
Apple will update iPhone 12 in France after regulators said it emitted too much radiation
Apple has agreed to install updates for the iPhone 12 in France after French regulators ordered the company to stop selling the model because it emits electromagnetic radiation levels that exceed European Union standards. The company, which just unveiled its newest generation of iPhones, insists the 12 model is safe and the phones have been certified in countries around the world since its introduction in 2020. It says the problem raised by the French government agency that manages wireless communications frequencies is “related to a specific testing protocol.” The French agency said the iPhone 12 recently failed one of two types of tests for electromagnetic waves capable of being absorbed by the body. On Tuesday, France’s government ordered a halt to sales of the iPhone 12 and told Apple to issue a software update to address the problem or face a recall. Apple said in a statement Friday that it “will issue a software update for users in France to accommodate the protocol used by French regulators.” It did not elaborate. The French ban could have extended to all 27 EU countries after three months if Apple had refused to issue updates and if no other government objected, European Commission spokesperson Sonya Gospodinova said Thursday. France’s digital affairs minister said the iPhone 12’s radiation levels are still much lower than what scientific studies consider potentially harmful to users, and the radiation agency acknowledged that its tests don’t reflect typical phone use. Cellphones have been labeled as possible carcinogens by the World Health Organization’s cancer research arm, putting them in the same category as coffee, diesel fumes and the pesticide DDT. The radiation produced by cellphones cannot directly damage DNA and is different from stronger types of radiation like X-rays or ultraviolet light. Experts have recommended that people concerned about their cellphone radiation exposure use earphones or switch to texting. Read More Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide
2023-09-15 18:54

Is China a threat to US? Joe Rogan shocked after reading TikTok's terms and conditions: 'It's best for sucking people in'
Joe Rogan has raised concerns about TikTok's privacy, claiming the app is tracking user data for the Chinese
2023-08-29 22:58

Foxconn may partner with TSMC and TMH to set up fabrication units - ET
Foxconn is in talks with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co and Japan's TMH Group for technology and joint venture
2023-07-14 08:46

Is Adin Ross in trouble? Cuffem alleges Kick streamer forced women to undergo abortions, labels him a 'baby killer'
Cuffem's provocative statements about Adin Ross evoked sharp responses on social media
2023-08-19 22:22

Top 5 most-watched 'Minecraft' Twitch streamers every gamer should follow in 2023
Are you working hard to become a 'Minecraft' streamer? Here's a cool list to follow
2023-05-21 18:46
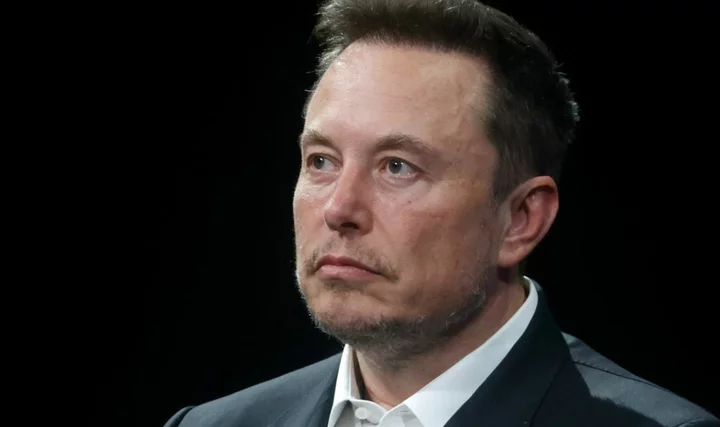

ElonJet, the banned Twitter bot that tracked Elon Musk's jet, is now on Threads
ElonJet is now on Threads, so you can once again track Twitter CEO Elon Musk's
2023-07-10 15:51

Fortnite Downtime Today (Nov. 23): When Servers Be Back Up
The Fortnite downtime on Thursday, Nov. 23, 2023, ends at 9 a.m. ET when servers will be back up with Fortnite OG Seasons 9 & X.
2023-11-23 05:17
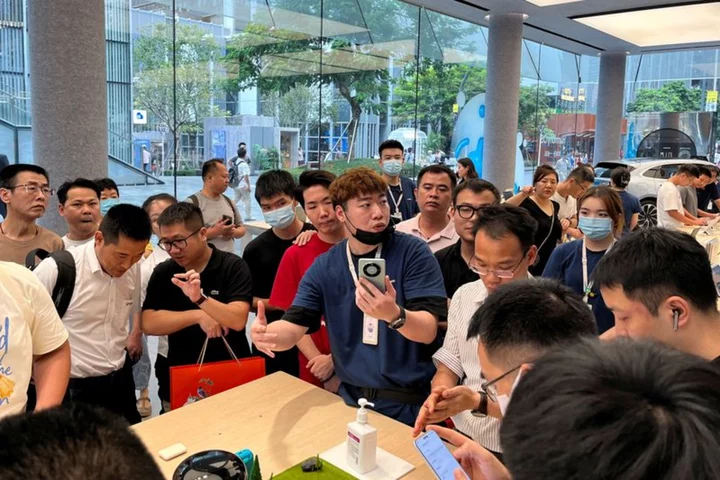

