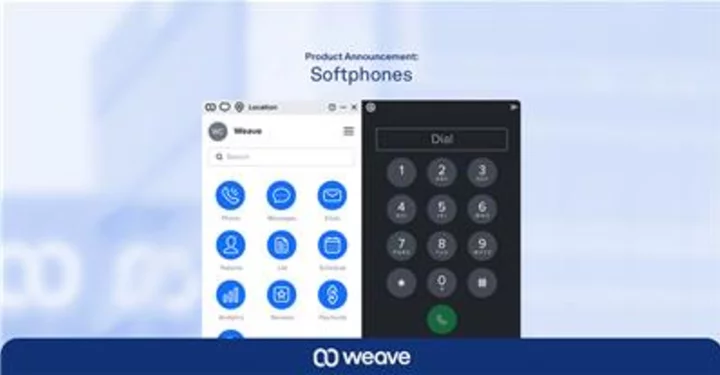
Weave Launches Softphones, New Features and Platform Enhancements to Help Small Businesses Better Leverage Remote Staff
LEHI, Utah--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 31, 2023--
2023-05-31 22:29

Tesla CEO Elon Musk On The EV Slowdown And ‘Terrible’ Human Drivers.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk had plenty to say on Wednesday in an interview with Dealbook's Andrew Ross Sorkin, including cursing out some advertisers formerly on X.
2023-11-30 20:58
Intel Unveils Industry-Leading Glass Substrates to Meet Demand for More Powerful Compute
SANTA CLARA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 18, 2023--
2023-09-18 21:19

Is xQc moving back to Canada? Streaming community speculates if he plans to start 'gambling' again: 'Just full restart everything'
xQc claimed he will book a flight to either Toronto or Vancouver in an effort to 'pull the plug' and 'full restart everything'
2023-08-01 16:16

China's regulator says finds serious security issues in US Micron Technology's products
BEIJING China's cyberspace regulator said on Sunday its review has found that US Micron Technology’s products have serious
2023-05-21 20:59

Here are all the best Doordash promo codes you can redeem this week
Summer temps are soaring, which means this might be prime time for you to stay
2023-07-29 04:48

Gannett to pause AI experiment after botched high school sports articles
Newspaper chain Gannett has paused the use of an artificial intelligence tool to write high school sports dispatches after the technology made several major flubs in articles in at least one of its papers.
2023-08-31 02:51

Huge Lenovo Back-to-School Sale: Save Up to 71% on Laptops and Desktops
Back-to-school can be a stressful time, but getting a big discount on a new Lenovo
2023-07-20 03:48
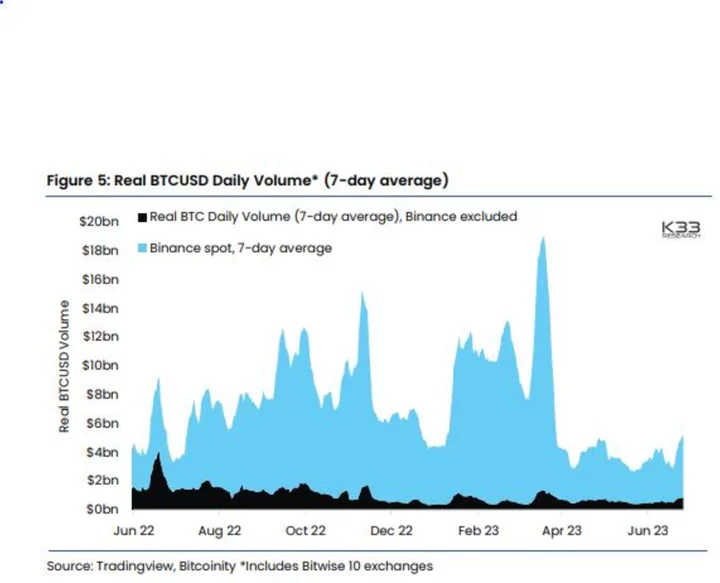
Bitcoin Prices Settle Into Narrow Range as ETF-Inspired Euphoria Dissipates
Bitcoin has quickly settled into a narrow trading range after reaching a fresh one-year high, leaving reinvigorated enthusiasts
2023-06-30 02:47

