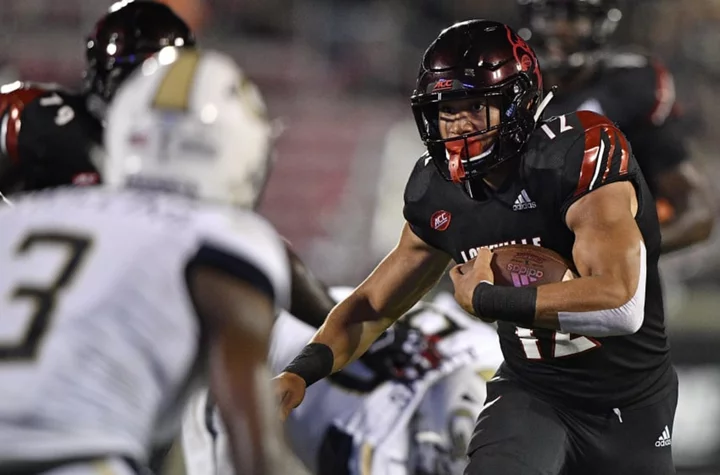

How to watch Louisville vs. Georgia Tech without ESPN on Spectrum
Friday night's Louisville vs. Georgia Tech game won't be available for Spectrum customers on ESPN because of a contract dispute with Disney. Here's how to watch without cable.
2023-09-02 06:49

Hackers advertise sale of 23andMe data on leaked data forum
By Raphael Satter WASHINGTON A hacker is advertising millions of "pieces of data" stolen from the family genetics
2023-10-07 05:23
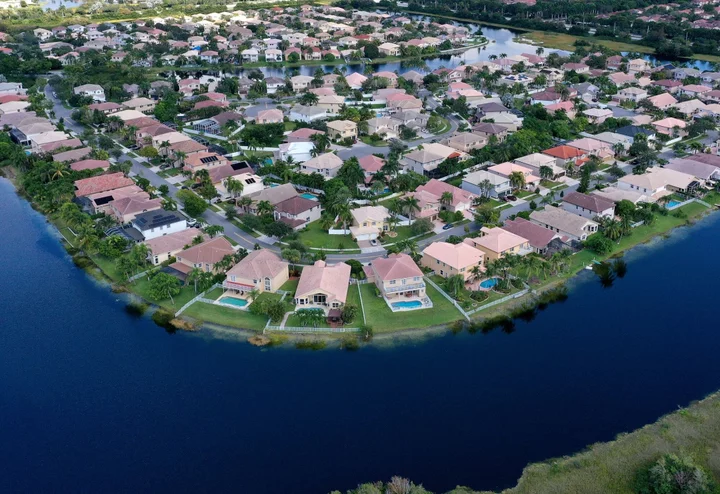

US Home Insurance ‘Bubble’ Closer to Popping as Climate Risks Mount
Home insurance costs that have soared in much of the US may get even higher. Tens of millions
2023-09-20 12:55

Crypto investment fraud warning issued by major bank
A major bank has issued a warning about crypto investment scams, with victims standing to lose more than £10,000 on average and young adults often being particularly at risk. Lloyds Bank has recorded a 23% rise in reports of cryptocurrency investment scams by customers in its banking group (including Lloyds Bank, Halifax and Bank of Scotland) between January and September 2023, compared with the equivalent period last year. Victims are losing £10,741 on average, up from £7,010 last year, the bank said, with many of the scams it analysed originating on social media. The most common age range for crypto scam victims is 25 to 34 years old, Lloyds said. Would-be crypto investors typically make an average of three payments before they realise they have been scammed, taking around 100 days from the date of the first transaction before they report it to their bank, Lloyds added. Crypto is a highly risky asset class and remains largely unregulated, which makes it an attractive area for fraudsters to exploit Liz Ziegler, Lloyds Bank Fraudsters often pose as investment managers, promising that any payments made by the victim will be invested on their behalf, often with the promise of huge returns. Sometimes the victim will be shown a fake investment account, suggesting that the funds are already making a profit, or a small amount of money will be transferred back into their bank account. But often there is no genuine crypto holding and the fraudster will disappear. In some cases, there will be an actual investment account held in the victim’s own name and registered with a legitimate platform. But once funds have been deposited, victims may be tricked into handing over their account login details, or passing control of their digital wallet over to the fraudster. They might also be directed to transfer cryptocurrency from within their own account to another digital wallet, which is under the control of criminals. Liz Ziegler, fraud prevention director at Lloyds Bank, said: “Crypto is a highly risky asset class and remains largely unregulated, which makes it an attractive area for fraudsters to exploit. If something goes wrong, you’re unlikely to get your money back.” Here are Lloyds’ tips for protecting yourself from crypto fraudsters: – Criminals often put adverts for scam crypto investments on social media. They can also send offers by direct message. They will promise returns that you cannot get elsewhere or make claims about “guaranteed” profits. If you are contacted out of the blue about an investment, it is likely a scam. – Fraudsters can easily set up fake companies, social media profiles and websites to clone real firms. Use the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) website to find genuine contact details for a company and check for warnings about fake firms. Always do your own research or seek professional financial advice. – Never share the log in details for your investment account or your private cryptocurrency keys with anyone else. A legitimate firm would never ask you for this. Remember, if you transfer funds to another account that is not in your name, you have lost control of your money. – Fraudsters may ask you to pay an account in a different name to the company you are meant to invest with. If the names do not match, it is a sign of a scam. Paying by card (rather than a bank transfer) may offer you more protection if something goes wrong. Read More Council investigating extent of cyber attack that affected website and systems Setback for Ireland as EU legal adviser recommends revisit of Apple tax case Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’ Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute Guidance urges parents not to buy smartphones for primary school children William ‘blown away’ by futuristic technology from Singapore start-ups
2023-11-10 08:28