Explainer-Why is Huawei's new smartphone generating so much buzz?
SHENZHEN, China The surprise launch of the latest high-end smartphone from Chinese tech giant Huawei Technologies has triggered
2023-09-01 17:17
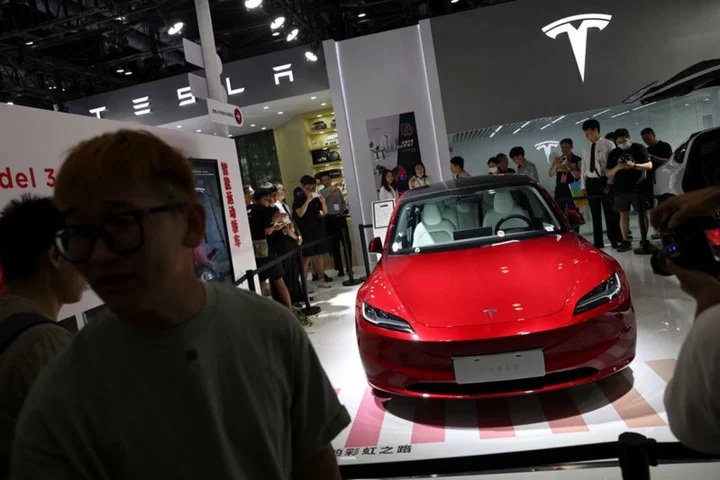

Tesla's deliveries expected to fall on plant shutdowns, soft demand
By Aditya Soni Tesla may miss estimates for third-quarter deliveries due to planned factory shutdowns and soft demand
2023-09-29 18:30
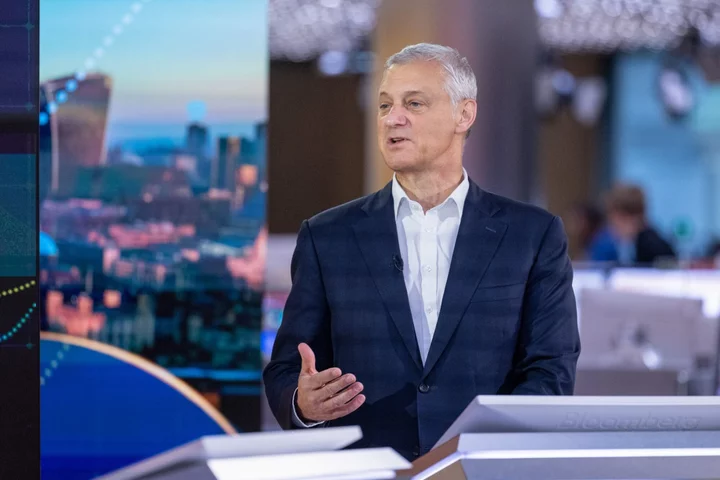

Barclays, StanChart Plan Bankers’ Return to COP28 Climate Summit
The world’s top bankers and investors mostly stayed away from last year’s United Nations climate conference in the
2023-10-04 14:45
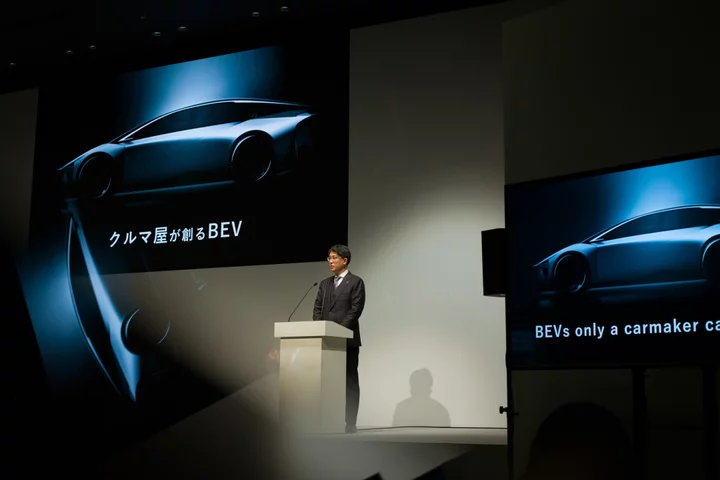

Toyota Braces for Investor Admonition Over EVs at Annual Meeting
Toyota Motor Corp.’s annual shareholder meeting is poised to become a referendum of sorts on the Japanese carmaker’s
2023-06-13 23:52
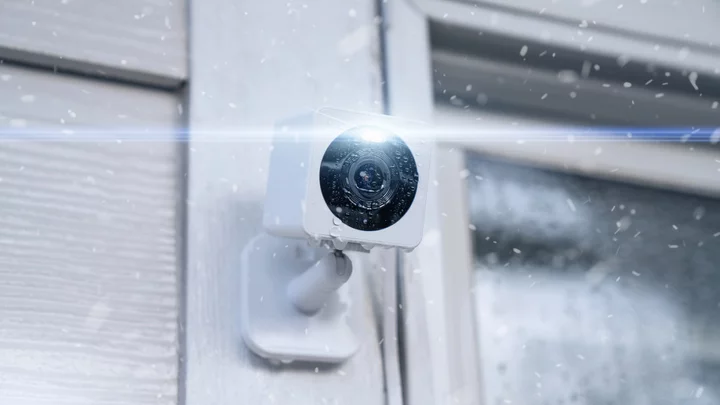

The Best Outdoor Home Security Cameras for 2023
If anyone ever stole a package from your porch or broke into your car while
2023-06-23 05:17
You Might Like...

Florida's Black history curriculum teaches children slavery was beneficial for Black people. It's creating outrage
AGs From All 50 States Call for Better Child Protection From AI

Samoa media guide

South Korea vows support for its chip sector amid China-US tension

Valorant Patch 6.11 Release Date

How tall is CoryxKenshin? Fans discuss height of popular YouTuber who they think is as tall as Kai Cenat

How to Create the Perfect Backyard Movie Night on the Cheap

For Mark Zuckerberg's Threads, the real rival is still TikTok -- not the former Twitter
