
"Groundbreaking Human-AI Collaboration Tool to Offer Any Organization a Uniquely Fine-Tuned Proprietary LLM”
MONTREAL--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 24, 2023--
2023-07-24 22:16

Google Axes Bad Reviews of Tracker Exposing Uyghur Forced Labor
Alphabet Inc.’s Google has removed hundreds of negative reviews for a tracker that identifies apparel brands linked to
2023-08-25 00:55

Vodafone down: Phone network not working as customers struggle to make calls
Vodafone customers say they are struggling to make calls, seemingly after technical issues at the network. Users said they were experiencing an array of unusual problems. Some said they were able to call other people on Vodafone – but not speak to people on other networks, for instance. Data connections appeared to be working as normal, however. On Twitter, Vodafone responded to affected users by apologising and asking for more information, and its online service checker indicated there were problems in some areas. The company did not immediately respond to a request for comment. Tracking website Down Detector also showed problems at Vodafone, starting on Monday afternoon. Other networks were also flagged as having issues – but that may be simply because Vodafone calls to those on other providers were failing to connect. Read More US Air Force is toying with idea of building this Batman villain’s weapon China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion likely Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns
2023-09-04 20:57

FBI warns on Scattered Spider hackers, urges victims to come forward
By Zeba Siddiqui SAN FRANCISCO The FBI warned organizations to guard against the Scattered Spider hacking group, which
2023-11-17 05:22

MrBeast gives away over $500,000 worth of Shop Cash to fans, says 'enjoy the $'
MrBeast has produced content centered on giving away expensive goods and incredible sums of money, earning the nickname 'the giveaway king'
2023-06-03 14:20

Are xQc and Kai Cenat close? Kick streamer labels Twitch king's short film 'Global Pursuit' a 'disaster'
Kai Cenat recently premiered the film 'Global Pursuit' on YouTube, which quickly garnered over 200,000 views within an hour
2023-08-26 15:49
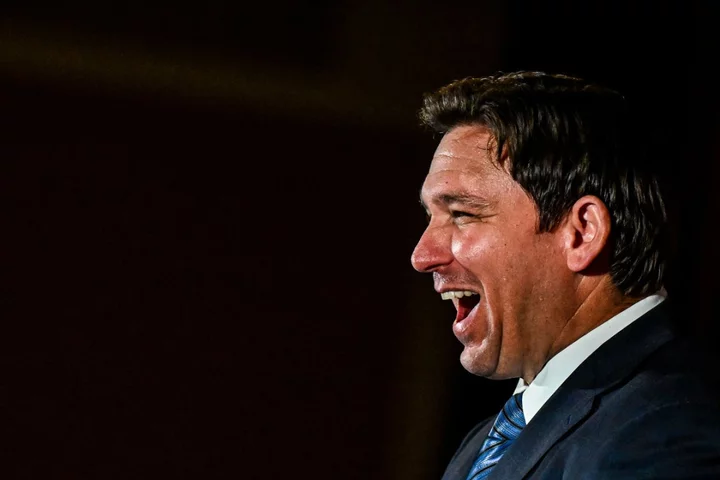

