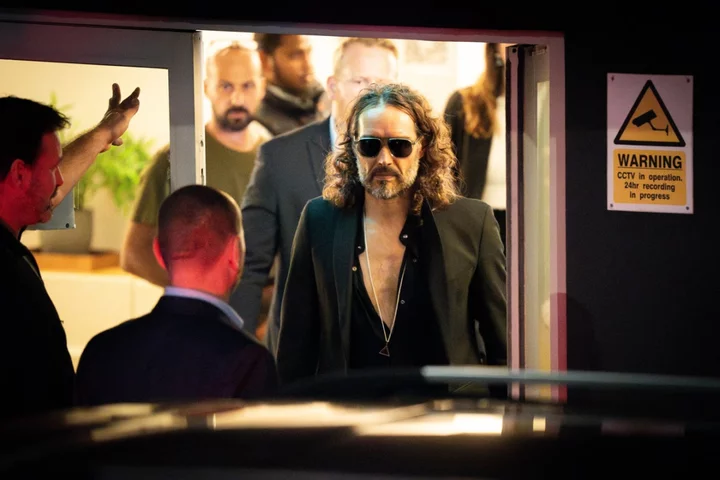

Monetisation of Russell Brand’s YouTube channel suspended
YouTube has suspended the monetisation of Russell Brand’s channel for “violating” its “creator responsibility policy”. In a statement to the PA news agency, a spokesperson for the Google-owned company said: “If a creator’s off-platform behaviour harms our users, employees or ecosystem, we take action to protect the community.” The news comes after the remaining shows of Brand’s Bipolarisation tour were postponed and the Metropolitan Police said it had received a report of an alleged sexual assault in the wake of media allegations about the comedian and actor. Brand’s YouTube account, which has 6.6 million subscribers, has been suspended from YouTube’s partner account “following serious allegations against the creator”, meaning the channel is no longer able to make money from advertising on the platform. The statement added: “This decision applies to all channels that may be owned or operated by Russell Brand.” The 48-year-old actor has been accused of rape, assault and emotional abuse between 2006 and 2013, when he was at the height of his fame and working for the BBC, Channel 4 and starring in Hollywood films, following a joint investigation by The Times, Sunday Times and Channel 4’s Dispatches. He has strongly denied the allegations, which also include claims of controlling, abusive and predatory behaviour. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-09-19 15:29
Anthropic releases Claude Pro, a paid version of its ChatGPT rival
ChatGPT's competitor, Claude now has a paid version with premium features. On Thursday, Anthropic announced
2023-09-08 04:27

Young Britons turning to AI chatbots for help with school and work – survey
More than half of young people in the UK have used an AI chatbot such as ChatGPT in the last year to help them with schoolwork, emails or their job, research suggests. Nominet’s latest annual Digital Youth Index, which examines young people’s online habits and attitudes, suggests that while most young people (94%) feel safe online, 76% said they had been exposed to an upsetting experience. That is a 7% rise on last year, with young people reporting an increase in exposure to fake news and hate speech, both up 4%, as well as sexual content, up by 6%. The study, conducted by Opinium, surveyed 4,000 people aged between eight and 25 in the UK. While society at large grapples with artificial intelligence at all levels, it’s encouraging to see young people embracing technology so quickly and using it in their daily lives Paul Fletcher, Nominet The young people surveyed claimed to spend an average of between four and five hours a day online – mostly on social media, chatting with friends or accessing entertainment. Most (95%) of those asked said they were on at least one social network, including children who are under the age limit for some of those services. According to the study, X, formerly known as Twitter, was identified as the platform where the most respondents (77%) had seen distressing content. On AI, the study showed that 53% of those asked said they had used an AI chatbot and were curious about how they could use them in their lives, while 54% said they were concerned about the impact AI could have on jobs in the future. Nominet chief executive, Paul Fletcher, said: “While society at large grapples with artificial intelligence at all levels, it’s encouraging to see young people embracing technology so quickly and using it in their daily lives. “We must continue to encourage this inquisitive nature from the next generation – and despite their adoption of AI, many still have concerns about the potential impact on their future. “When it comes to online safety, it looks like young Brits are growing in confidence, but the rise in exposure to upsetting content highlights that tackling online harm remains important to young people.” The study also indicated that 14% of young people lack access to a laptop or desktop computer, while 15% did not have broadband access at home. Meanwhile, 11% said they had to change or cancel their internet package this year as a direct result of the cost-of-living crisis. “Our data shows us the reality that despite young people’s lives and their education system going online, a concerning 14% of two million of them still don’t have access to a laptop or desktop computer, and this has the potential to significantly disadvantage those that would benefit the most,” Mr Fletcher said. Read More Businesses embracing generative AI but fear cyberattacks, survey finds Police to trial use of drones as first responders to emergencies Apple to adopt system to improve texting between iPhones and Android devices ICO seeks permission to appeal against Clearview AI tribunal ruling Users of iPhones can now check bank balance from Wallet app VR tool aims to help rail passengers spot and safely tackle sexual harassment
2023-11-20 08:18

