
Ford shares fall after pulling full-year forecast, wider losses in EV unit
By Shivansh Tiwary (Reuters) -Shares of Ford Motor Co closed down 12.3% on Friday, after the automaker reported a wider
2023-10-28 07:53
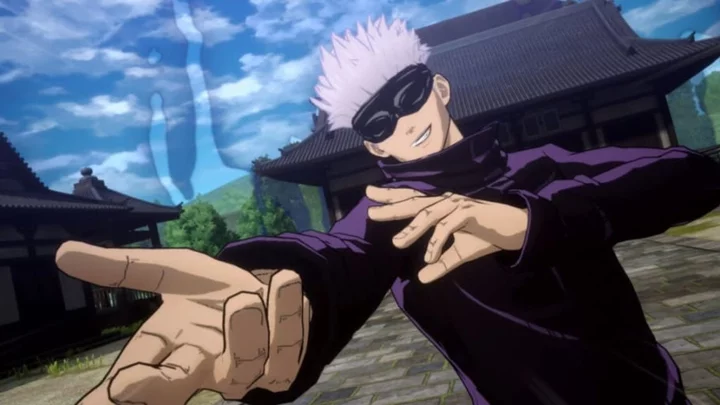

Every Playable Character in Jujutsu Kaisen: Cursed Clash
Every playable character in Jujutsu Kaisen: Cursed Clash, answering questions about JJK Season 2 characters, release date information and playable platforms.
2023-11-14 01:50
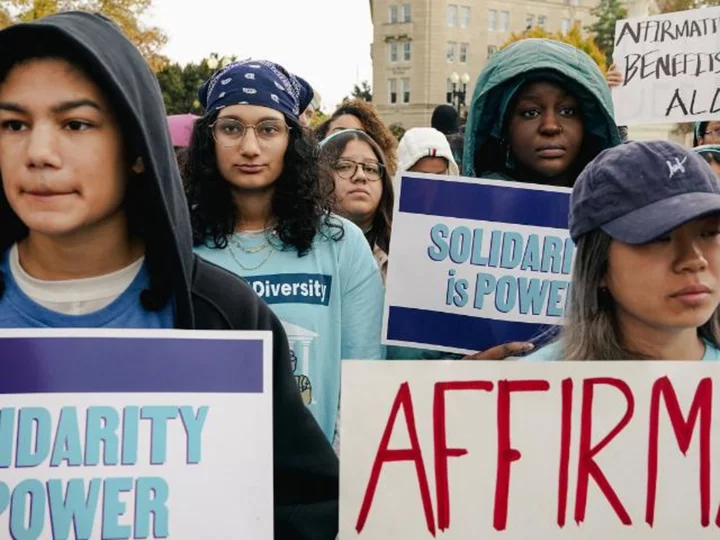

The gutting of affirmative action is a 'clear and present danger' to equal education, critics say
The Supreme Court's landmark decision to bar colleges and universities from considering race as a specific basis for admission will make it more difficult for schools to achieve a diverse student population, civil rights leaders and education advocates say.
2023-06-30 00:47

XiFin Named to Inc. 5000 List of Fastest-Growing Private Companies in America for 13th Time
SAN DIEGO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 17, 2023--
2023-08-17 22:21

Save 55% on a refurbished ThinkPad with Microsoft Office Pro
TL;DR: As of June 20, you can get a refurbished Lenovo ThinkPad 11e and a
2023-06-21 17:46
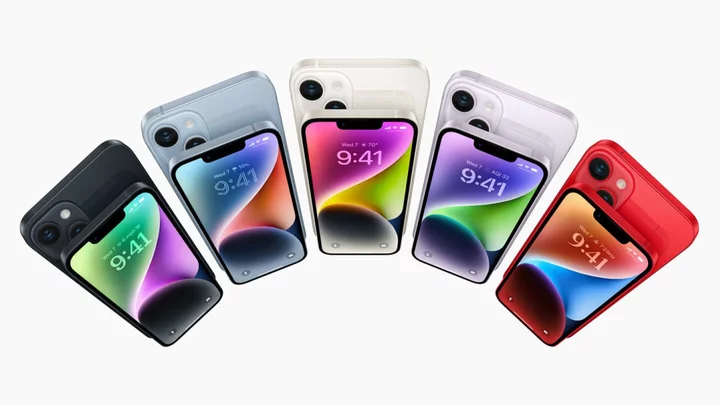

