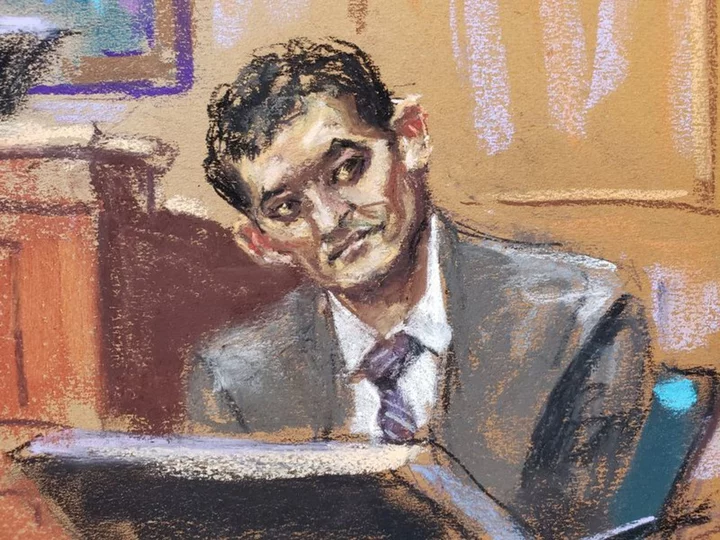
Sam Bankman-Fried grilled on 'cozy' relationship with Bahamas officials
By Luc Cohen NEW YORK FTX founder Sam Bankman-Fried was grilled on Tuesday about what a U.S. prosecutor
2023-10-31 23:15

World’s Highest Puffs Charge Free Battery Technology “TOPOWER” — Real Disposables Exhibited in Dubai
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 25, 2023--
2023-06-25 19:52

Ninja: 5 things you didn't know about pro YouTuber and Twitch streamer
Ninja became an esports sensation by broadcasting games like Fortnite and Valorant for an average of six hours a day
2023-06-07 15:15
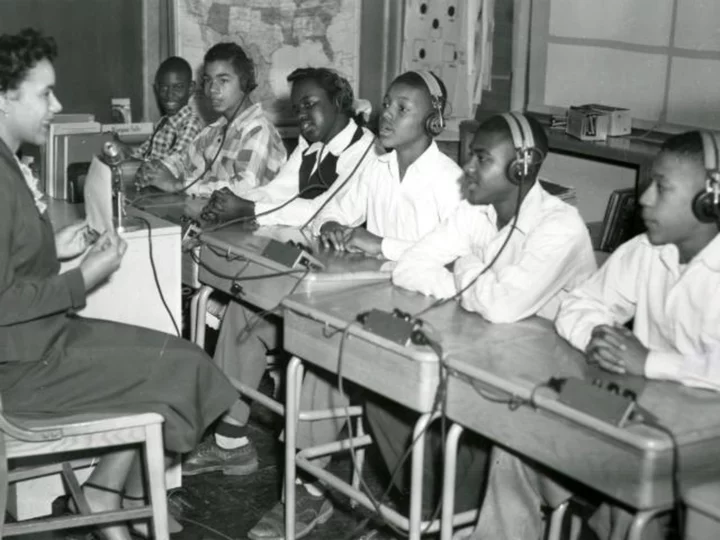

Black deaf students who attended 1950s segregated school will finally get their high school diplomas
At least 24 Black deaf students who attended a segregated school on the grounds of Gallaudet University in Washington, DC, in the early 1950s never received their high school diplomas.
2023-07-22 20:16
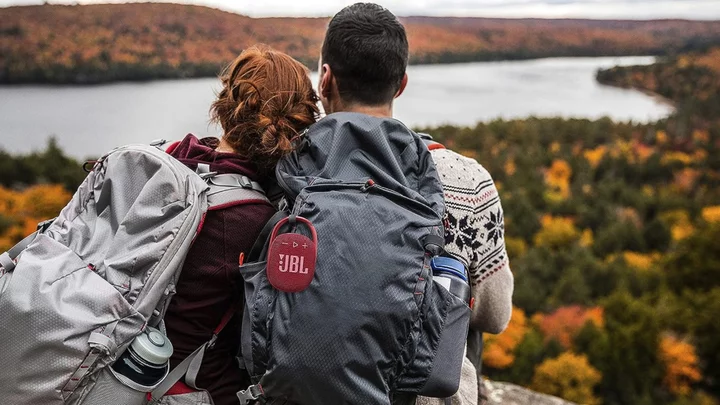

