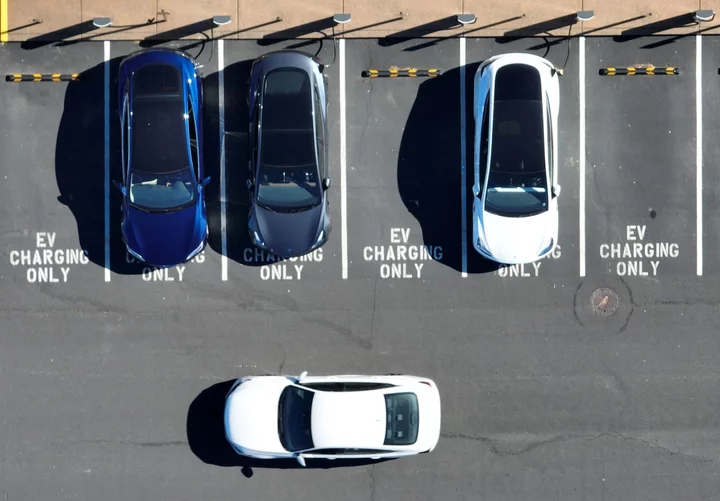

California Says Electric Cars Now Make Up a Fifth of Auto Sales
One out of every five cars sold in California is now powered by a battery, registration data released
2023-11-02 04:59
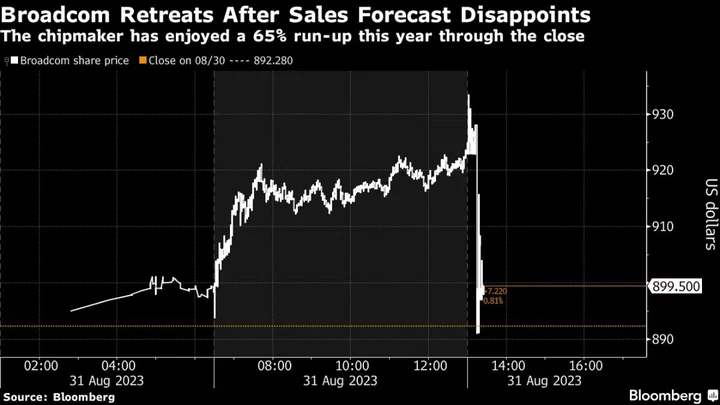
Broadcom Gives Downbeat Forecast, Signaling Sluggish Chip Demand
Broadcom Inc., one of the world’s five biggest chipmakers, gave a disappointing forecast for the current period, signaling
2023-09-01 05:50

Nintendo Download: Finish Him!
REDMOND, Wash.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 14, 2023--
2023-09-14 21:17

Leadership Doubts Threaten Fortescue Founder’s Green Reinvention
Three years after he first embarked on a mission to transform an iron ore giant into a clean-energy
2023-09-08 07:49
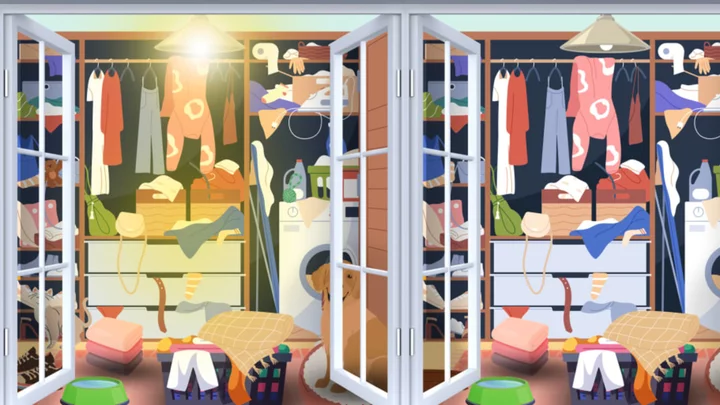

There Are Seven Differences Separating These Scenes—Try Spotting Them All
There are seven differences separating these messy scenes—see if you can spot them all in under a minute.
2023-11-24 04:24

Next Call of Duty instalment to be set during the Gulf War
The 2024 'Call of Duty' video game will reportedly be set during the Gulf War.
2023-11-23 19:55

“Which Side Are You On?”: How Florence Reece Gave Strikers a Theme Song
The classic labor song "Which Side Are You On?" was born during the Harlan County Wars of the 1930s.
2023-05-25 04:54

