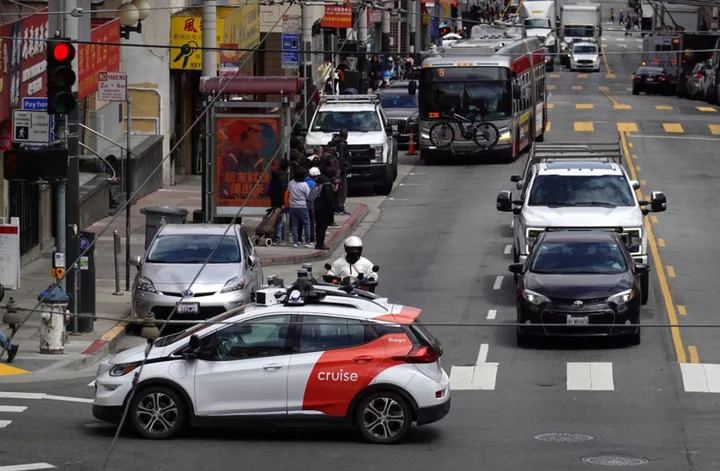

Traffic, wet concrete, and a collision with a fire truck: Robotaxis cause chaos in San Francisco after expansion
On 10 August, California regulators voted to expand the footprint of paid taxi services by autonomous, driverless cars from Cruise and Waymo in San Francisco. Since then, it’s been utter chaos, with the AVs involved in traffic jams, slapstick malfunctions, and a car accident with a fire truck. A day after the vote, video went viral on social media showing about 10 frozen Cruise taxis snarling traffic in the North Beach neighbourhood, which company officials later said was caused by a connectivity issue due to a spike in cell traffic because of a nearby music festival. The following Tuesday, a Cruise taxi was stuck in wet concrete at a construction site. “I can see five different scenarios where bad things happen and this is one of them,” resident Paul Harvey told SFGATE. “It thinks it’s a road and it ain’t because it ain’t got a brain and it can’t tell that it’s freshly poured concrete.” Two days after that, a Cruise taxi had what might be its most serious accident yet, colliding with a fire truck in the Tenderloin neighbourhood, giving the taxi’s passengers non-severe injuries. A firefighter in the truck said the AV “lurched” as it passed through an intersection ABC 7 reports, while Cruise said its vehicle detected the emergency sirens but was unable to get out of the way in time from the truck, which drove into the oncoming traffic lane. “The AV’s ability to successfully chart the emergency vehicle’s path was complicated by the fact that the emergency vehicle was in the oncoming lane of traffic, which it had moved into to bypass the red light,” the company wrote in a statement. “Cruise AVs have the ability to detect emergency sirens, which increase their ability to operate safely around emergency vehicles and accompanying scenes. In this instance, the AV identified the siren as soon as it was distinguishable from the background noise. “The Cruise AV did identify the risk of a collision and initiated a braking maneuver, reducing its speed, but was ultimately unable to avoid the collision,” the company added. Following the repeated mishaps, the California Department of Motor Vehicles asked Cruise to cut its 400-strong deployment of AVs in San Francisco in half, with the agency saying it was “investigating recent concerning incidents.” As The Independent reported, critics of AVs warned ahead of their expansion in San Francisco that the driverless cars weren’t ready for primetime, particularly when it comes to interfacing with emergency vehicles. According to data Cruise shared with the state earlier this month, between January and mid-July of 2023, Cruise AVs temporarily malfunctioned or shut down 177 times and required recovery, 26 of which such incidents occurred with a passenger inside, while Waymo recorded 58 such events in a similar time frame. Meanwhile, according to the San Francisco Municipal Transit Agency (SFMTA), between April 2022 and April 2023, Cruise and Waymo vehicles have been involved in over 300 incidents of irregular driving including unexpected stops and collisions, while the San Francisco Fire Department says AVs have interfered 55 times in their work in 2023. Last year, Cruise lost contact with its entire fleet for 20 minutes according to internal documentation viewed by WIRED, and an anonymous employee warned California regulators that year the company loses touch with its vehicles “with regularity.” Since being rolled out in San Francisco, robotaxis have killed a dog, caused a mile-long traffic jam during rush hour, blocked a traffic lane as officials responded to a shooting, and driven over fire hoses. Jeffrey Tumlin, San Francisco’s director of transportation, has called the rollout of robotaxis a “race to the bottom,” arguing Cruise and Waymo weren’t yet definitive transit solutions, and instead had only “met the requirements for a learner’s permit.” Read More How a vote to empower autonomous ‘robotaxis’ from Cruise and Waymo has divided San Francisco GM's Cruise autonomous vehicle unit agrees to cut fleet in half after 2 crashes in San Francisco San Francisco launches driverless bus service following robotaxi expansion GM's Cruise autonomous vehicle unit agrees to cut fleet in half after 2 crashes in San Francisco Chinese military launches drills around Taiwan as 'warning' after top island official stopped in US San Francisco launches driverless bus service following robotaxi expansion
2023-08-20 03:57
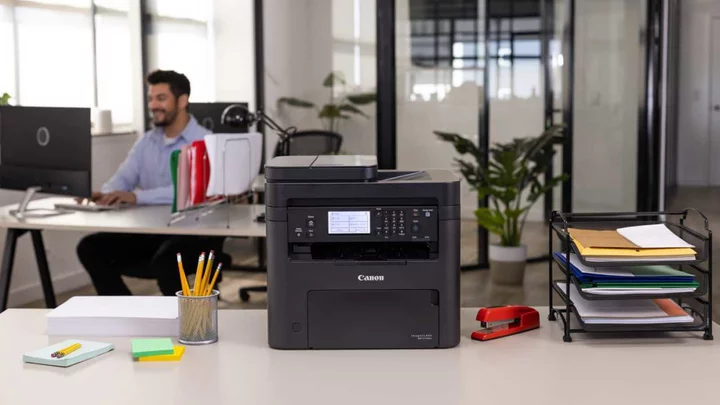

