
Sydney Blanketed in Toxic Smoke for Days Following Planned Burns
Sydney ranked in the top five most polluted cities in the world for air quality on Wednesday, as
2023-09-13 11:19
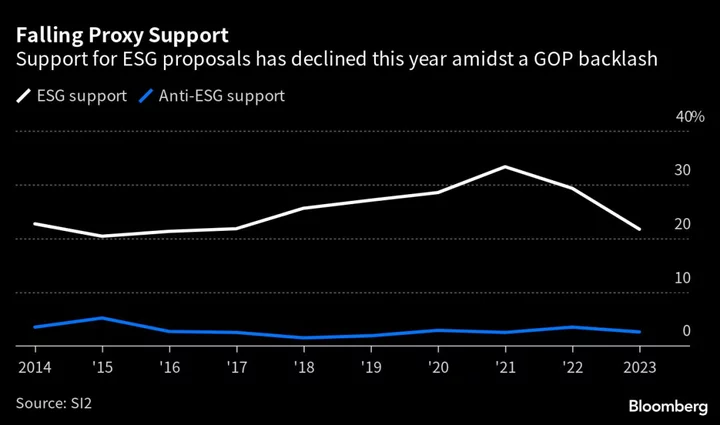
Support for ESG Shareholder Proposals Plummets Amid GOP Backlash
Investor support for environmental and social shareholder proposals slumped to the lowest in six years amid the Republican
2023-06-09 20:21

Coinbase Sued by SEC for Breaking US Securities Rules
The Securities and Exchange Commission sued Coinbase Global Inc. in federal court in New York on Tuesday, alleging
2023-06-06 21:19
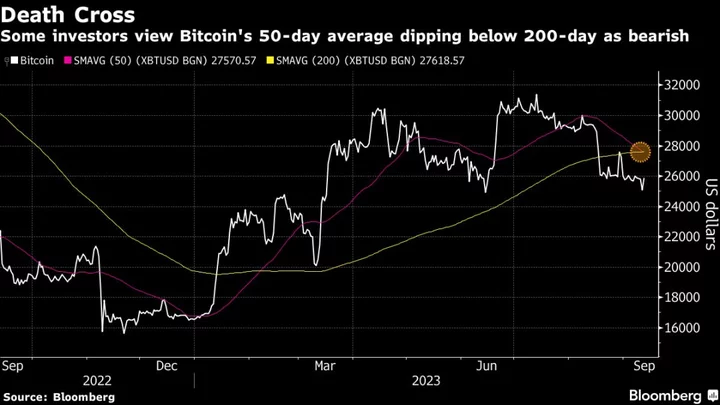
Crypto Volatility Picks Up on Looming Sales From FTX’s $3.4 Billion Token Hoard
Volatility picked up in digital-asset markets as traders evaluated the prospect of crypto disposals by the defunct FTX
2023-09-12 13:50

Is Outlook down? Thousands of users report problems with Microsoft's email platform
Thousands of Microsoft Outlook users reported issues with accessing and using the email platform Monday morning
2023-06-06 00:17

TikTok: How to see who has looked at your profile
TikTok is now letting people around the world see who has visited their profile. The feature means that users can see when a person clicked onto their account – with some restrictions. Like other platforms such as LinkedIn, it means that when a logged-in users visits a profile they will appear in a list. That list can then be seen by the owner of the account, but nobody else. TikTok has been slowly rolling out the feature for more than a year. It was initially spotted by users who saw references to it hidden in the app, before it rolled out more generally – and it is now available to everyone. But it must be manually turned on, and so the change does not mean that you will have been exposed as visiting a profile without knowing about it. It can also be switched back off when it is enabled. There are a number of limitations on the feature, which are seemingly intended to protect privacy. Users need to be at least 16 to see it, for instance, and also have fewer than 5,000 followers. But mostly importantly the tool will only work for other people who have it turned on: users can only see people who visited their profile if they too have the profile view history option turned on. In that way, it is similar to other privacy features in apps such as WhatsApp. There, for instance, users can only see read receipts and information about when a user is online if they choose to give that information away about themselves. The feature is switched on by opening the profile page, clicking the settings button in the top-right corner, and then choosing the settings option. Click on settings and privacy, then privacy, and then profile views. That will open up the page and show the people who have been on a profile in the last month or so. If it is not switched on already, then that same page will offer the option to do so. The data only starts being shown from the moment the switch is turned on, meaning that there will be no way of seeing who had visited an account before then. To switch the feature off, click on one of the notifications that the app sends when someone has viewed your profile. That will take you to the same profile views page, which includes a settings cog that can be used to switch the history tool back off again. Read More Schoolboy almost dies from swallowing magnets for TikTok challenge Woman shares honest review of New York City apartment TikTok mom slammed after making 5-year-old son run in 104 degree heat
2023-07-01 00:29

Quantum-Si Appoints Biotech Executive and Entrepreneur, Amir Jafri, to its Board of Directors
BRANFORD, Conn.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 21, 2023--
2023-09-21 20:17

Top Offset Project Must Hand Zimbabwe Revenue or Close
Zimbabwe’s Environment Minister said the operators of a project generating carbon credits from an area almost the size
2023-05-18 04:50

What happened between Joe Rogan and Brian Redban? Ex-JRE co-host shares email from 'hustling' days with creators of GTA and Red Dead Redemption
Joe Rogan removed Brian Redban from The Joe Rogan Experience in 2013 due to his lack of technical knowledge
2023-07-06 16:22

EV maker Rivian delivers 12,640 vehicles in second quarter
Electric-vehicle maker Rivian Automotive said on Monday it delivered 12,640 vehicles in the second quarter, a 59% jump
2023-07-03 20:46

Amazon.com's Ring mishandled customers videos and will pay $5.8 million fine
WASHINGTON (Reuters) -Amazon.com's doorbell camera unit Ring has reached a settlement with the U.S. Federal Trade Commission regarding privacy, according
2023-06-01 02:29

US tightens crackdown on crypto with lawsuits against Coinbase, Binance
By Jonathan Stempel, Hannah Lang and John McCrank NEW YORK The top U.S. securities regulator sued cryptocurrency platform
2023-06-07 09:46
You Might Like...

More than half of Americans have experienced online harassment, says ADL report

Elon Musk says Twitter will start 'purging' dormant accounts

8 great ways to organize your Gmail inbox to improve productivity

Archive of Our Own is down, and it could be offline for weeks

GameStop beats quarterly revenue estimates on strong videogame demand

Tech’s Rally Isn’t Done. Why These 10 Stocks Are the Next to Gain.

How to Get Competitor's Time Brella in Fortnite OG

Dr.Evidence® Appoints Ken Kobayashi, MD, FACP to its Medical Strategy Advisory Board