Ford, SK joint venture set to receive $9.2 billion US government loan for battery plants
WASHINGTON The U.S. Energy Department on Thursday said it intends to loan a joint venture of Ford Motor
2023-06-22 20:18
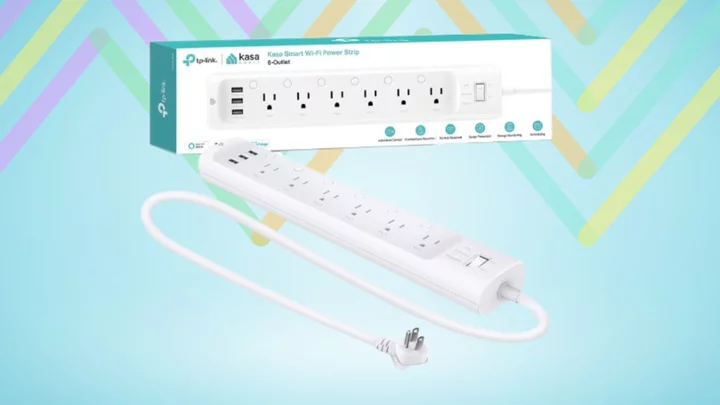

Save 46% on a Kasa Smart Plug Powerstrip at Amazon right now
Save $37: As of August 11, the Kasa Smart Plug Power Strip is on sale
2023-08-12 01:51
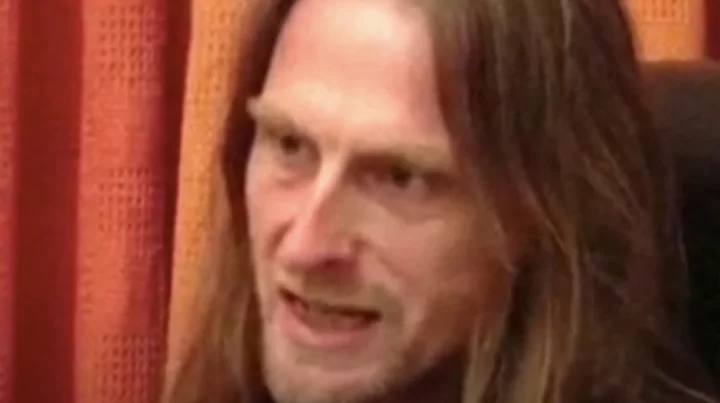

Man who stayed awake for 11 straight days shares how his brain ‘broke down’
A man who stayed awake for 11 straight days to set a world record has spoken about how he experienced his brain starting to ‘break down’. Englishman Tony Wright went an incredible 266 hours without sleep back in 2007 and set a new record – only to see it broken by someone else just a month later. Wright spoke about his experience in a clip posted by the YouTube channel Sleep Gods, saying that an entirely different part of his brain was activated during his record attempt. "Basically, you're starving the rational mind, the egotistical mind of sleep, and it's battery is running down. And of course, it doesn't feel very good, it feels tired. Wright added: "But if you push beyond that, its ability to stay in charge starts to break down as well. And that's where you can start to get glimpses of access to the other side of the brain, the other self." Man Who Didn't Sleep For 11 Days Explains Sleep Deprivation www.youtube.com "I've spoken to a lot of people about this. Most people have recollections where they've been partying, or they've been working hard, and sure they get tired, but within that they get glimpses of something else.” He went on to say: "That kind of softness, or a more relaxed state - often more emotional, because again, there's more access to that emotional side of the brain. "Even feeling quite good, quite an altered state for brief windows, or getting a second wind even. You know, be really, really tired, no sleep, and then suddenly feeling fine for half an hour or an hour. "So all I really did, or what I was interested in, is making sense of that. And is it possible to exploit that and bring in combining techniques to tie the left side of the brain up, which initially doesn't feel great, but the reward on the other side of that makes it worth the effort." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-17 19:56
Sushi could secretly be spreading antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are an increasing area of concern for health experts and scientists are concerned that the popular food sushi could be spreading it. Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology were interested in looking at the health implications of sushi, which is considered pretty standard fare in the country. Dr. Hyejeong Lee, who recently completed her PhD at the Department of Biotechnology and Food Science at NTNU, investigated different varieties of Aeromonas bacteria in seafood products that aren’t processed in a way that reduces bacteria, such as sashimi (raw fish) and cold-smoked fish. Lee explained: “The goal was to gain more knowledge about Aeromonas in this type of seafood – both the bacteria’s role in the deterioration of the product and in causing disease. Furthermore, we wanted to see if raw seafood can spread antibiotic-resistant bacteria.” While Listeria monocytogenes is the most well-known bacteria that can cause illness from unprocessed seafood, the prevalence of Aeromonas in similar products is an increasing worry for scientists for another reason. This is because Aeromonas bacteria frequently exchange genetic material with other bacteria in the sea, which means they can inherit and spread resistance to antibiotics before ending up in sushi. Lee explained: “Some strains of Aeromonas can also spread antibiotic resistance from one type of bacteria to another. Eating seafood infected by resistant bacteria is a likely way these bacteria can spread from marine animals and environments to humans.” Resistant bacteria are foreseen to be a big problem in the future, with the worst-case scenario being that few or no antibiotics will work at treating them. Experts believe it is important that antibiotic resistance is seen as a broad approach that is seriously considered in all aspects of society. Anita Nordeng Jakobsen, associate professor at NTNU’s Department of Biotechnology and Food Science, explained: “To combat the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, it is important that we adopt a broad approach that looks at animal and human health, food production and the environment together in order to achieve better public health.” Still, Lee was quick to emphasise that the risk of getting sick from Aeromonas is very small, especially for healthy people. But, she stressed: “Aeromonas is often ignored when we talk about food safety. I think my research highlights that the food industry needs to pay more attention to these bacteria." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-28 16:22