Apple's iPhone 15 might come in glorious pink color
Any Barbie fans out there that are also iPhone users? Apple might be preparing a
2023-07-17 21:21

Every Modern Warfare 3 Verdansk POI in the Reveal Trailer
Full list of Modern Warfare III Verdansk POIs shown in the Gameplay Reveal Trailer aired at the end of the Warzone Shadow Siege event.
2023-08-18 23:51
Pepper Grinder Preview
Many modern indie games are passionate fan homages to forgotten cult hits underappreciated in their
2023-09-27 01:23

TikTok: Here are 7 best ways to get 1 million followers
Struggling to get more followers on TikTok? Here are a few ways to get 1 million followers
2023-05-15 14:47
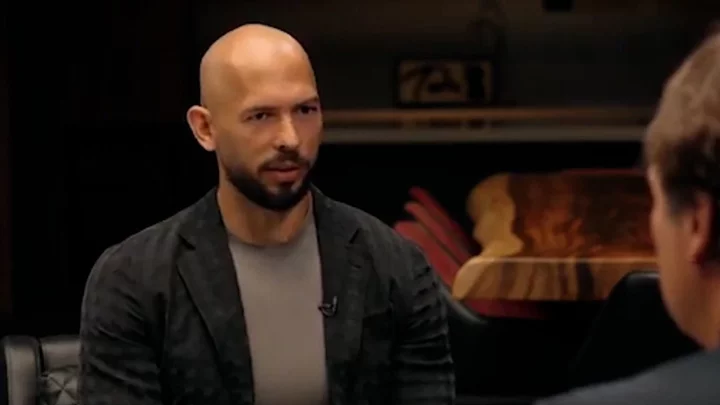

Is Andrew Tate's interview with Tucker Carlson the most watched interview ever?
Controversial influencer Andrew Tate has put himself in the spotlight again after sitting down for an interview with right-wing media personality Tucker Carlson. Carlson shared the two-and-a-half-hour-long conversation between the pair on Twitter as part of his new independent talk show named “Tucker on Twitter”, following his sacking from FOX News in April. Tate, along with his brother Tristan and two other associates, has been charged in Romania with rape, human trafficking and forming an organised crime group. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter During his interview with Carlson, he discussed his opinions “masculinity” and other aspects of his life and personal experiences. The tweet containing the interview has been viewed more 107 million times, according to Twitter statistics. Is it the most-watched television interview ever? Some of Tate’s fans have made the claim that the interview is the most-watched TV interview of all time, with one “fan” Twitter account, writing: “Andrew Tate's interview with Tucker Carlson is the most watched interview of all time. With the tweet, they shared a screenshot of a Wikipedia page with the title “List of most watched television interviews”. An arrow pointing to the top of the table listed the Tate and Carlson interview in the number one spot, however, the interview was never aired on television and instead was posted on Twitter. Sportskeeda revealed the Wikipedia screenshot with either edited or photoshopped because the current page lists a 1993 Oprah Winfrey interview with Michael Jackson as the most-watched television interview with an average viewership of 62.3 million. The false claim by Tate’s fans was made despite the Wikipedia page stating: “This is specifically on broadcast television and not on other television sources such as YouTube, Twitter or other online source.” However, the interview might be able to claim the title of 'most watched ever' if the television side of the discussion is ignored. The interview has outperformed the widely reported most viewed video on Twitter, which was a piece of skill by Lionel Messi that had more than 19 million views. However, its got a long way to go before it can outperform the biggest video on YouTube; 'Babyshark' which has been viewed an astonishing 13 billion times. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-18 15:23

Mega Refining and Petrochemical Plant Selects Hytera as Provider of Professional Communications System
SHENZHEN, China--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 9, 2023--
2023-06-09 16:26

Why Do Cats Lick Tape and Plastic?
Your cat's weird snacking habits may be related to compulsive behavior condition—or they might just like the crinkly sound.
2023-07-03 21:28
You Might Like...