What is Twitter Spaces and why did it go so wrong during DeSantis’s 2024 launch?
Ron DeSantis’s long-anticipated 2024 campaign bid for the White House on Twitter Spaces was marred by a host of glitches that gave his political rivals enough ammunition to mock the Florida governor. Long silences and persistent echoes marred Mr DeSantis’s Wednesday announcement that he made on Twitter’s audio group-chat feature with billionaire Elon Musk who has long boasted about several overhauls to the social media platform to make it better than it was under previous leadership. The Twitter feature is a way in which users can gather in a “space” and have live audio conversations, with anyone in a space being allowed to “join, listen, and speak”, as per the website. At one point of time, the controversial Republican governor himself disappeared from the audio-only livestream. The Twitter app repeatedly crashed for users who tuned in for the announcement. Tech investor David Sacks, who was roped in to introduce the event, reportedly remarked that “the servers are melting”. When the former military officer-turned-politician finally managed to speak – about 20 minutes after the scheduled start – Mr Musk shut the initial Spaces event and started a new one. “That was insane, sorry,” said the Tesla billionaire. The buggy start to Mr DeSantis’s bid for the top job was dismissed by several Twitter users as a “disaster”. “Great start to his campaign!” said one sarcastic tweet. The second Spaces event kickstarted by Mr Musk, where Mr DeSantis read a short speech, seems to have attracted about 161,000 users, Twitter’s public-facing data revealed. Mr Sacks, however, claimed the number of attendees was one of the platform’s largest. He claimed that the glitches were an indication of people flooding Twitter, eager for Mr DeSantis’s entry into the presidential race. “We got so many people here that we are kind of melting the servers, which is a good sign,” Mr Sacks said in the first livestream. But this assessment was met with derision by former Twitter employee Earnest Wilkins, who helped produce the Twitter’s Spaces feature. “Lol this isn’t in the top 150 spaces by size in the history of the product,” he tweeted. Mr Sacks’s claim was also mocked by Democrat Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, who said her non-campaign-related Twitch stream of her playing Among Us in 2020 attracted more people. “There was so much enthusiasm for Governor DeSantis’ vision for our Great American Comeback that he literally busted up the internet,” tweeted Mr DeSantis’s press secretary, adding that the event raised “$1 million” for the the campaign in one hour. The Wednesday event, according to many users on the platform, is a reflection of how Twitter under Mr Musk is far from operating smoothly. “Holy f***ing shit, Ron DeSantis’s campaign launch crashed and burned faster than a Tesla,” said one tweet. Since the Tesla titan laid off nearly three-fourths of Twitter’s workforce after taking over the social media company, the platform has been mired with technical issues. Users have faced frequent outages and bugs that have surfaced frequently and inconvenienced them. Several users earlier this week flagged a bug that caused some of their deleted tweets from the past to resurface on their timelines and, weeks before that, many were unable to tweet with the platform mistakenly stating they went over “the daily limit for sending tweets”. In March, many users also reported problems with posting images and sharing external links, with the Tesla chief himself noting that the platform “is so brittle”. The embarrassing tech glitches in Mr Musk’s platform were mocked by Mr DeSantis’s rivals on both sides of the political spectrum. They have also likely become a source of embarrassment for the Tesla chief, who had previously proclaimed that he prefers “to stay out of politics”. Donald Trump, the current Republican frontrunner for president, gleefully dubbed the event Mr DeSantis’s “failure to launch”. Joe Biden’s official Twitter account also jumped in and tweeted a link to Mr Biden’s own fundraising page, saying, “This link works”. Mr DeSantis’s campaign launch was widely anticipated, with many Republicans viewing him as a contender against Mr Trump. His controversial policies as Florida governor, including moves to restrict transgender and abortion rights, and backing a law that restricts classroom instruction on race and racism, led to him amassing a following in the American far right. The NAACP and Equality Florida have issued travel advisories to the state, warning that it is no longer safe for Black people or for those from the LGBT+ community. Read More Ron DeSantis news – live: Elon Musk’s Twitter Spaces crashes ruining Florida governor’s 2024 campaign launch Trump and DeSantis' rivalry intensifies as Florida governor formally enters 2024 presidential race Elon Musk complains about David Duke comparison during disastrous DeSantis 2024 launch event Ivanka and Jared split over attending Trump 2024 launch – follow live Why was Donald Trump impeached twice during his first term? Four big lies Trump told during his 2024 presidential announcement
2023-05-25 16:15

