
Karnataka High Court's Twitter verdict sparks debate on free speech
A court has fined Twitter $61,000 for not complying with a government order to take down tweets.
2023-07-03 13:53

UAE to Set Up Carbon Registry to Gauge Companies’ Emission Cuts
The United Arab Emirates is developing a carbon registry that will measure companies’ progress in reducing emissions, and
2023-11-16 22:29
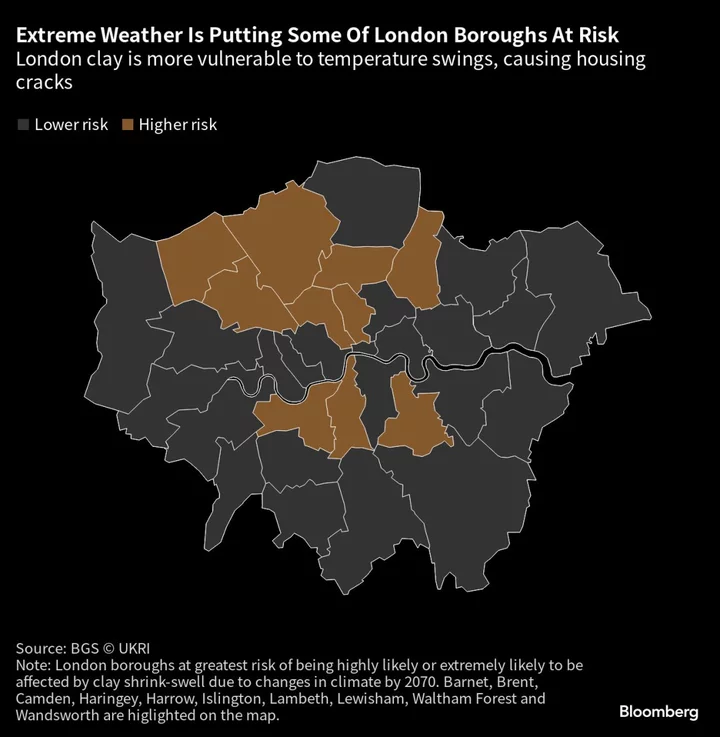
London Is Falling Down and It's Because of Climate Change
Britain’s increasingly extreme weather is shaking the very foundations of its centuries-old history. The nation has been experiencing
2023-07-08 12:52

'Singing the Blues': How to try cool relationship trend going viral on TikTok?
Many TikTok users are participating in the 'Singing the Blues' trend by uploading their 'glow up' videos
2023-05-20 18:54

Can Doctors Self-Prescribe Medications?
Doctors can self-prescribe, but it's generally discouraged and the practice has quite a few stipulations.
2023-07-06 01:28
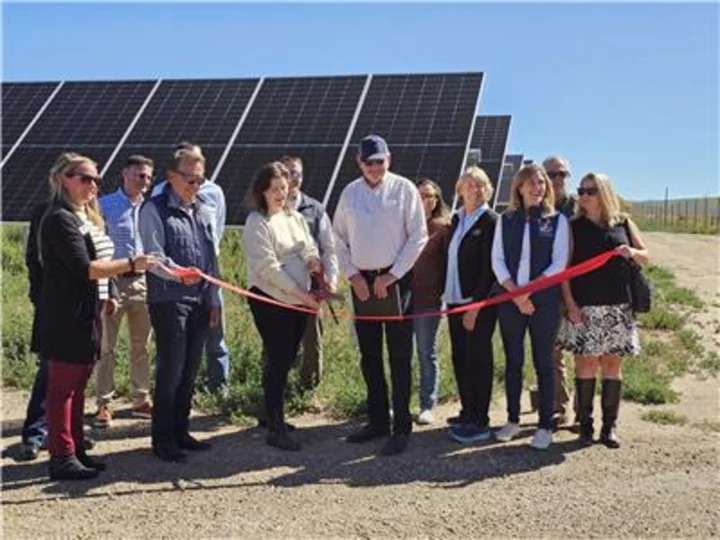

Ameresco Announces Innovative Regional Solar Array Project in Collaboration with City of Craig, Yampa Valley Electric Association, and the Colorado Department of Local Affairs
FRAMINGHAM, Mass. & CRAIG, Colo.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 11, 2023--
2023-09-12 00:25