This smart outlet can control your appliances
This outlet is a solution to too many gizmos cluttering your decor. InvisOutlet connects directly
2023-08-03 22:25

HSBC Offers Trading in Crypto ETFs to Customers in Hong Kong
HSBC Holdings Plc is offering trading of crypto-linked exchange traded funds to customers in Hong Kong amid a
2023-06-27 15:59

Hacker Deepfakes Employee's Voice in Phone Call to Breach IT Company
A hacker used AI to deepfake an employee’s voice and break into an IT company.
2023-09-16 05:15
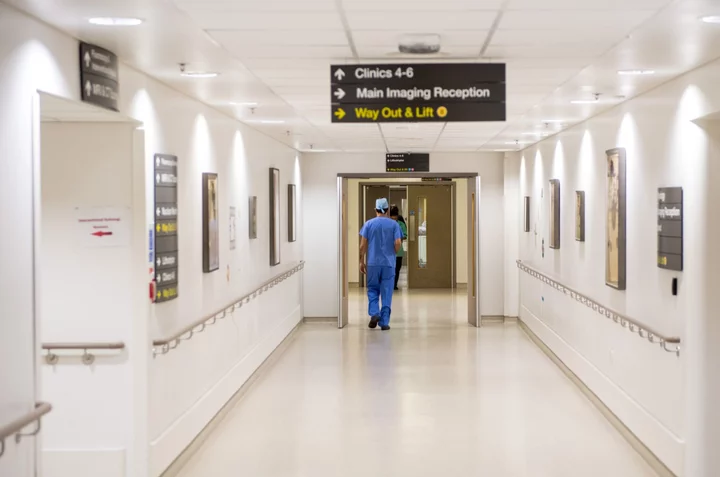

UK Cybersecurity Officials Investigating Breach Affecting London Hospitals
British cybersecurity officials are investigating an alleged cyberattack on a group of hospitals in London that has led
2023-07-06 00:26
You Might Like...

A look back at every iPhone ever

Ford Hands Tesla a Big Win in VHS Versus Betamax-Like Battle

Diesel Cars Moved From London to the North After Ulez Expansion
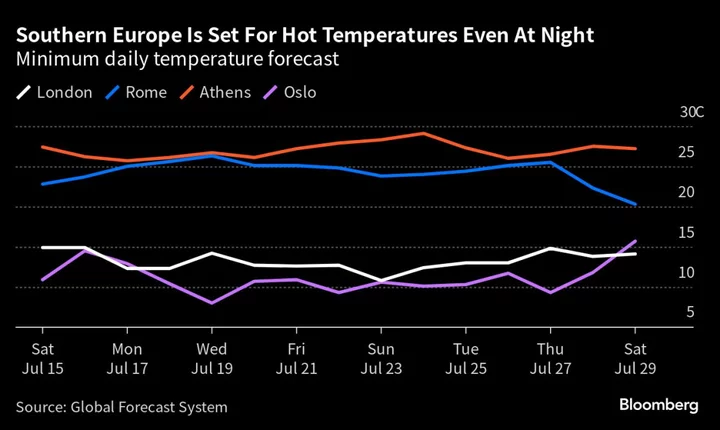
Extreme Heat Rips Through Europe, Bringing Health Risks for Millions

One year on: A timeline of Elon Musk's farcical first year as Twitter/X owner

MAPCO Opens Next Checkout-Free Store

US climate change lawsuit seeks $50 billion, citing 2021 heat wave

Who is Jessica Banks? MIT engineer and robotics prodigy joins Netflix's 'Hack My Home' as co-host
