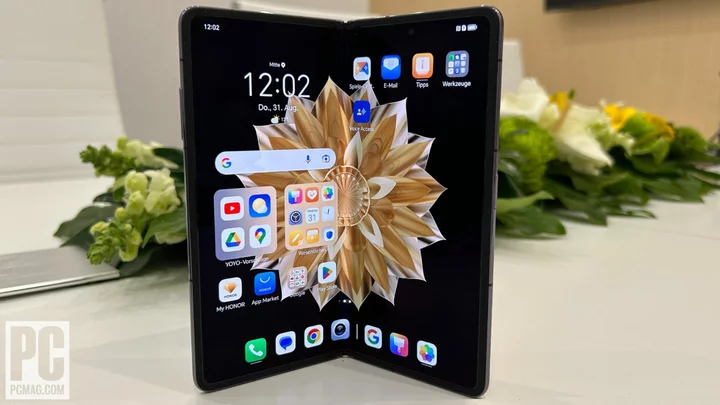
Honor Shows Off the World's Thinnest Book-Style Folding Phone at IFA
BERLIN—At IFA 2023, Honor presented its latest folding phone, the Honor Magic V2, which the
2023-09-01 17:54

xQc claps back at Logan Paul's skepticism regarding his lucrative $100M Kick deal, Internet dubs WWE superstar 'dislikeable'
xQc said, 'I just think it's odd, it's just a weird way to approach things, dude, I get it they're joking, but, there needs to be some civility there'
2023-07-08 18:48
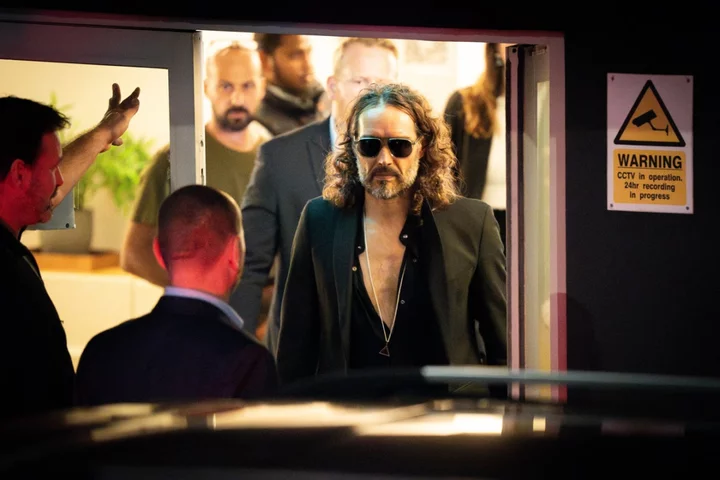

Monetisation of Russell Brand’s YouTube channel suspended
YouTube has suspended the monetisation of Russell Brand’s channel for “violating” its “creator responsibility policy”. In a statement to the PA news agency, a spokesperson for the Google-owned company said: “If a creator’s off-platform behaviour harms our users, employees or ecosystem, we take action to protect the community.” The news comes after the remaining shows of Brand’s Bipolarisation tour were postponed and the Metropolitan Police said it had received a report of an alleged sexual assault in the wake of media allegations about the comedian and actor. Brand’s YouTube account, which has 6.6 million subscribers, has been suspended from YouTube’s partner account “following serious allegations against the creator”, meaning the channel is no longer able to make money from advertising on the platform. The statement added: “This decision applies to all channels that may be owned or operated by Russell Brand.” The 48-year-old actor has been accused of rape, assault and emotional abuse between 2006 and 2013, when he was at the height of his fame and working for the BBC, Channel 4 and starring in Hollywood films, following a joint investigation by The Times, Sunday Times and Channel 4’s Dispatches. He has strongly denied the allegations, which also include claims of controlling, abusive and predatory behaviour. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-09-19 15:29
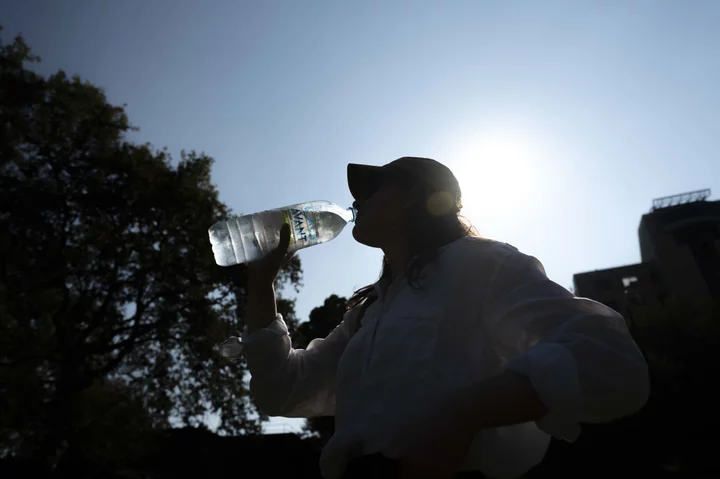

