
Binance sees $956 million in outflows after Zhao steps down to settle U.S. probe
(Reuters) -Investors pulled about $956 million from crypto exchange Binance over the past 24 hours, data firm Nansen reported on
2023-11-23 00:18

BLAST.tv Paris Major 2023 Legends Stage Results, Matches
BLAST.tv Paris Major 2023 Legends Stage results live and up-to-date at the final CS:GO Major.
2023-05-12 00:52

'Queen of pop' Addison Rae thrills fans by dropping much-awaited 'Lost Album' tracks: 'I Got it bad is coming'
Addison Rae will be joining A-list celebs like Jason Momoa, Ryan Reynolds, and Aubrey Plaza in 'Animal Friends' soon
2023-08-15 19:59

Fortnite Last Resort Trailer Explained: New Map, Mythics, and Vampires
The Fortnite Last Resort trailer gives fans their first look at Chapter 4 Season 4's new map, Mythic weapons, Battle Pass skins, and the vampire ruling the season.
2023-08-25 00:56

Spotify to Cut Back Promotional Spending on White Noise Podcasts
Spotify Technology SA is cracking down on white-noise podcasters, reducing the advertising support for programmers that provide little
2023-09-02 00:50

Paysign Successfully Completes Certification and Establishes Connection with Mastercard
HENDERSON, Nev.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-13 20:24

Exclusive-OpenAI investors considering suing the board after CEO's abrupt firing -sources
By Anna Tong, Krystal Hu and Jody Godoy (Reuters) -Some investors in OpenAI, makers of ChatGPT, are exploring legal recourse
2023-11-21 22:45

Why you should delay your first coffee of the morning
For a lot of people, coffee is one of the few things that gets them out of bed and out the door in the mornings. But while it’s tempting to whack the kettle on first thing, a health expert has stated that delaying our first coffee of the day could be much more beneficial to our health. Nutritionist Gabi from The Fast 800 urged people to wait at least 90 minutes before getting their first coffee hit [via the Mirror]. Gabi claims that we can all boost energy levels by doing so. In fact, eating on an empty stomach could even cause your body to enter stress mode and release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. "Supporting your morning coffee routine with some smart practices can be a game changer for your overall well-being,” Gabi said. She recommends drinking water, as well as eating a meal packed with fibre and protein to balance sugar levels. “Elevated blood sugar can trigger inflammation and set us up to be on a blood sugar roller coaster for the rest of the day, thereby tanking our energy supply,” the health guru said. "Within the first hour of waking, our cortisol levels ideally acutely rise and fall in a response known as our cortisol awakening response. This rise and fall of cortisol represents a healthy nervous system and actually has a big influence on our immune health and even the risk of autoimmune development." She also states that delaying coffee for a minimum of 90 minutes promotes high energy levels. Gabi said: "Morning light exposure is a huge regulator of circadian rhythm and light exposure triggers the healthy release of cortisol in the morning to support the body’s natural rhythm. Getting natural light exposure within the first hour or so of waking is a great way to support optimal hormone balance." It comes after it was revealed that the drink also gives us an extra ‘special boost’ as well as just a caffeine hit. Scientists have claimed that the act of drinking a cup of joe gives the body a lift, making us more alert, which can’t be replicated merely with caffeine. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-21 17:17

Slack Unveils New Sales-Specific Edition at $60 Per Month
Salesforce Inc. released a new version of Slack specifically designed for salespeople as it works to integrate its
2023-08-02 21:28

Twitter to pay verified creators for ads in replies, Musk says
(Reuters) -Twitter will soon begin paying verified content creators for ads in their replies, with the first payment block of
2023-06-10 08:27
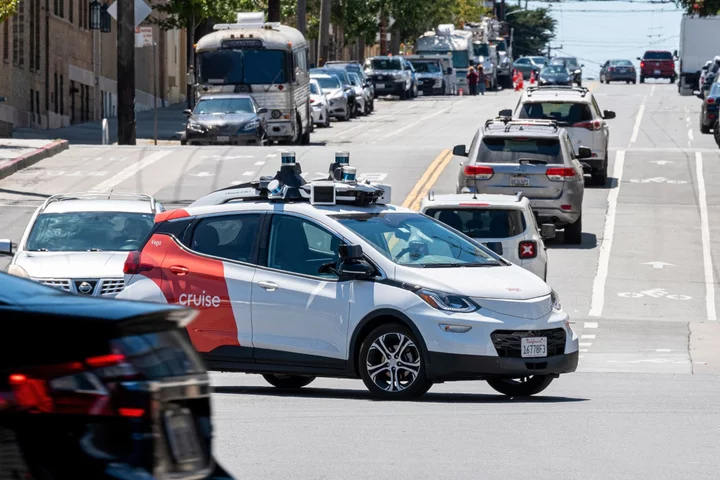

Robotaxis Are Making Enemies as They Go Around San Francisco
Just before Patti Smith took the stage in San Francisco this month, the emcee thanked sponsors, including robotaxi
2023-08-24 21:45

Threads active users have halved in a week, report says
Meta's Threads had a moment in which it seemed it would overtake Twitter in a
2023-07-18 15:20
You Might Like...
Harpak-ULMA Announces Online Parts Portal

Quantum-Si Appoints Biotech Executive and Entrepreneur, Amir Jafri, to its Board of Directors

What to stream this week: 'And Just Like That' back, Kelly Clarkson sings, Robert Downey Jr. drives

Medable Ranks in Top 8% of 2023 Inc. 5000 List of America’s Fastest-Growing Private Companies

The Best Pre-Prime Day Laptop Deals

New Spotify feature gives Calm content for free
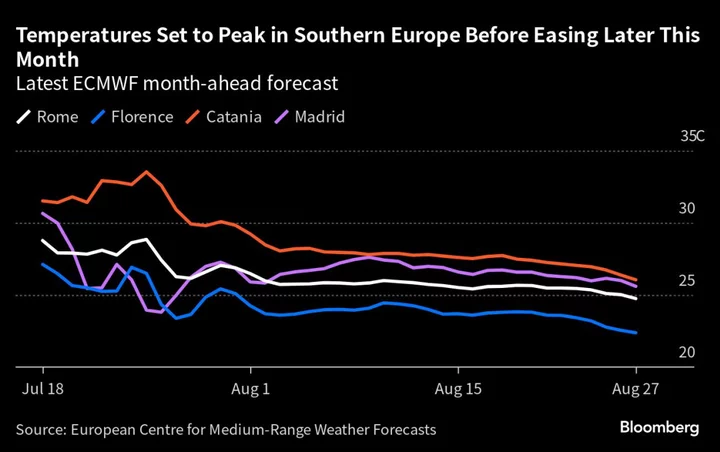
Europe Braces For Record Temperatures as Wildfires Hit Greece

Who stars in 'Hack My Home' Season 1? Netflix's Dream Team ready to make family house renovation a success
