
Intel Patches 'Critical Weakness' Found in Billions of Processors
Intel fixed the security flaw known as "Downfall" this week, which is described as a
2023-08-09 23:19

European firms urge China to give more clarity on data transfer laws
By Joe Cash BEIJING European firms "urgently" need China to give clearer definitions of key terms in its
2023-11-16 05:52

Reference Customers “Praise” Boomi’s Ease of Use and Speed of Integration in Independent iPaaS Report
CHESTERBROOK, Pa.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 10, 2023--
2023-08-10 21:21

Dell's revenue forecast signals AI boost will take longer to materialize
(Reuters) -Dell Technologies on Thursday reiterated that it expects revenue to grow at a compounded annual rate of 3% to
2023-10-05 23:27

xQc claps back at Linus Tech Tips' jab at his 'failed relationship' and gambling adventures: 'I don’t even f**king get it'
The cheeky remarks added fuel to the ongoing conversation xQc's use of other creators' content in his videos
2023-08-06 21:16

Scientists are claiming an alien spaceship crashed straight into Mars
Is there life on Mars? Well, according to new research, an alien crash landing there could explain puzzling new findings on the surface of the Red Planet. It comes after Nasa’s Curiosity Rover captured images of spiked protrusions on the surface back in April. The strange formations captured in the pictures seem to show a row of spikes and sharp angles emerging from rocks at the base of the Gale Crater, which is 154km long. The odd discovery has put scientists on high alert and it marks one of the most peculiar things ever recorded on the surface of Mars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Astrobiologist Dr Nathalie Cabrol, who is from the NASA Ames Research Centre and Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Institute, even said that it’s the “most bizarre” rock she’s seen in 20 years of studying the planet. The findings are so irregular, in fact, that experts cannot rule out the idea that they’re extraterrestrial in origin. “A fragment from an extraterrestrial or terrestrial spacecraft cannot be discounted with absolute certainty” the authors of new research published in the Journal of Astrobiology stated. The odd protrusions could be “sand spikes”, which form in certain sands as a result of strong earthquakes. Another theory posits that the formation could be debris from crashed spacecraft, and authors of the study have not ruled out that it could be the result of crafts launched by humans landing on the surface. "Given that possibly 10 or more craft have crashed upon the surface, coupled with the jettison of equipment associated with landing the rovers, it is possible the spikes and its substrate are human-made and consist of debris that fell onto the surface of Gale Crater," the paper reads. “Nevertheless, no debris field is evident and no evidence of any additional debris that may have originated on Earth. “Given its small size and that there are no known human-made analogs and no logical explanation as to what purpose these spikes may serve, it does not seem likely these specimens are the remnants of craft or equipment that fell into Gale Crater. One can only speculate about extraterrestrial origin." However, speaking to The Telegraph, Prof Richard Armstrong, of Aston University, Birmingham said: “There is no way of proving for certain what the spikes are but the balance of the evidence would suggest ‘sand spikes’ resulting from seismic activity on Mars.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-25 20:54

Wilson Sonsini Adds Space and Technology Veteran Curt Blake in Seattle
PALO ALTO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 15, 2023--
2023-06-15 21:48

Qualcomm to supply Apple with 5G chips until 2026 under new deal
By Stephen Nellis Qualcomm on Monday said it had signed a new deal with Apple to supply 5G
2023-09-11 19:48

Netherlands: Phone ban announced to stop school disruptions
Secondary schools are being asked to ditch devices to try and improve students' learning.
2023-07-05 18:47
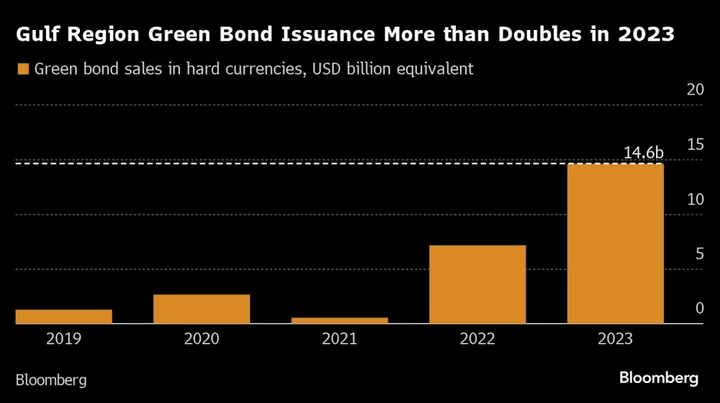
Green Bond Sales Surge in UAE Before It Hosts Climate Summit
A record amount of green debt has been raised this year by issuers in the United Arab Emirates
2023-11-23 18:17

Parents File Another Class-Action Lawsuit Against Roblox
Back in August, a class-action lawsuit was filed against Roblox alleging that the gaming platform
2023-11-20 13:49

Informatica Reports Second Quarter 2023 Financial Results
REDWOOD CITY, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 2, 2023--
2023-08-03 04:15
You Might Like...
Elon Musk renames Twitter to 'X' - 21 of the funniest jokes and memes

Take the stress out of applying to jobs with LazyApply — get it for $68 for life

Apple Moves to End Goldman Sachs Card Partnership. Why It’s for the Best.

Kyokugon Shrine TOTK Location and Guide
Vicarius Introduces vuln_GPT: The World’s First LLM Model to Find and Fix Software Vulnerabilities

Northern Europe’s Cool Spell Shifts to Warmer Weather by Weekend
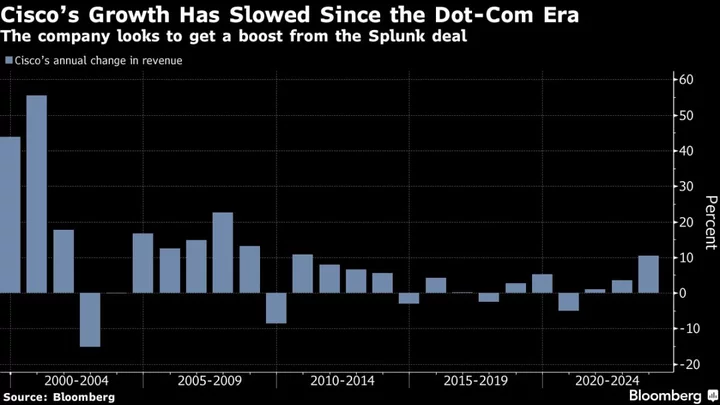
Once Silicon Valley’s Star, Cisco Looks to Splunk for Fresh Mojo

FTC to Appeal Court’s Ruling Favoring Microsoft-Activision Deal