UK Has Hottest Day of the Year as September Heat Tops Record
The UK had its hottest day of the year on Thursday, and the autumnal heat wave that’s baking
2023-09-08 22:00

10 of the best University of Michigan courses you can take online for free
TL;DR: A wide range of online courses from the University of Michigan are available for
2023-07-05 12:15

Saw Video Games: Are They Canon to the Franchise, Where to Buy
With Saw back in the limelight with Saw X, there are two video games players can dive into if they never have. Here's where players can buy the game and if they are canon to the franchise as a whole.
2023-10-04 01:48

The Apple iPad Mini (6th Gen) is down to its lowest-ever price for Prime Day
TL;DR: The Apple iPad Mini (6th Gen) is on sale for $379.99 this Prime Day.
2023-07-11 21:58

A 3-month subscription to Disney+ is on sale for under £2 per month
SAVE £18: Until Sept. 20, new and returning customers can subscribe to Disney+ for £1.99
2023-09-06 19:16

Personal data of more than 700,000 retired California workers and beneficiaries have been stolen
California officials are notifying state retirees and other beneficiaries whose personal information has been stolen
2023-06-23 04:21

Pokimane's 2023 livestreaming highlights: The top 3 viral moments
Here, we present the top 3 most-watched clips from 2023, each garnering hundreds of thousands of views:
2023-09-17 20:51
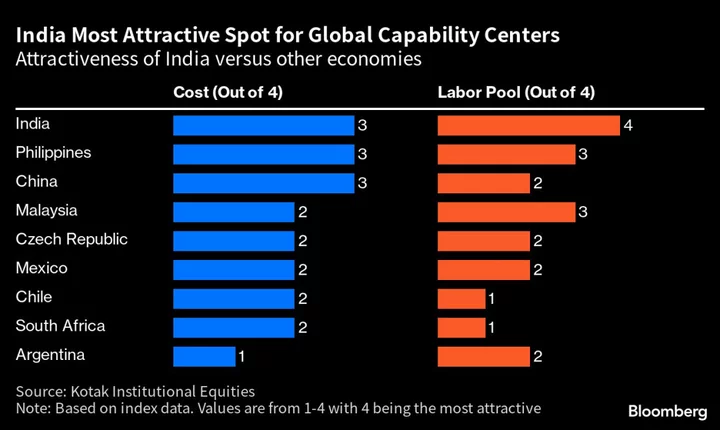
Goldman’s Biggest Office Beyond New York Attests to India’s Rise
On the eastern side of Bengaluru, the city sometimes called the Silicon Valley of India, sits a campus
2023-06-14 07:15

Deutsche Bank Tests Out AI to Detect Rogue Traders’ Phonecalls
Deutsche Bank AG is testing out artificial intelligence tools that aim to detect possible signs of misconduct from
2023-09-13 17:24
You Might Like...
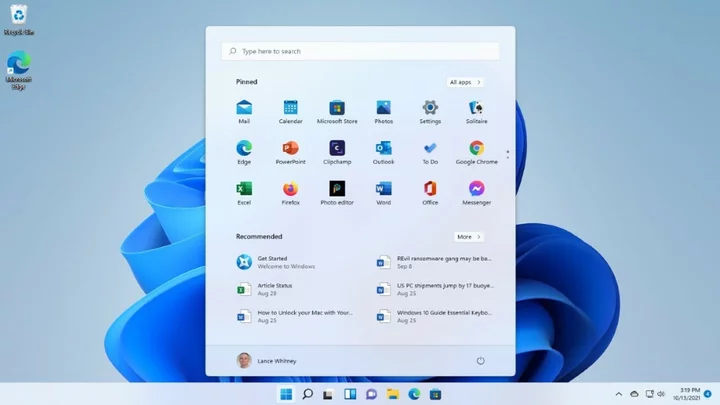
Hate the Windows 11 Start Menu? Here's How to Change or Replace It

Score a like-new Lenovo laptop for $360, plus a free lifetime license to MS Office

Bumble takes a stand against flakes in new guidelines

Bungie hires ex-Warner Bros. Discovery executive to lead Destiny expansion including films and more

AGL Will Spend A$10 billion in Shift to Renewables From Coal

Hasbulla arrested in Russia for 'unbridled wedding fun'

News Corp in negotiations with AI companies over content usage - CEO

Warzone Resurgence Vengeance Icon Explained