Gannett sues Google, Alphabet claiming they have a monopoly on digital advertising
Gannett is suing Google and its parent company Alphabet, claiming that they unlawfully acquired and maintain monopolies on the advertising technology tools that publishers and advertisers use to buy and sell online ad space
2023-06-20 23:50
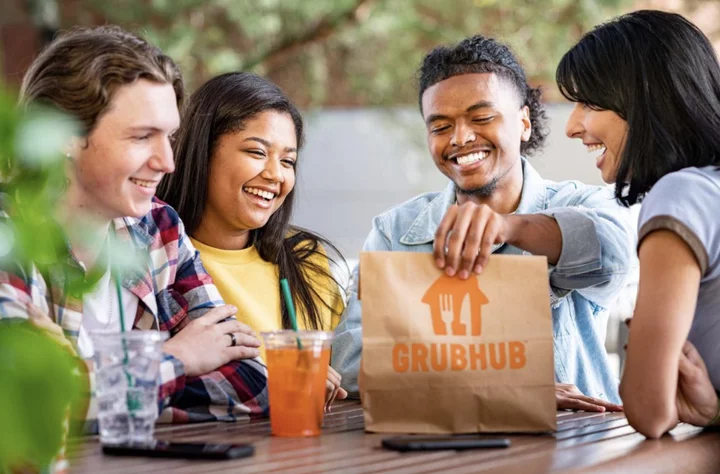

You can now get two years of free Grubhub+ with the purchase of Amazon Prime
SAVE $240: As of June 6, new and existing Amazon Prime members will get two
2023-06-06 23:56

Amazon's $1.7 billion deal to buy Roomba maker iRobot gets UK approval
British antitrust regulators have cleared Amazon’s purchase of robot vacuum maker iRobot
2023-06-16 19:26
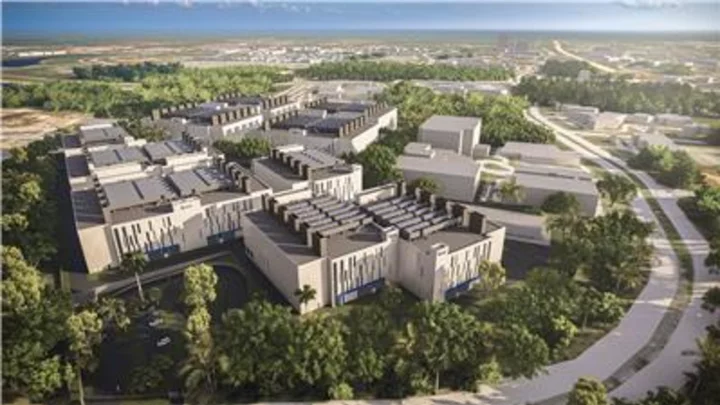

Vantage Data Centers Announces Second Campus in Cyberjaya
DENVER & SINGAPORE--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 16, 2023--
2023-05-16 20:29

Meta's Threads could lure ads from Twitter but it's early days, analysts say
By Akash Sriram, Samrhitha A and Sheila Dang Threads, Meta Platform's broadside to Twitter, is seen by some
2023-07-24 18:30

Apex Legends Revenant Prestige Skin Leaked
New leaks claim an Apex Legends Revenant Prestige skin is coming to the Mythic Store, available for 150 Heirloom Shards, sometime in Season 18.
2023-08-15 00:53
You Might Like...

Katy Perry responds to viral video of her at King Charles III's coronation

Can You Beat Lethal Company?

Korea Superconductor Experts Seek to Test Breakthrough Claims

Perfect Corp. Partners with Parfums Christian Dior to Launch Online Consultation with AR Makeup Virtual Try-On Experience at Viva Technology 2023
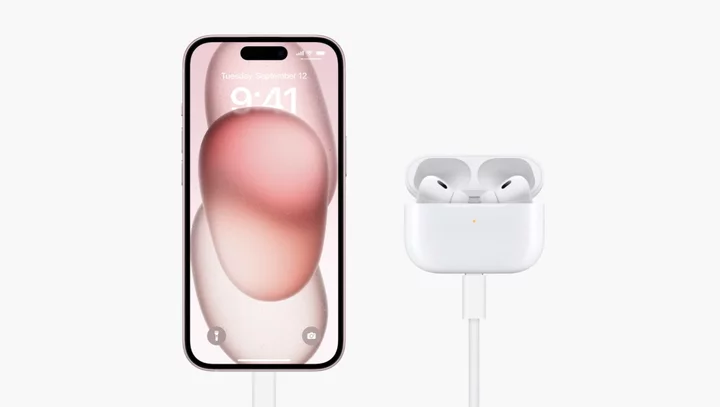

USB-C is coming to Apple AirPods

RWE Draws Up Plans to Exit Controversial German LNG Project

Federal appeals court rules Microsoft can close its Activision merger

Activists Sue South Africa’s Environment Authorities Over Arcelor Pollution