Canadian publishers seek antitrust probe of Meta blocking news
OTTAWA (Reuters) -Canadian news industry groups on Tuesday asked the country's antitrust regulator to investigate Meta Platforms' decision to block
2023-08-08 23:15
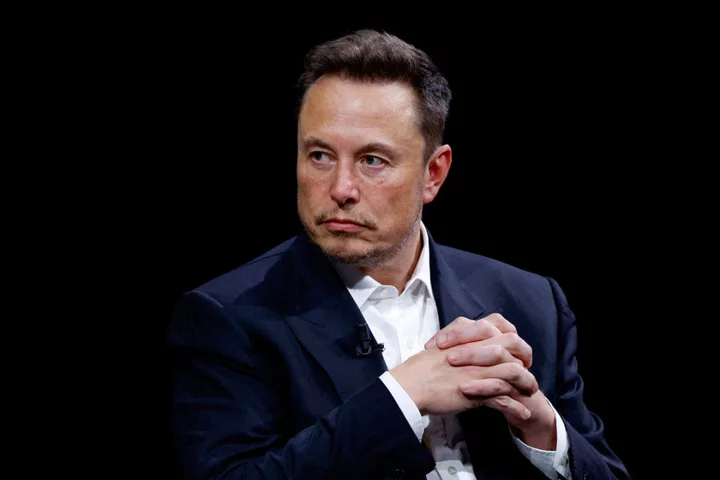

Elon Musk believes OpenAI may have made ‘dangerous’ discovery
Elon Musk has suggested that OpenAI may have discovered “something dangerous,” leading to chaos at the company. He made the comments after the research organisation recently fired and re-hired its CEO, Sam Altman, under mysterious circumstances. Musk, a co-founder of OpenAI, said that he had attempted to find out what happened behind the scenes, but had failed to do so. The billionaire had reached out to numerous people working at the company, including Ilya Sutskever, a chief scientist and board member, who is believed to have led the rebellion against Mr Altman, but had not heard anything. He has previously criticised the company’s shift toward profit-oriented operations and decision to cease open-sourcing its work. Read More Elon Musk meets Netanyahu for tour of Israeli kibbutz devastated on October 7 Sunak defends Elon Musk interview after MP says ‘world cringed at fawning welcome’ Bears chase cars on mountain road in Romania
2023-11-30 23:29

Grab Microsoft Office 2021 on Windows or Mac for Just $30
Whether you use a Windows PC or a Mac, it's possible to pick up Microsoft
2023-05-29 20:17

Kris Jenner branded ‘ridiculous’ over new filtered snaps
Kris Jenner's latest Instagram post has posed a few questions about her flawless appearance. The reality star and famed momager of the Kardashian-Jenner clan took to the app on Monday (28 August) to showcase a glam look by make-up artist Samer Khouzami. The clip shows the 67-year-old innocently smiling for the camera – but many have gone as far as to accuse her porcelain skin as being "AI". One person hit back at MUA Khouzami: "Please post an unfiltered photo so we can see her true beauty. Being a master makeup artist this just gives clients the wrong illusion and this is things they expect instead of seeing pours which is totally normal." Another added: "She is f***ing stunning - but please show us this look without the ridiculous filter though? She doesn’t need it." "What the hell is happening that’s not her face," one fan quipped. Meanwhile, the editing app Facetune, which has become a popular hit among influencers and celebrities, snubbed: "This is a great time to tell everyone we have Facetune for videos." This isn't the first time eagle-eyed fans have accused the family of editing their photos online. Kim Kardashian even admitted to one hilarious mishap that got the internet talking. In a post last year, the SKIMS founder confessed to replacing Kylie Jenner's daughter, Stormi, with Khloe Kardashian's daughter, True. At the time, Kim shared the original image at Disneyland to her Instagram story, writing: "The original pics were Stormi! However, I asked @kyliejenner if I could post them and she said [insert crying face] she wasn't really feeling posting at the moment and so I respect that! But it wasn't going to mess up my IG feed. Chi was wearing pink and it matched perfectly." She continued: "It wasn't the aesthetic I was going for and I can own up to that! You know how much a good aesthetic means to my soul and I will be dammed if Kylie will ruin that for me and mess up my IG grid. So thank you True for taking one for the team!" Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-29 18:48

Save 87% on a 3-year subscription to this secure VPN
TL;DR: A three-year subscription to UltraVPN is on sale for £23.35 and includes a free
2023-07-27 12:24
You Might Like...