Regulators Want Fashion Brands to Pay for Their Textile Waste

When is Nintendo Live Seattle?

Europe is leading the race to regulate AI. Here's what you need to know
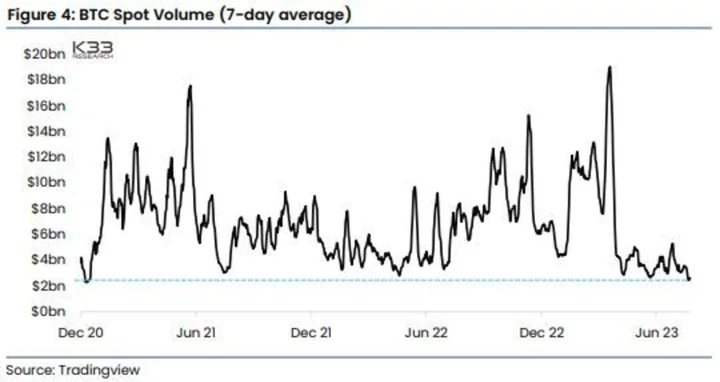
Sputtering Bitcoin’s Spot Trading Volumes Sink to a 30-Month Low

Disney, Netflix, Other Media Stocks Rise With End in Sight for Hollywood Writers Strike
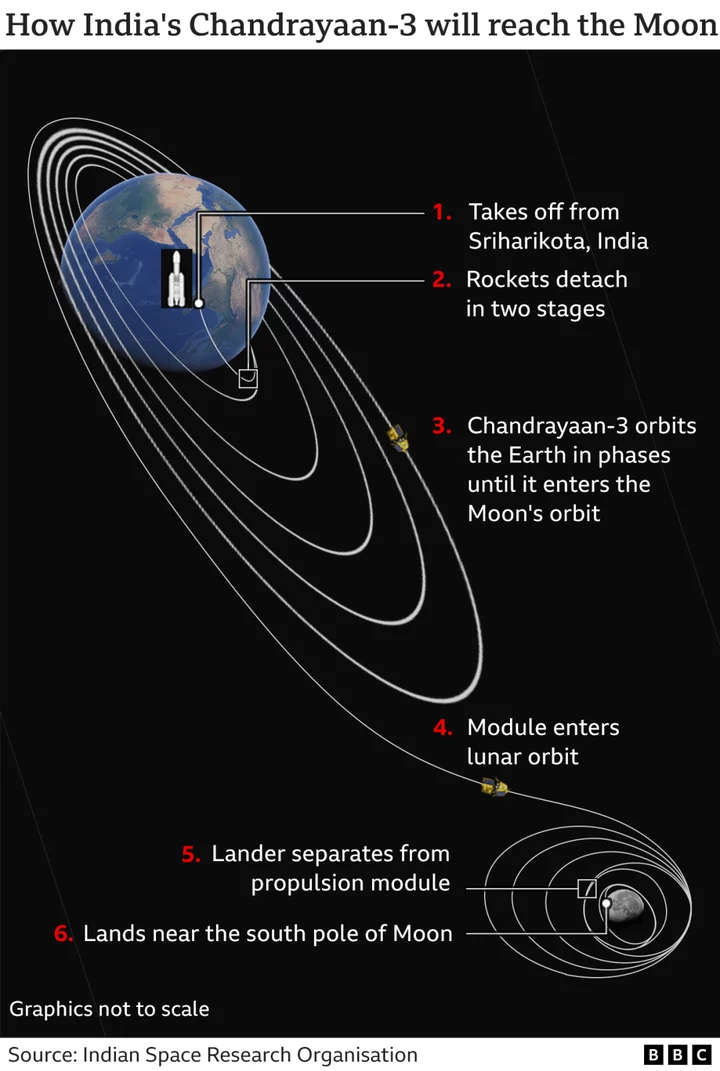
Chandrayaan-3: India's historic Moon mission lifts off successfully

Google DeepMind co-founder calls for US to enforce AI standards - FT

xQc: Did Fran confirm dating Twitch star? Fans say they're 'always meant to be'