Canon imageClass MF275dw Review
The Canon imageClass MF275dw ($219.99) violates the rule of thumb for printers that higher numbers
2023-07-21 23:24

Fortnite Crew Pack August 2023 Revealed
The Fortnite Crew August 2023 will feature two skins, Princess Lexa and Price Orin, along with matching cosmetics. The August Crew Pack comes out on July 31.
2023-07-27 01:54

Climate change trial pits youths against Montana
By Clark Mindock The first trial in several U.S. climate change cases brought by youths kicked off on
2023-06-13 03:58

Meta Shares Climb After Revenue, Forecast Beat Estimates
Meta Platforms Inc. topped forecasts for second-quarter sales and gave a rosy outlook for the current period, signaling
2023-07-27 05:56
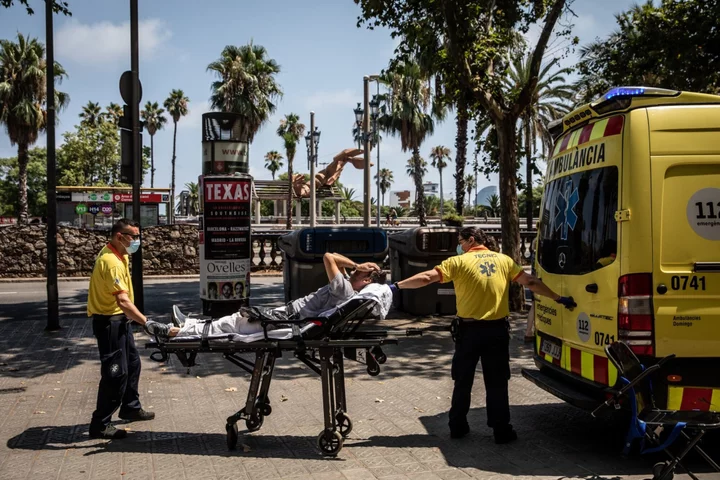

Warming World Risks Adding 9 Million Deaths Annually, WHO Says
Rising temperatures are making it increasingly difficult to reach global health goals. There is a risk of more
2023-05-19 16:20

Zoom shares jump as CEO says company to develop and deploy AI tools
Shares of Zoom jumped in after-hours trading Monday after the company said it expects to rake in stronger-than-expected earnings in the rest of this fiscal year.
2023-08-22 05:48

