
Spotify raises premium subscription price for millions
For the first time since 2011, Spotify confirms a price hike for about 200m ad-free subscribers.
2023-07-25 05:53

Kai Cenat puts 'skinny' Fanum's diet determination to test, Internet says 'he’s actually slimming down'
Kai Cenat recently garnered attention by putting Fanum's diet to the test
2023-09-22 17:52
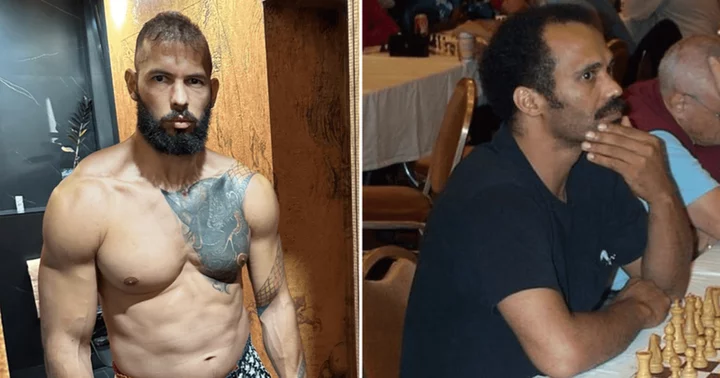
Andrew Tate claims his father's bad spelling misled AI bots into thinking he was 'crazy', trolls say 'even secret service dads don’t text like that'
Andrew Tate acknowledged that his dad often misspelled words and used poor grammar in his emails and Facebook messages
2023-07-30 19:48

100 Thieves and Higround Announce Dual Collections in Collaboration with Dragon Ball Z
LOS ANGELES--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-23 03:25

US FTC asks court to temporarily halt Microsoft's acquisition of Activision
WASHINGTON (Reuters) -The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) asked a federal court on Thursday for a stay that would prevent
2023-07-14 03:18
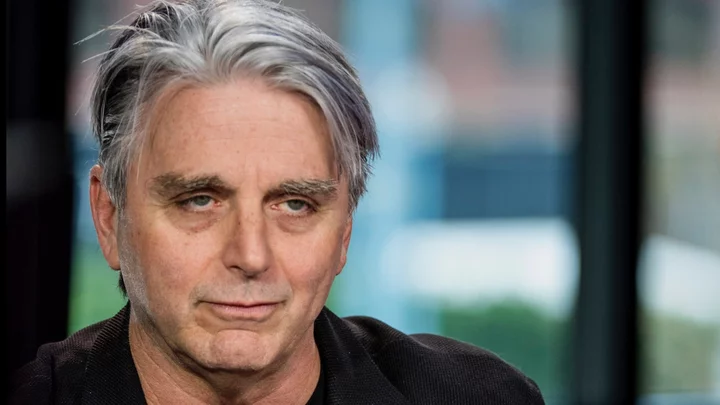

Unity Says Goodbye To Company CEO After Backlash Over Game Install Fees
Unity is parting ways with the company’s controversial CEO following weeks of backlash from the
2023-10-10 08:50
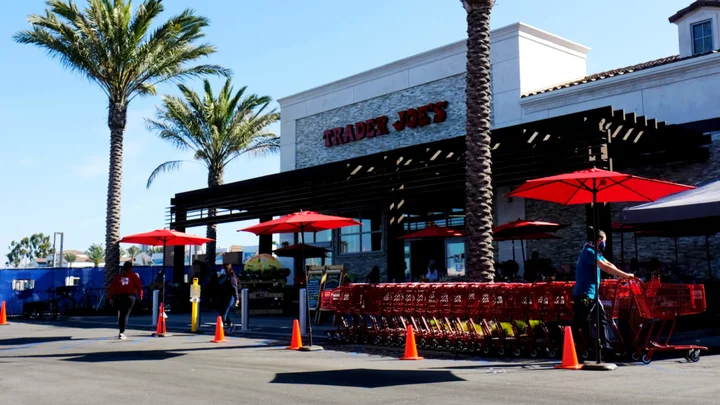

The Reason Trader Joe's Parking Lots Are So Small
Trader Joe's admits their parking lots are small, and they don't plan on changing that anytime soon.
2023-06-22 01:22
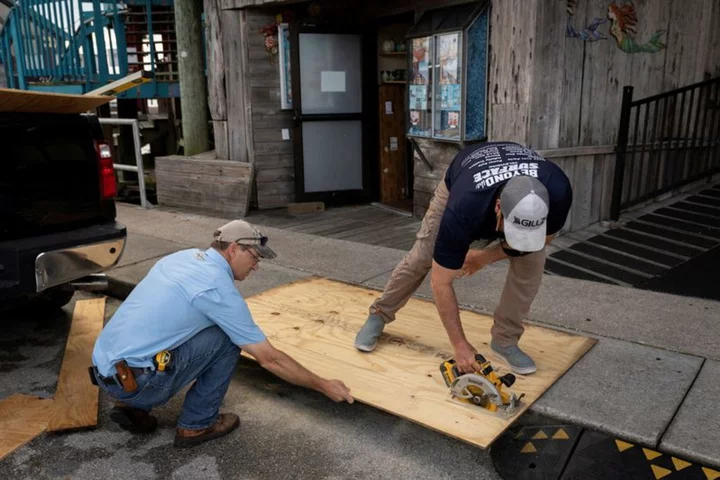

