Yext to Announce First Quarter Fiscal Year 2024 Financial Results on June 6, 2023
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 23, 2023--
2023-05-24 06:45

Factbox-Amgen-Horizon deal joins mega mergers facing regulatory heat
A U.S. antitrust regulator said on Tuesday it will sue to stop Amgen's $27.8 billion deal for Horizon
2023-05-16 23:47

How to watch the UCI Cycling World Championships 2023 for free
The Tour de France has only just finished, and we're not too far away from
2023-07-27 12:26
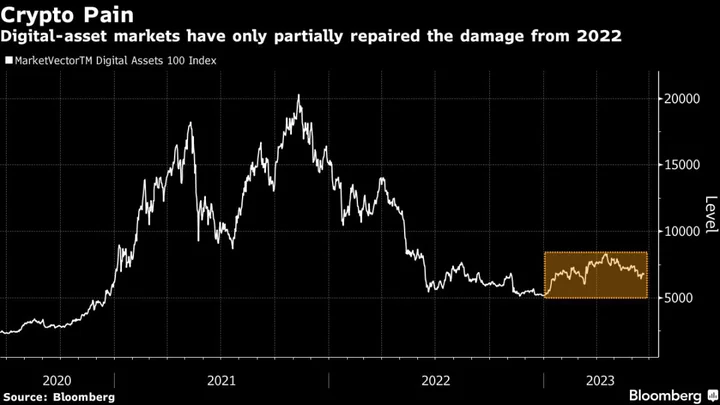
Japan’s Crypto Exchanges Are Pushing for Looser Margin Trading Rules to Help the Sector Grow
Japan’s crypto exchanges are pushing for a relaxation of curbs on margin trading, unbowed by last year’s global
2023-06-20 11:24
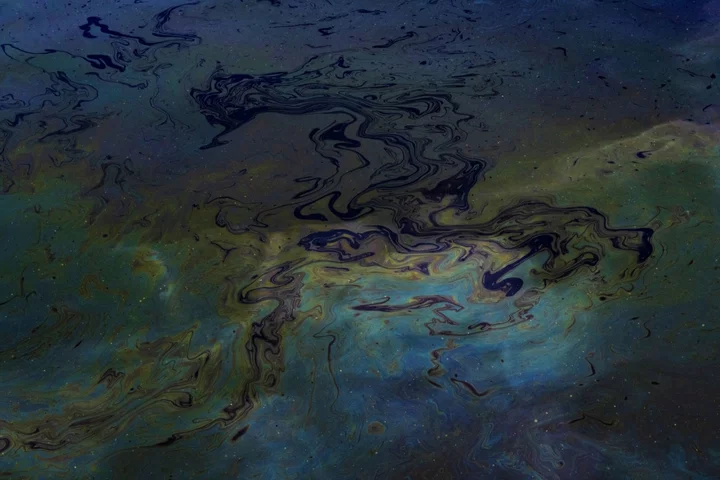
Large Oil Spill Reported Near Site of Pemex Platform Blast in Gulf of Mexico
A large oil spill has been spotted in the Gulf of Mexico near the site of a deadly
2023-07-19 00:56

Get a head start on the school year with up to 29% off laptops at Amazon
Our top picks Best deal overall Acer Aspire 3 (A314-23P-R3QA) $384.99 at Amazon (save $65
2023-08-04 23:57
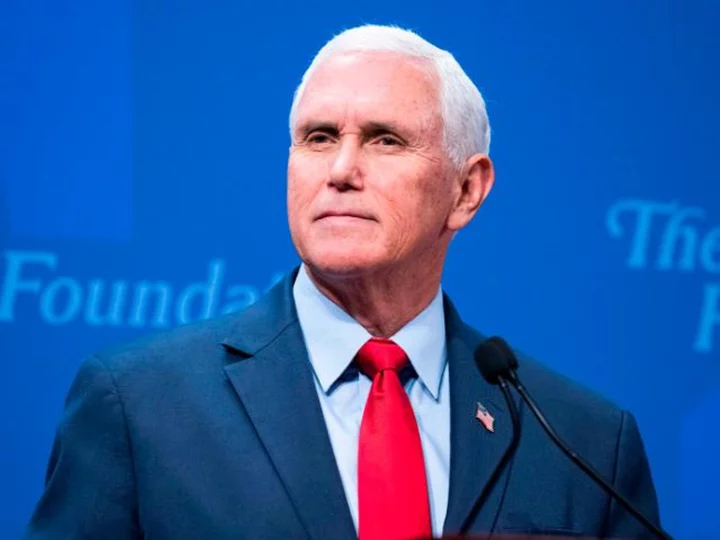

CNN to host Republican town hall with former Vice President Mike Pence June 7
CNN will host a town hall with former Vice President Mike Pence early next month in Iowa, the network announced Thursday.
2023-05-25 21:15

Video game superstars to commentate on The Hundred cricket
Three popular video game influencers will swap controllers for the commentary box at The Hundred presented by Compare The Market next month.
2023-07-26 23:56