CEO of Fortnite game maker casts Google as a 'crooked' bully in testimony during Android app trial
Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney has portrayed Google as a ruthless bully that resorts to shady tactics to protect a predatory payment system
2023-11-21 09:19

Sega Pulls Back From Blockchain Gaming as Crypto Winter Persists
Sega Corp., the gaming studio once regarded among the staunchest advocates of blockchain gaming, is pulling back from
2023-07-07 06:17
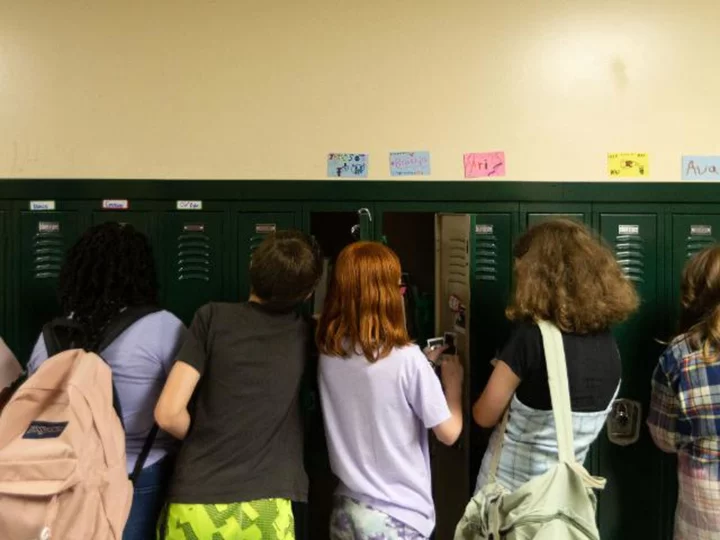

Test scores for 13-year-olds drop several points since the start of pandemic, building on decade-long decline, report says
Average test scores for 13-year-old students in both mathematics and reading have declined several points since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, building on a decline that's been trending over the last decade, according to a new report released from the National Assessment of Educational Progress.
2023-06-21 22:50

Gulf-UK Free Trade Talks Are ‘Progressing Well’, Says Official
Free trade negotiations between the UK and the six members of the Gulf Cooperation Council are “progressing well”
2023-09-26 20:27

Dr.Evidence® Appoints Ken Kobayashi, MD, FACP to its Medical Strategy Advisory Board
SANTA MONICA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 23:57
You Might Like...

Photos of The Legend of Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom Launch Event at the Nintendo NY Store Are Available on Business Wire’s Website

China Accuses US of Hacking Huawei Servers as Far Back as 2009

Ford CEO Predicts 1,000% Growth for In-Car Software Services

Discover Unbeatable Deals on Premium and Affordable Home Appliances From Tineco at Cdiscount's Summer Sales Event
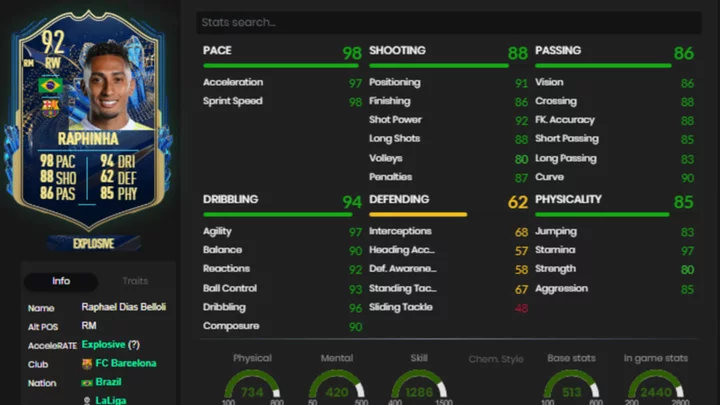
Raphinha FIFA 23: How to Complete the Team of the Season SBC

Starfield Factions: All Factions, Details, Can You Join Any?

ADL says it will resume advertising on X following feud with Elon Musk
iPhone Hacked Using NSO Group’s Pegasus Spyware