ByteDance to wind down Nuverse in full retreat from gaming -sources
By Josh Ye HONG KONG (Reuters) -TikTok maker ByteDance is set to internally announce on Monday the winding down of
2023-11-27 10:45

Boomi Appoints Josh Rutberg as Chief Customer Officer
CHESTERBROOK, Pa.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 23, 2023--
2023-05-23 21:26
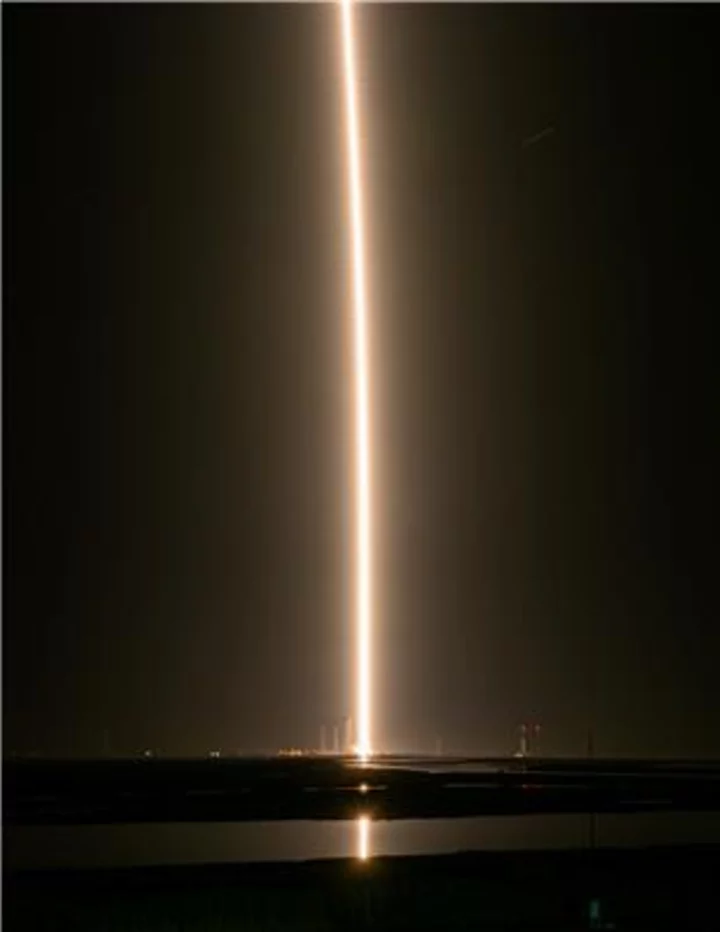

Rocket Lab Debuts HASTE Rocket with First Successful Suborbital Launch from Virginia
WALLOPS ISLAND, Virginia--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 17, 2023--
2023-06-18 10:59

China to allow road trials of intelligent connected vehicles
BEIJING China will allow road trials of some intelligent connected vehicles (ICVs) in designated city areas, the industry
2023-11-17 20:16

Justin Trudeau went to see Barbie and 'fragile' men are absolutely raging
Canadian prime minister Justin Trudeau shared a photo of himself and his son Xavier attending a showing of Barbie to social media, and men are absolutely rattled. Thousands of users responded to the tweet with a range of insults, with some suggesting that it makes Trudeau unfit to be a world leader, all because he went to see one the highest-grossing films of the year. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter One user called him a "man-child" while Charlie Kirk, the founder of the conservative organisation Turning Point USA, decided to mention Trudeau's recent announcement about his split from his wife: Charlie Kirk, the founder of the conservative organisation Turning Point USA, decided to mention Trudeau's recent announcement about his split from his wife: Scrolling through reactions to the post it wasn't hard to find lots of fragile men struggle to comprehend a man wearing pink: Andrew Tate took a slightly more satanic tone with his reaction: Some even believed Trudeau was gay and that his 15-year-old son was actually his boyfriend: Many criticised the replies, calling the men fragile and homophobic: Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-08 00:25

TweetDeck is no longer free
The latest change to Elon Musk's X? TweetDeck — rebranded as XPro — is now
2023-08-16 17:52

Cuba media guide
An overview of the media in Cuba, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-08-29 20:56

Warzone Season 6: All Weapon Buffs and Nerfs
The weapon buffs and nerfs in the Warzone Season 6 patch notes include huge nerfs to the Kastov 762, M13B, and more.
2023-09-27 23:16

Grab the Echo Pop — Amazon's latest smart speaker — for 43% off
Save $17: As of September 15, the Echo Pop (1st gen) is on sale for
2023-09-15 23:27
You Might Like...