Keep the party going all summer long with 25% off JBL Clip 4 Bluetooth speakers
SAVE $20: As of August 9, you can buy a JBL Clip 4 Bluetooth speaker
2023-08-09 23:22
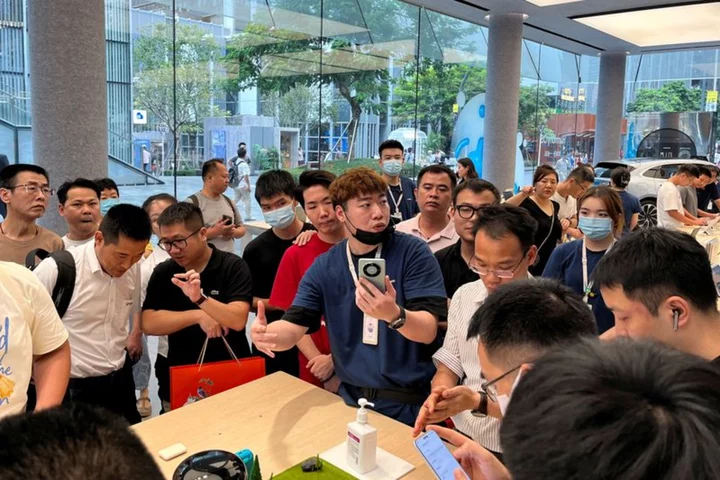

Explainer-Why is Huawei's new smartphone generating so much buzz?
SHENZHEN, China The surprise launch of the latest high-end smartphone from Chinese tech giant Huawei Technologies has triggered
2023-09-01 17:17

The dark web is overflowing with stolen ChatGPT accounts
There's no doubt about it: ChatGPT, the AI chatbot from OpenAI, is extremely popular and
2023-06-23 05:45

Apple launches Vision Pro, a VR headset it hopes will be most important product since iPhone
Apple has announced the ‘Vision Pro’, a headset it hopes will be its most important product since the iPhone. The new virtual reality tool will allow people to see apps projected on top of the room around them, allowing apps to be “freed from the confines of a display”, Apple said. Users will be able to sit in their living room and see their apps – messages, phone calls, web browsing and more – projected on top of their coffee table, for instance. As such, it is the first Apple product “you look through, not at”, said Tim Cook as he introduced it during Apple’s Worldwide Developers Conference. Other apps, such as games, will take over the full view, Apple said. But even then the goggles had been made to ensure that users were never cut off from the world around them. :: Follow The Independent’s live coverage of Apple’s event here That includes a feature that means that if someone comes into the room, the headset will spot them and superimpose them. But the headset also has a feature called “EyeSight” – a display on the outside of the goggles, which shows people’s eyes, and gives an indication of what they are doing inside the headset. Read More Apple just added loads of new features to your iPhone Apple reveals big version of its smallest laptop Apple is about to update all its products – and release a very big new one
2023-06-06 02:47

Valorant Knight's Market Buddy: How to Get for Free
To get the Valorant Knight's Market Buddy for free, players must link their Riot Games account to their Amazon Prime account and then claim the reward.
2023-08-31 04:49
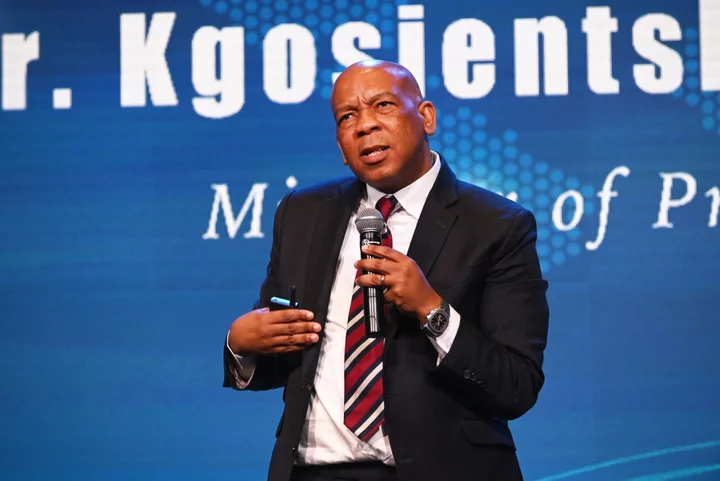

South African Electricity Minister Attacks Climate Finance Pact
South Africa’s electricity minister attacked the country’s groundbreaking $8.5 billion climate finance pact with some of the world’s
2023-07-25 18:45