Explainer-What to expect when Hurricane Idalia hits Florida on Wednesday
By Julia Harte (Reuters) -Millions of residents could be affected by Hurricane Idalia as it hurtles toward Florida's Gulf Coast,
2023-08-30 07:27
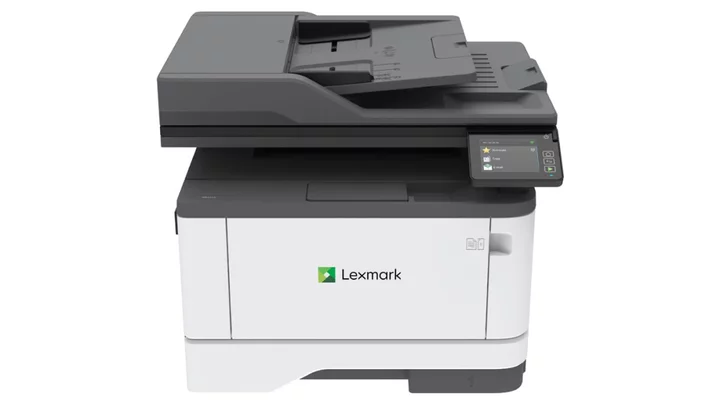

Lexmark MB3442i Review
Whatever's on your features checklist for your next mono laser all in one printer meant
2023-06-16 06:29
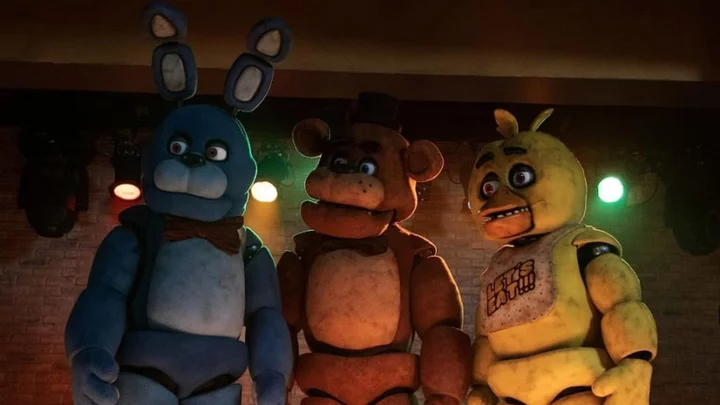

Is the Five Nights at Freddy's Movie Canon to the Games?
Many Five Nights at Freddy's fans wonder if the movie will be canon to the video game series.
2023-10-05 01:52

Twitter says Microsoft broke its rules for developers
Twitter on Thursday accused Microsoft of breaking the social network's rules for developers who access the platform's data, according to a copy of...
2023-05-19 09:27
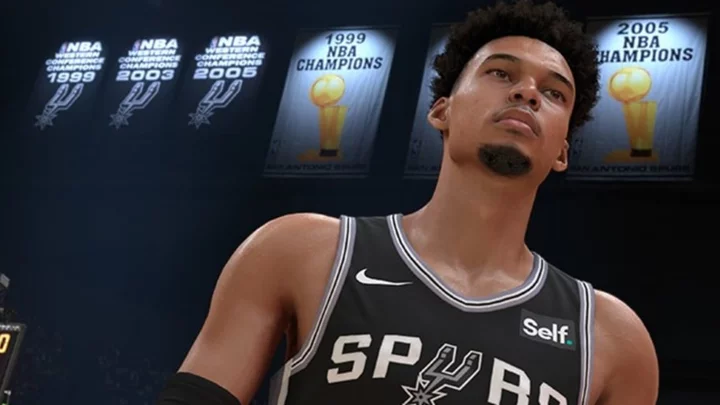

What Does NBA 2K24 Stability Mean?
NBA 2K24 Shot Timing Stability helps lessen the impact of shooting fatigue in the fourth quarter, adding more stability to your jump shot.
2023-09-21 08:22
You Might Like...

MrBeast breaks his own YouTube record as he dominates most-viewed video yet again, fans say 'bro’s only competition is mirror'

How to Get F1 Manager 2023 Early Access

Stocks Poised for Muted Open

US DoD Directive 8140 Broadens Approval of EC-Council Certifications to Encompass 31 Critical Job Roles within the DoD Cyberspace Workforce Framework (DCWF)

Deutsche Bank Tests Out AI to Detect Rogue Traders’ Phonecalls

World Series of Warzone Finals Twitch Drops: How to Get

Save 29% on Apple AirPods this Prime Day
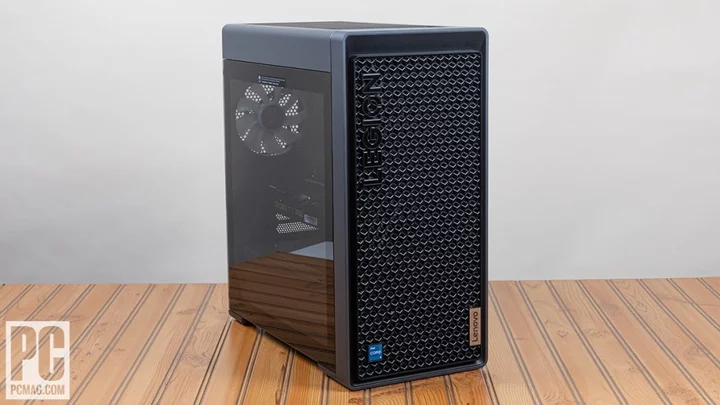

Lenovo Legion Tower 5i Gen 8 Review