The Best Amazon Black Friday Deals to Shop on Wireless Earbuds, Kitchen Gadgets, and More
Whether you're looking for Apple AirPods Pro earbuds or a better stand mixer, these Amazon Black Friday deals can help you save more on holiday gifts and essentials.
2023-11-26 08:45
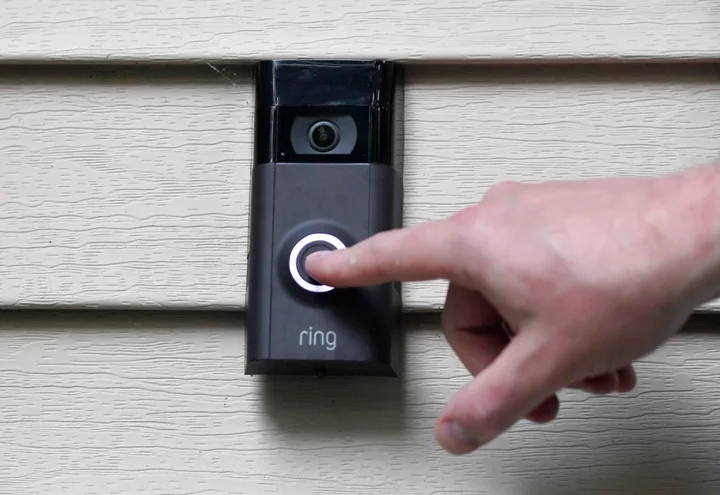

Amazon staff spied on women in bedrooms and bathrooms through Ring cameras, US officials say
An employee used Amazon’s Ring cameras to spy on female users in their bedrooms and bathrooms, according to US officials. Various staff members used the company’s smart home cameras – intended to allow people to watch their own homes when they are away – to watch people without their knowledge, according to the US Federal Trade Commission. Amazon settled for $5.8 million in this case, which said that one employee had watched 81 female customers and Ring employees through their cameras. The company has been hit by two substantial fines over violating users’ privacy. The other accused of breaching childrens’ rights by failing to delete Alexa recordings, even when requested by their parents, leading to a separate $25 million fine. The FTC is also probing Amazon.com’s $1.7 billion deal to buy iRobot Corp, which was announced in August 2022 in Amazon’s latest push into smart home devices, and has a separate antitrust probe underway into Amazon. Amazon, which purchased Ring in April 2018, pledged to make some changes in its practices. “While we disagree with the FTC’s claims regarding both Alexa and Ring, and deny violating the law, these settlements put these matters behind us,” Amazon.com said in a statement. The FTC said Ring gave employees unrestricted access to customers’ sensitive video data: “As a result of this dangerously overbroad access and lax attitude toward privacy and security, employees and third-party contractors were able to view, download, and transfer customers’ sensitive video data.” In one instance in 2017, an employee of Ring viewed videos made by at least 81 female customers and Ring employees using Ring products. “Undetected by Ring, the employee continued spying for months,” the FTC said. A colleague noticed the misconduct and the employee was eventually terminated, the FTC complaint said. In May 2018, an employee gave information about a customer’s recordings to the person’s ex-husband without consent, the complaint said. In another instance, an employee was found to have given Ring devices to people and then watched their videos without their knowledge, the FTC said. As part of the FTC agreement with Ring, which expires after 20 years, Ring is required to disclose to customers how much access to their data the company and its contractors have. In February 2019, Ring changed its policies so that most Ring employees or contractors could only access a customer’s private video with that person’s consent. FTC Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya told Reuters the settlements should send a message to tech companies that their need to collect data was not an excuse to break the law. “This is a very clear signal to them,” he said. The fines, totaling $30.8 million, represent a fraction of Amazon’s $3.2 billion first-quarter profit. In its complaint against Amazon.com filed in Washington state, the FTC said that it violated rules protecting children’s privacy and rules against deceiving consumers who used Alexa. For example, the FTC complaint says that Amazon told users it would delete voice transcripts and location information upon request, but then failed to do so. “The unlawfully retained voice recordings provided Amazon with a valuable database for training the Alexa algorithm to understand children, benefiting its bottom line at the expense of children’s privacy,” the FTC said. Additional reporting by agencies Read More Mark Zuckerberg reveals new VR headset ahead of Apple AI chatbot taken down after it gives ‘harmful advice’ on eating disorders Famous torrent site RARBG shuts down with final parting message Mark Zuckerberg reveals new VR headset ahead of Apple AI chatbot taken down after it gives ‘harmful advice’ on eating disorders Famous torrent site RARBG shuts down with final parting message
2023-06-02 01:24