YouTube won't ban IShowSpeed for 'accidentally' showing his 'meat' during livestream as fans back streamer: '#SaveSpeed, it was a mistake'
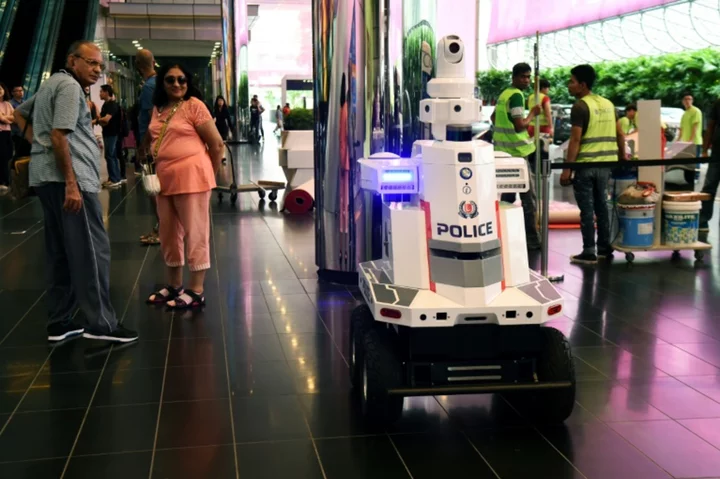

Singapore to put more police robots on the streets

How to unblock Netflix Germany for free

Walmart’s CISO, Jerry Geisler Joins Team8’s Enterprise Board
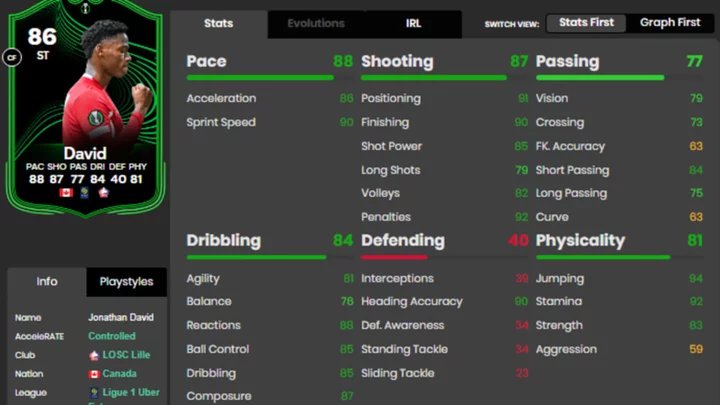
Jonathan David FC 24: How to Complete the Road to the Knockouts SBC

Spotify makes AI voice clones of podcasters and uses them to speak other languages

proteanTecs to Showcase the Future of Health and Performance Monitoring at DAC and SEMICON West 2023
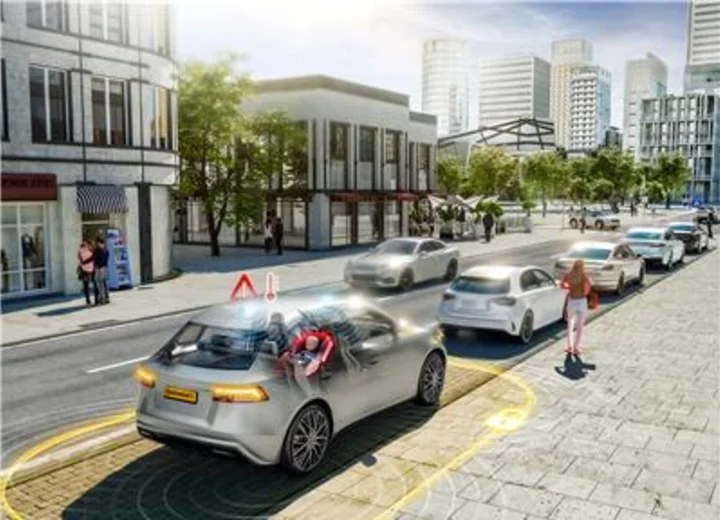

Continental Develops Child-Presence Detection Technology Aimed at Reducing Child Fatalities