Stockbreeding Startup Farmpro Signs MOU with Global IoT Company Telenor

Nvidia invests $50 million in Recursion to train AI models for drug discovery

iOS 17 release: See what's new in iPhone features

Tesla’s Former Partnerships Cast Shadow Over Ford EV Charging Pact
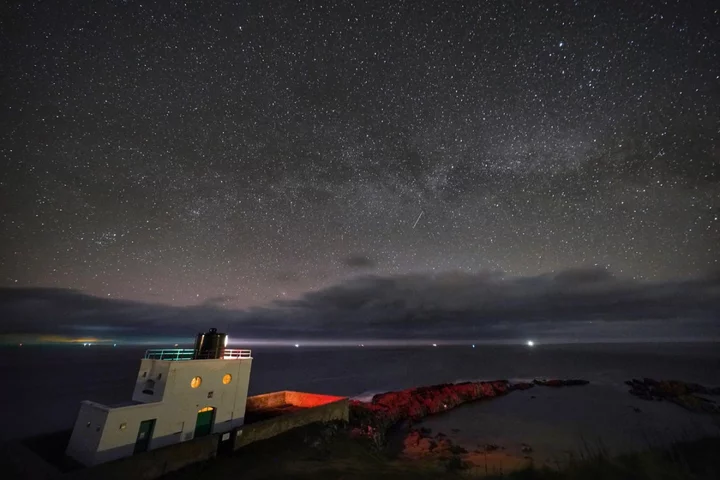

Scientists make the biggest simulation of our cosmos ever, with the mass of 300 billion galaxies
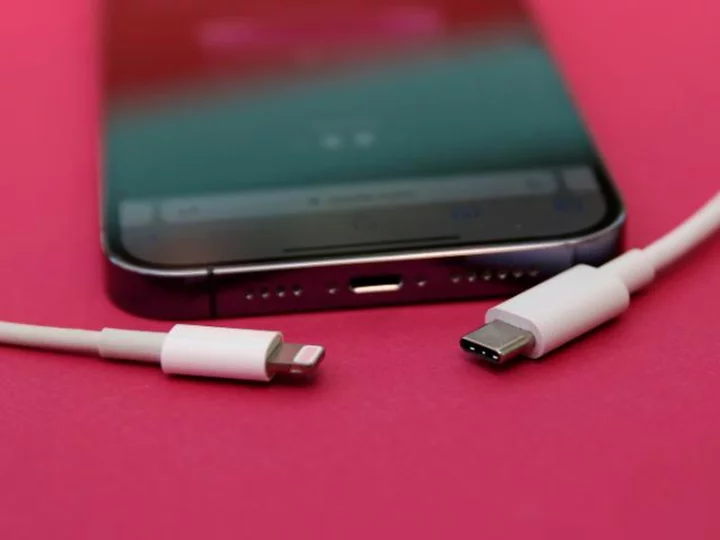

Apple just killed the iPhone Lightning connector. What to do with your old chargers

The world's shortest IQ test will reveal how average your intelligence is in 3 questions
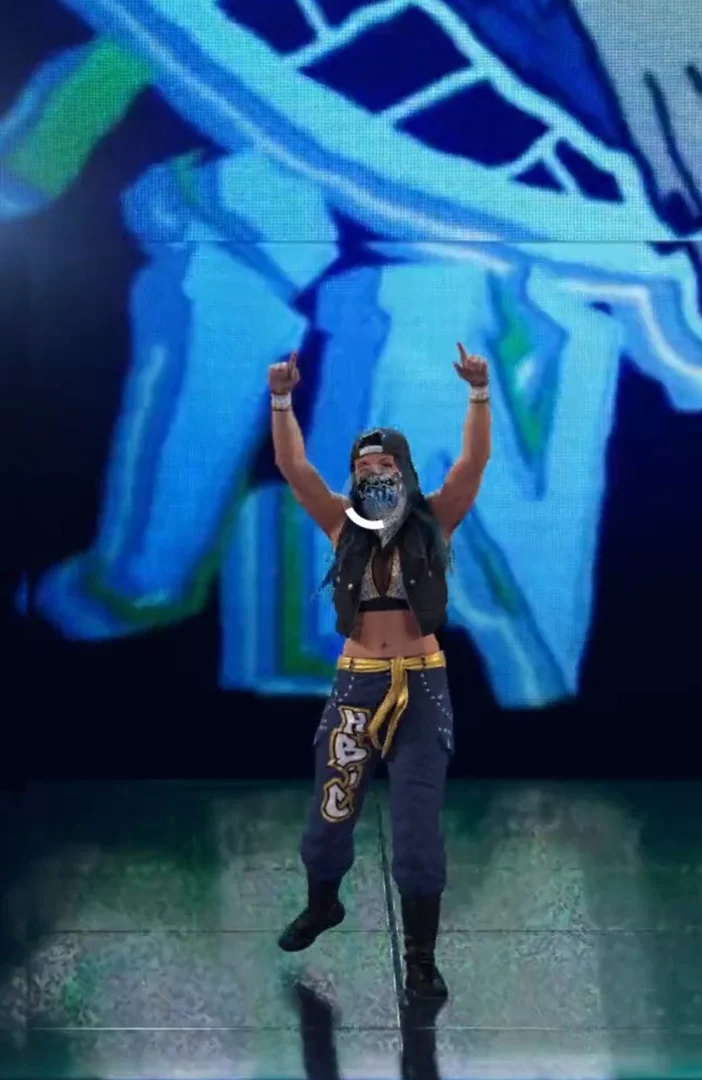

WWE Superstar Mia Yim is heading to WWE 2K23
