
Travelshift Secures $10 Million USD Capital Raise
REYKJAVIK, Iceland--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 29, 2023--
2023-08-29 20:27
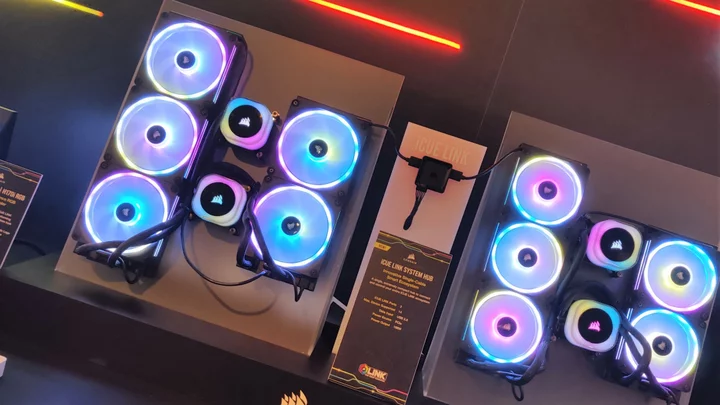

Slay the Cables: Corsair’s iCUE Link Is a Brilliant Cleanup Job for PC DIY Building
We were especially looking forward to seeing Corsair’s suite at Computex 2023 because during CES
2023-06-01 07:52
Google's New AI Model Controls Robots
Forget AI that can draw pictures, Google’s latest AI model can control a robot. On
2023-07-30 03:28

Here's why MrBeast's main YouTube channel with 156M subscribers is considered a loss maker
From developing his own Squid Game to giving out thousands of dollars to complete strangers, MrBeast has done it all
2023-05-10 13:57
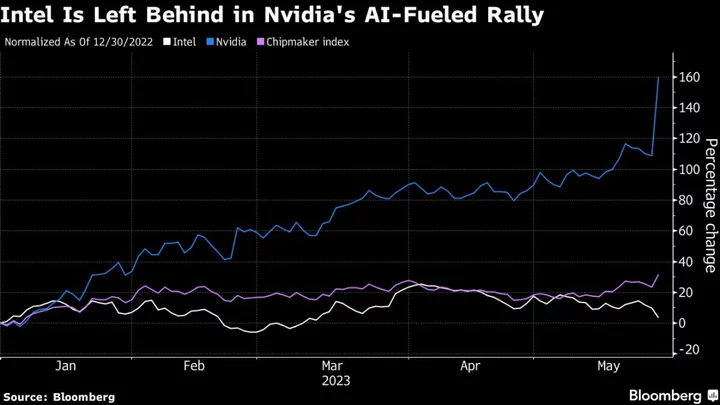
Intel Risks Being Left Behind as Nvidia Ups AI Lead
Nvidia Corp. gave investors what they were looking for this week: concrete evidence that the surge in artificial
2023-05-26 18:23

Tears of the Kingdom: Here is how you can buy the game for less than $70
Tears of the Kingdom is also the first Nintendo game to see a price increase
2023-05-16 15:52

Can't Afford a New iPhone? Upgrade to iOS 17 on Sept. 18
Apple’s latest mobile operating systems will be available to download on Sept. 18, Apple announced
2023-09-13 03:52

5 Stock Picks From Top Money Managers
Barron’s asked veteran fund managers and investment strategists how a financially secure individual with a diversified portfolio should invest $100,000 now. Here’s what they said.
2023-10-13 13:15

Square Enix could drop Final Fantasy numbers for future games
Square Enix is considering dropping numbers from 'Final Fantasy' titles.
2023-05-23 19:19

What is Tactical Stance in Modern Warfare 3?
Tactical Stance in Modern Warfare 3 is a new mechanic that is a middle-ground between hip-fire and ADS, encouraging aggressive close-quarter fights.
2023-10-06 02:52

Equip your car with a dashcam and backup camera for just $96
TL;DR: As of September 10, you can get a 10-inch rearview mirror touchscreen that doubles
2023-09-10 17:46
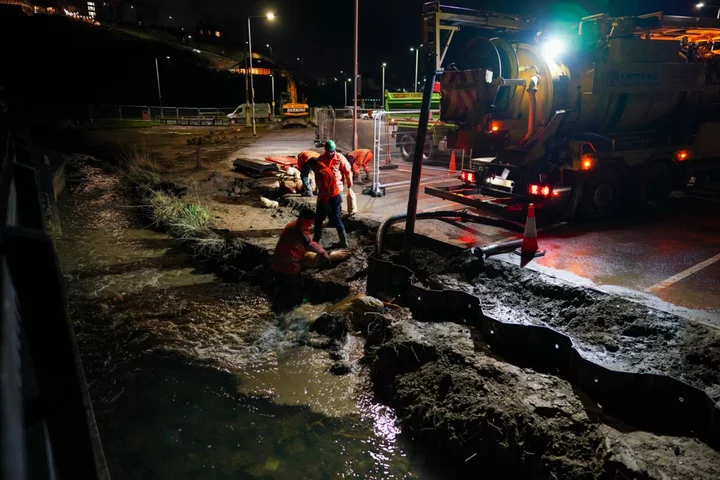

Sewage Spills Push Apologetic UK Water Companies to Spend More
UK water companies have publicly apologized and laid out a multi-billion pound modernization plan to curb the volume
2023-05-18 07:23
You Might Like...
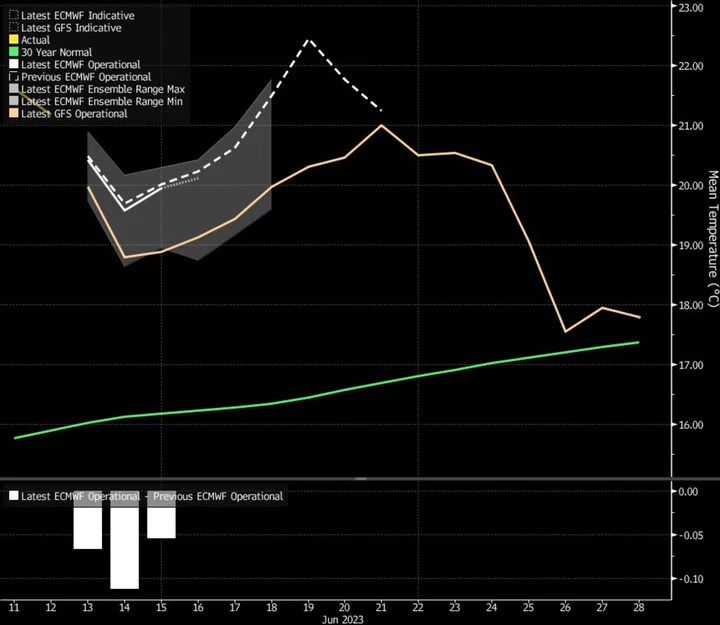
Heat Scorches Europe as Southern Spain Temperature to Reach 45C This Month

Pokimane roasts Mizkif over controversial call with xQc, Asmongold and Trainwreckstv, Internet says 'none of these people are friends'

EU officials warn Google and YouTube about Hamas-Israel disinformation and graphic content

Nothing Phone 2 gets U.S. availability date, price

Spotify raises premium subscription price for millions

Sonos Move 2 has stereo sound and an all-day battery

Baidu Claims Its Ernie Bot Now Beats ChatGPT on Key Measures

Microsoft's Zune Returns From the Dead (as a Movie Giveaway)