AI could replace 80% of jobs 'in next few years': expert
Artificial intelligence could replace 80 percent of human jobs in the coming years -- but that's a good thing, says US-Brazilian researcher Ben...
2023-05-09 05:26
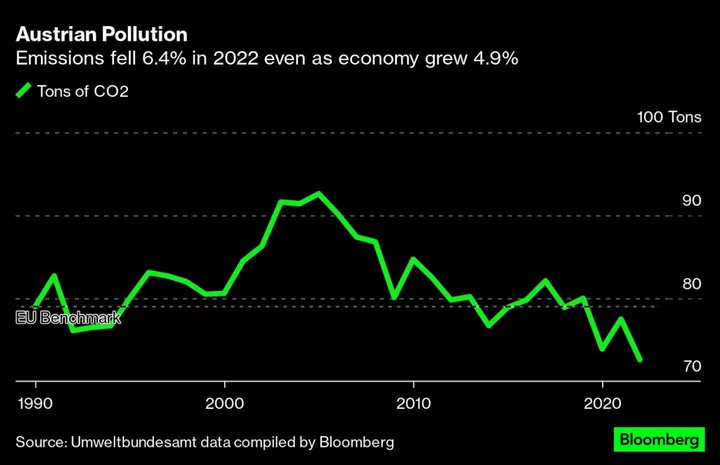
Energy Crisis, War Inflation Drive Down Austria’s CO2 Pollution
Austria slashed its greenhouse gas pollution in 2022 despite producing more goods as its industrial economy responded to
2023-08-17 21:47
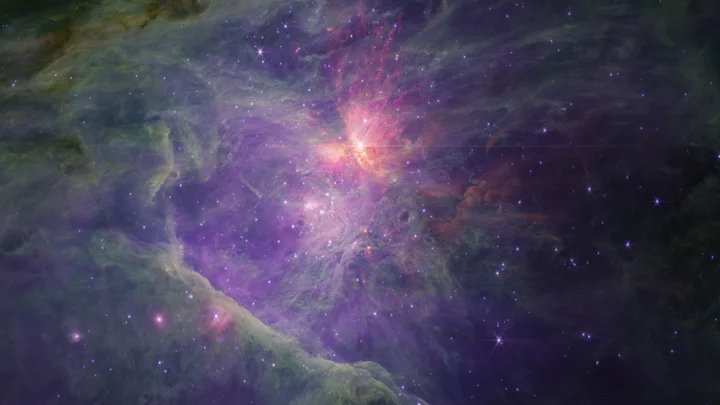

New discovery of rogue planets defies scientific theory and leaves experts baffled
Planet-like objects in the Orion Nebula have been revealed for the first time in images from the James Webb Space Telescope. The Orion Nebula, one of the brightest nebulae in the night sky, has long presented astronomers with an abundance of celestial objects to study. It is identifiable as the sword in the Orion constellation and is located 1,300 light-years from Earth. Astronomers managed to discover unprecedented details by capturing mosaics of the Orion Nebula in short and long wavelengths of light. Whilst searching for low-mass objects, astronomers Samuel G. Pearson - a European Space Agency research fellow at the European Space Research and Technology Centre in the Netherlands - and Mark J. McCaughrean - senior adviser for science and exploration at the European Space Agency - came across something they had never before seen. Their discovery appears to defy some fundamental astronomical theories: pairs of planet-like objects with masses between 0.6 and 13 times the mass of Jupiter. They have been dubbed Jupiter Mass Binary Objects, or JuMBOs. "Although some of them are more massive than the planet Jupiter, they will be roughly the same size and only slightly large," said Pearson. The astronomers found 40 pairs of JuMBOs, and although they exist in pairs, the objects are typically about 200 astronomical units apart, or 200 times the distance between Earth and the sun. This means it can take between 20,000 and 80,000 years for the objects to complete an orbit around each other. McCaughrean and Pearson have written two research papers based on their discoveries in the Orion Nebula. The preliminary findings are available on a preprint site called arXiv whilst the studies have been submitted to academic journals for publication. But many questions about JuMBOs remain. "Scientists have been working on theories and models of star and planet formation for decades, but none of them have ever predicted that we would find pairs of super low mass objects floating alone in space - and we're seeing lots of them," Pearson said. "The main that we learn for this is that there is something fundamentally wrong with either our understanding of planet formation, star formation, or both." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-08 21:17
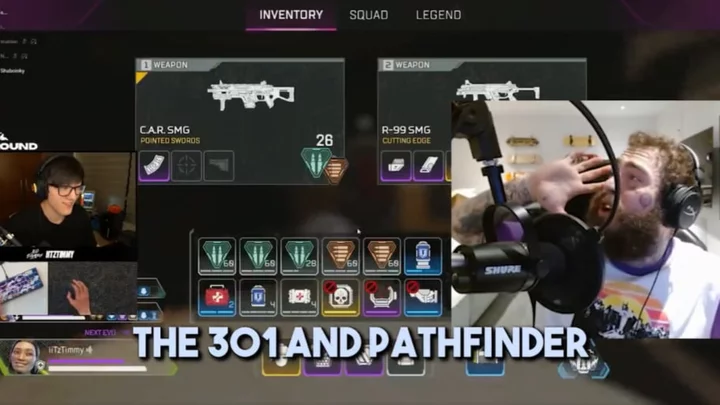
Post Malone Calls for Pathfinder and R-301 Buffs in Apex Legends
Post Malone and iiTzTimmy called for Pathfinder and R-301 buffs in Apex Legends Season 19 during a stream for the Post Malone x Apex Legends Event.
2023-11-16 02:46
You Might Like...

These Stocks Are Moving the Most Today: Roivant Sciences, Textainer, Okta, Microsoft, Alphabet

Juniper Group Acquires Vervotech, a Leading Hotel and Room Mapping Solutions Provider

EU Makes Deal to Advance Controversial Nature-Restoring Law

Microsoft ‘Bears Responsibility’ For China-Tied Hacks, Senator Says

Save 10% on all Squarespace subscriptions with this voucher code

Databricks Is in Talks to Raise Funds at a $43 Billion Valuation

X appears to slow load times for links to several news outlets and rival platforms

Tesla begins notifying workers who were affected by data breach