Salem Media Announces New Podcast with Ben Taatjes and Jerrid Sebesta on the Senior Resource Podcast Network
IRVING, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 21:23
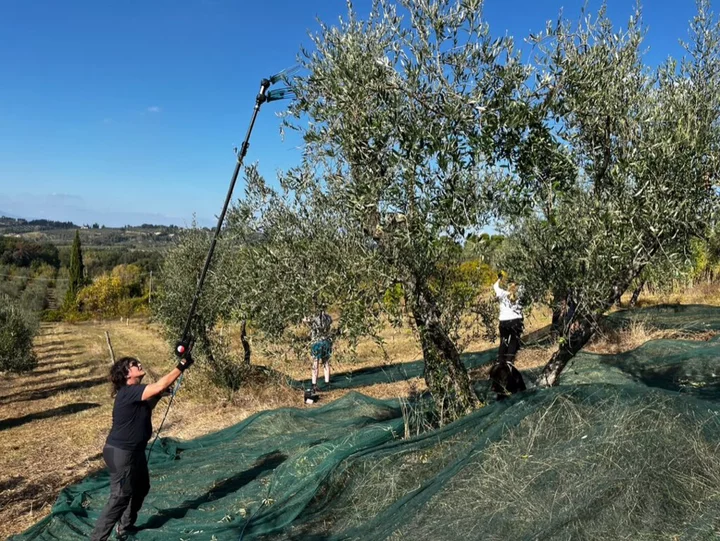

Olive Oil Producers Turn to Tourists to Combat Soaring Costs, Extreme Weather
Maria Angela Macchia jams a 10-foot pole topped with an electric comb into the upper reaches of a
2023-11-22 17:47

US Supreme Court rules against EPA in wetlands regulation challenge
By John Kruzel and Andrew Chung WASHINGTON (Reuters) -The U.S. Supreme Court on Thursday put another dent in the regulatory
2023-05-26 01:51
You Might Like...

Who is Hennessy? Kai Cenat expresses desire to meet Cardi B's sister during livestream with rapper Offset
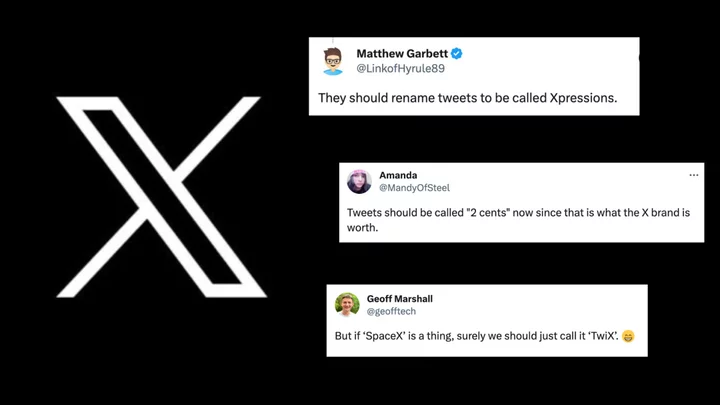
What are tweets called now that Twitter is X? Users weigh in

Who is Amelia Giordano? Wyoming teacher pleads not guilty to child endangerment charge in connection to Paul Pine's, 11, suicide

Save up to 25% on Google Pixel phones even after Prime Day

Google Pixel's battery drainage issue has been fixed
Bitcoin price dramatically crashes amid market worries

When do BLAST.tv Paris Major 2023 Stickers Go on Sale?

Threads: Elon Musk posts series of explicit tweets about Mark Zuckerberg
