signed by chief executives from Google Deepmind and ChatGPT creators OpenAI, along with other major figures in artificial intelligence research. The fact that the statement has been signed by so many leading AI researchers and companies means that it should be heeded. But it also means that it should be robustly examined: why are they saying this, and why now? The answer might take some of the terror away (though not all of it). Writing a statement like this functions as something like a reverse marketing campaign: our products are so powerful and so new, it says, that they could wipe out the world. Most tech products just promise to change our lives; these ones could end it. And so what looks like a statement about danger is also one that highlights just how much Google, OpenAI and more think they have to offer. Warning that AI could be as terrible as pandemics also has the peculiar effect of making artificial intelligence's dangers seem as if they just arise naturally in the world, like the mutation of a virus. But every dangerous AI is the product of intentional choices by its developers – and in most cases, from the companies that have signed the new statement. Who is the statement for? Who are these companies talking to? After all, they are the ones who are creating the products that might extinguish life on Earth. It reads a little like being hectored by a burglar about your house’s locks not being good enough. None of this is to say that the warning is untrue, or shouldn't be heeded; the danger is very real indeed. But it does mean that we should ask a few more questions of those warning us about it, especially when they are conveniently the companies that created this ostensibly apocalyptic tech in the first place. AI doesn't feel so world-destroying yet. The statement's doomy words might come as some surprise to those who have used the more accessible AI systems, such as ChatGPT. Conversations with that chatbot and others can be funny, surprising, delightful and sometimes scary – but it's hard to see how what is mostly prattle and babble from a smart but stupid chatbot could destroy the world. They also might come as a surprise to those who have read about the many, very important ways that AI is already being used to help save us, not kill us. Only last week, scientists announced that they had used artificial intelligence to find new antibiotics that could kill off superbugs, and that is just the beginning. By focusing on the "risk of extinction" and the "societal-scale risk" posed by AI, however, its proponents are able to shift the focus away from both the weaknesses of actually existing AI and the ethical questions that surround it. The intensity of the statement, the reference to nuclear war and pandemics, make it feel like we are at a point equivalent with cowering in our bomb shelters or in lockdown. They say there are no atheists in foxholes; we might also say there are no ethicists in fallout shelters. If AI is akin to nuclear war, though, we are closer to the formation of the Manhattan Project than we are to the Cold War. We don’t need to be hunkering down as if the danger is here and there is nothing we can do about it but “mitigate it”. There's still time to decide what this technology looks like, how powerful it is and who will be at the sharp end of that power. Statements like this are a reflection of the fact that the systems we have today are a long way from those that we might have tomorrow: the work going on at the companies who warned us about these issues is vast, and could be much more transformative than chatting with a robot. It is all happening in secret, and shrouded in both mystery and marketing buzz, but what we can discern is that we might only be a few years away from systems that are both more powerful and more sinister. Already, the world is struggling to differentiate between fake images and real ones; soon, developments in AI could make it very difficult to find the difference between fake people and real ones. At least according to some in the industry, AI is set to develop at such a pace that it might only be a few years before those warnings are less abstractly worrying and more concretely terrifying. The statement is correct in identifying those risks, and urging work to avoid them. But it is more than a little helpful to the companies that signed it in making those risks seem inevitable and naturally occurring, as if they are not choosing to build and profit from the technology they are so worried about. It is those companies, not artificial intelligence, that have the power to decide what that future looks like – and whether it will include our "extinction". Read More Opinion: Age gap relationships might seem wrong, but they work. Trust me Hands up if you trust Boris Johnson | Tom Peck Boris’s ‘ratty rat’ rage against Sunak could bring the Tories down | John Rentoul Opinion: Age gap relationships might seem wrong, but they work. Trust me Hands up if you trust Boris Johnson | Tom Peck Boris’s ‘ratty rat’ rage against Sunak could bring the Tories down | John Rentoul
2023-05-31 18:58

Honkai: Star Rail Review
With Honkai: Star Rail, developer Hoyoverse takes a stab at a space opera, and the
2023-08-01 23:59

Why Won’t My Cat Use the Litter Box?
A certified cat trainer suggests reasons why a cat won’t use its litter box—and offers some possible solutions.
2023-11-12 04:24

HP Victus 16 (2023) Review
We reviewed the HP Victus 16 gaming laptop back in 2021, but new CPU and
2023-08-01 04:53
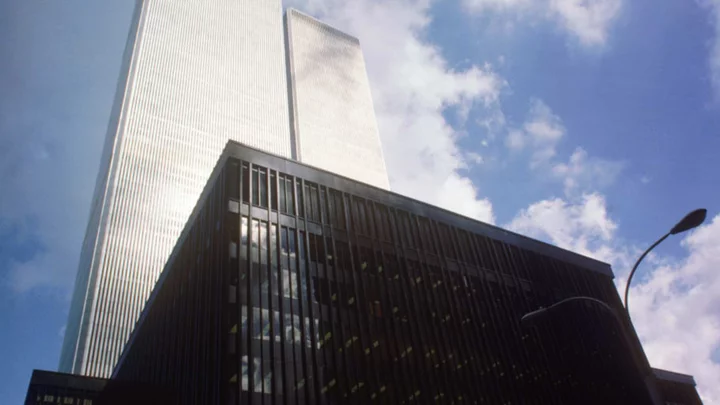

George Willig, the ‘Human Fly’ Who Climbed the World Trade Center
In 1977, climber George Willig decided his next great challenge would be scaling 110 stories in lower Manhattan.
2023-06-17 03:24
Comcast Offers Metro Detroit Xfinity Customers NOW TV: A $20 Entertainment Option With 60+ Streaming and Fast Channels, Plus Peacock Premium
DETROIT--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 7, 2023--
2023-06-07 21:23