Pixis, a Leading Codeless AI Infrastructure Company for Marketing, Secures Funding of $85 Million in Series C1 Funding
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-14 21:48

Accenture Invests in Open Cosmos to Expand Access to Satellite Data
PARIS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 11, 2023--
2023-09-11 15:56
You Might Like...
This celebrity fitness app is only $200 for life
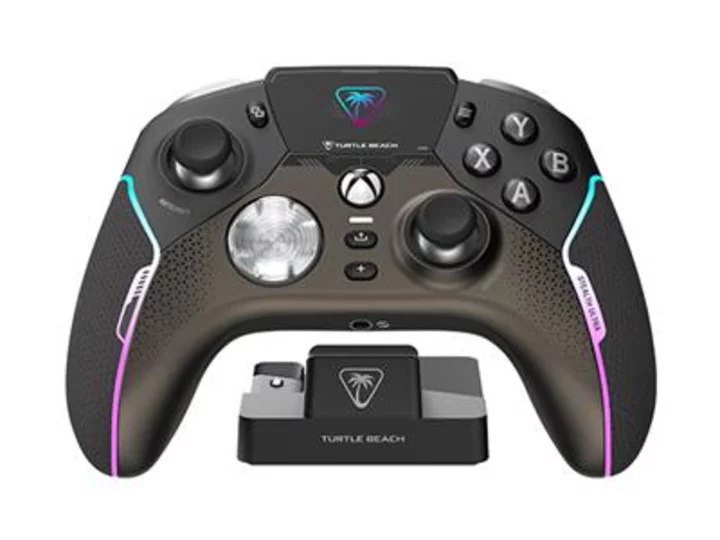

Turn Your Controller Into a Command Center – Introducing Turtle Beach’s Groundbreaking Designed for Xbox Stealth Ultra Wireless Controller

FiscalNote Announces Partnership With Korea’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs to Provide AI-Powered Policy and Data Intelligence, Legislative and Regulatory Monitoring, and Global Issues Management

Amazon Music Unlimited Prime Day Deal: New Subscribers Get 4 Months Free
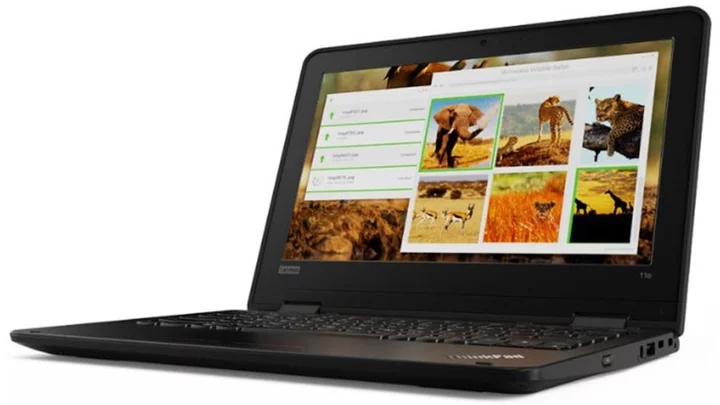

Get a Refurbished ThinkPad with Microsoft Office Professional for $200
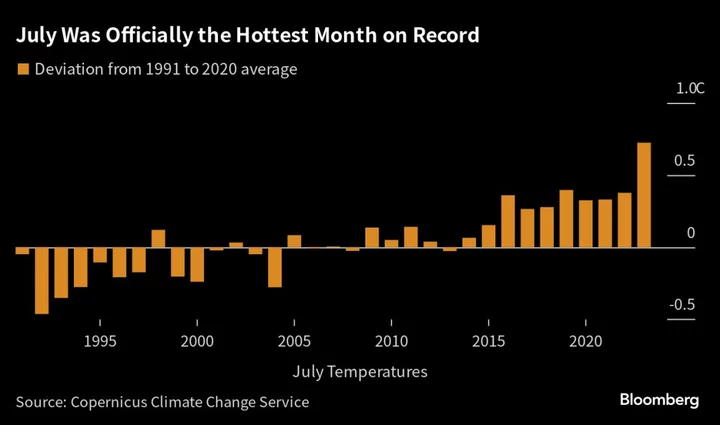
July Was the Hottest Month on Record

Model has Maui fundraiser shut down for offering to sell spicy images to donors

'I had no idea:' Florida teacher under investigation for showing Disney movie with gay character says she didn't know LGBTQ restriction applied to her class