Melania Trump hawks $50 NFTs to ‘celebrate our great nation’ ahead of July 4
Melania Trump is launching a collection of $50 non-fungible tokens (NFTs) featuring US landmarks in time for the 4th of July. The former first lady’s “1776 Collection” includes images of Mount Rushmore, the Statue of Liberty and the Liberty Bell, set to patriotic-themed music. Ms Trump’s office said in a statement that each NFT was designed to celebrate the “foundations of American ideals”. “The 1776 Collection of artwork draws inspiration from several iconic landmarks of our nation, which I had the privilege of visiting during the time I served as first lady,” Ms Trump said. “I am proud to celebrate our great nation and remain inspired by the words contained within the Declaration of Independence.” An NFT is a blockchain-based certificate verifying ownership. The 1776 Collection was created on the Solana blockchain, and went on sale on Thursday. Ms Trump’s office said a portion of the sale price would go to support foster children. The site did not immediately respond to a request for further details about what percentage of the proceeds would be donated. Ms Trump has previously dabbled in NFTs since leaving the White House. In 2021, she launched a digital watercolour painting of her eyes for $180 each. Then in 2022, Ms Trump faced accusations of bidding $185,000 in an auction for her “Head of State Collection 2022.” An analysis of Solana blockchain transactions by Bloomberg found the winning bid of 1800 SOL came from a wallet that belonged to the entity that originally listed the project for sale. Read More Trump news - live: DOJ prepares to hit Trump with new charges as ex-official cooperates in 2020 election probe Trump lashes out at ‘fake’ Jake Tapper after CNN host cuts away from arraigned ex-president meeting fans Meet Jesse Watters, the Fox News host helming Tucker Carlson’s primetime slot Prosecutors are prepared to hit Trump and his allies with new charges, sources say
2023-06-30 22:19

Zimbabwe Exchange to List Carbon Credits as State Upends Trade
Zimbabwe’s Victoria Falls Stock Exchange plans to set up trading in carbon credits by September, seeking to capitalize
2023-05-24 22:21

Expel Appoints Seasoned Hyper-Growth Chief Product Officer to Leadership Team
HERNDON, Va.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 28, 2023--
2023-08-28 21:25
You Might Like...
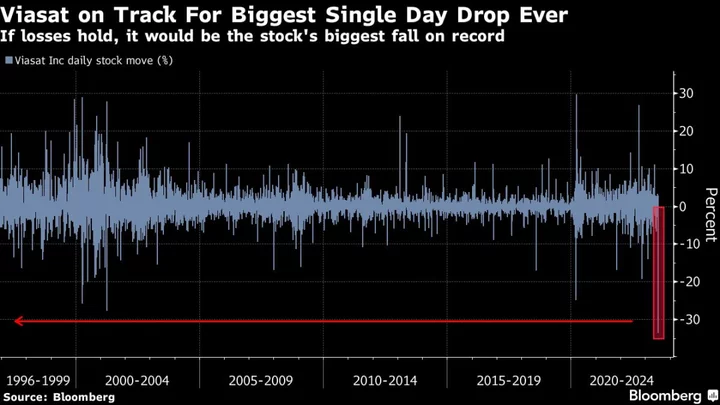
Satellite Firm Viasat Stock Falls After ‘Unexpected’ Deployment Event
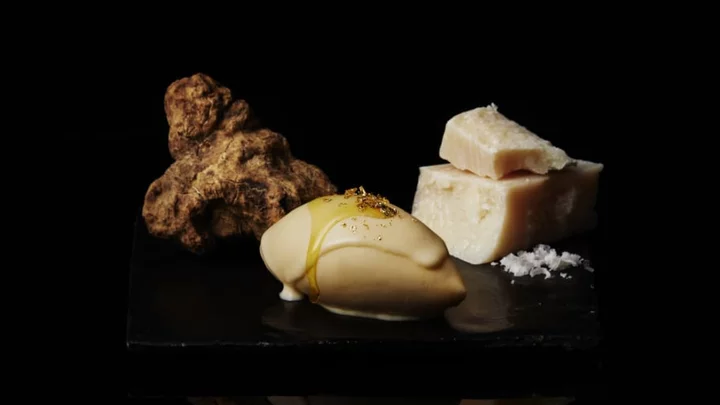

One Scoop of the World’s Most Expensive Ice Cream Will Set You Back Nearly $7000
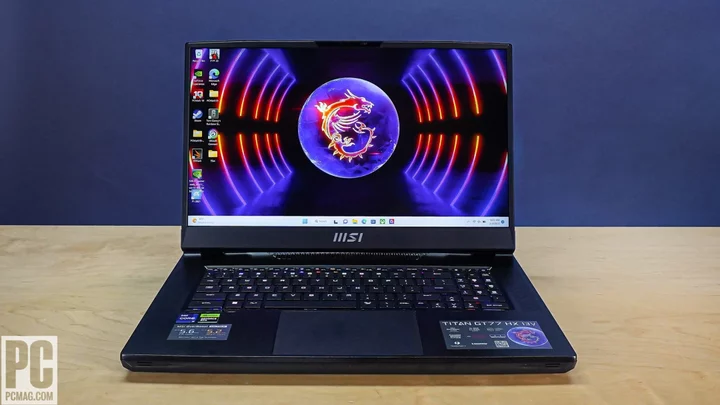

The Best 17-Inch Laptops for 2023

It’s been 11 years since Danny Dyer called the 9/11 attackers ‘slags’ on Twitter

Curt Wood Appointed Executive Director of 2023-2024 Cybersecurity Priorities Report

Musk says Twitter is losing cash because advertising is down and the company is carrying heavy debt
Taiwan parents protest after preschool allegedly gave sedatives to children

Goldman Executive Has ESG Strategy to Dodge Hedge Fund Attacks