Accenture Federal Services Wins Position on IRS Blanket Purchase Agreement with $2.6B Ceiling Value
ARLINGTON, Va.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 24, 2023--
2023-05-24 21:18
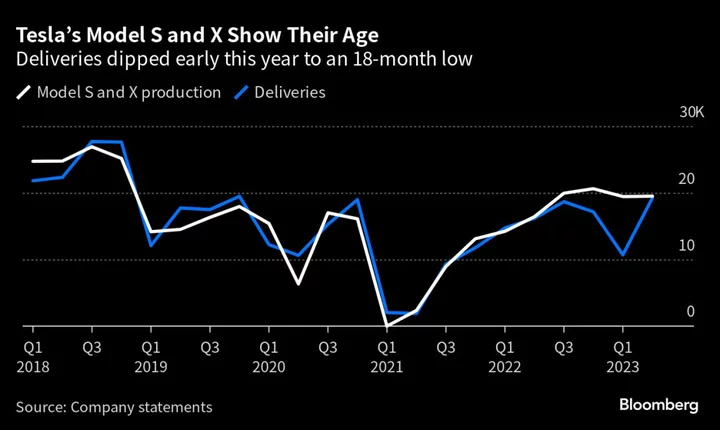
Tesla’s $41,000 Model X Discount Unlocks Subsidies Musk Wanted Gone
Tesla Inc.’s latest discounts will newly qualify one of its models for federal subsidies that Elon Musk said
2023-09-01 20:18
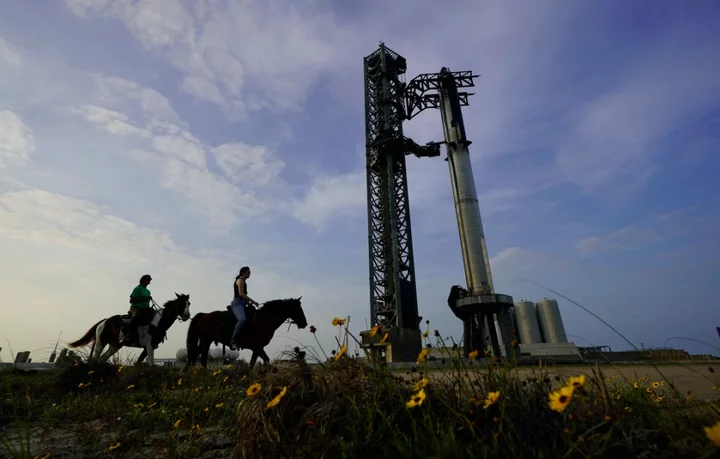

Elon Musk makes prediction for imminent Starship launch
Elon Musk has revealed new details about the next major test flight for SpaceX’s Mars-bound Starship rocket, which he claims is ready to launch. SpaceX is still awaiting approval from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to launch the biggest rocket ever built, with the US regulators currently undertaking a “mishap investigation” for the previous Starship launch in April. The 400-foot-tall (121 metre) rocket exploded over the Gulf of Mexico just three minutes into a planned 90 minute flight on 20 April, breaking up into pieces over the water. An inadequate launchpad was also destroyed by Starship’s huge engines, blasting concrete chunks and metal shards across a 700-acre area. The SpaceX boss had predicted that the rocket would explode, saying ahead of the attempt: “I am not saying it will get to orbit but I am guaranteeing excitement.” The tech billionaire is more hopeful for the latest launch attempt, having made several key changes to how it operates. “We are doing a new staging technique called hot staging where you light the upper stage engines while the booster stage is still firing,” Mr Musk told the All-In Podcast this week. This is the most efficient way to do stage separation of a rocket going to orbit but we did not try that on the last mission... I think, I hope, we have a well over 50 per cent chance of getting through stage separation, and maybe a close to 50 per cent chance of getting to orbit if the hot staging separation method works. “I’d say it’s above 50 per cent chance of getting to orbit this time, whereas previously I said below 50.” Once in orbit, Starship will travel around the planet before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean just north of Hawaii. The Starship rocket is currently fully stacked at SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Texas, though it is not clear how long the private space firm will have to wait before receiving FAA approval. “The SpaceX Starship mishap investigation remains open,” the FAA said in a statement last week. “The FAA will not authorise another Starship launch until SpaceX implements the corrective actions identified during the mishap investigation and demonstrates compliance with all the regulatory requirements of the licence modification process.” Read More SpaceX launch of Starship rocket on hold amid ‘mishap investigation’ SpaceX launch of Starship rocket on hold amid ‘mishap investigation’ Starship ‘ready to launch’, Elon Musk says SpaceX smashes rocket launch record as Musk eyes historic Starship mission
2023-09-13 22:17
A lawsuit by TikTok users challenging Montana's ban is being funded by the social media company itself
A high-profile lawsuit brought by TikTok users and creators last month challenging Montana's statewide ban against the short-form video app is being funded by the social media giant itself, the company told CNN on Wednesday.
2023-06-29 00:52
Georgia school board fires teacher for reading a book to students about gender identity
A Georgia school board has voted to fire a teacher after officials said she improperly read a book on gender fluidity to her fifth grade class
2023-08-18 09:57
You Might Like...

OpenAI's Sam Altman launches Worldcoin crypto project

Google rolls out a major expansion of its Bard AI chatbot

'Waiting patiently': Internet disappointed as 'Emily in Paris' Season 4 gets delayed due to writers stirke

A lifetime subscription to Microsoft Windows 11 Pro is on sale for 84% off
Solar panel tech breakthrough generates electricity from rain

Future space missions could use all-female crews because they are more ‘efficient’

Top Tech Companies Pledge Not to Be Reckless With Their AI Tools

A 3-year subscription to this powerful VPN is on sale for 61% off
