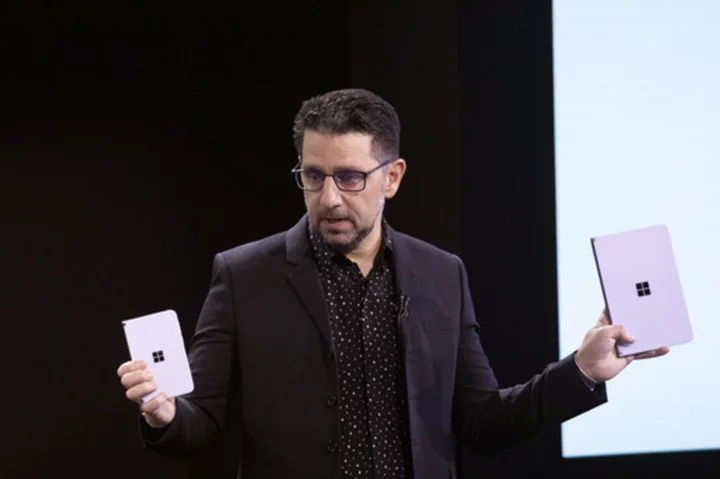

Microsoft's chief product exec to step down. Panos Panay was behind Surface devices and Windows 11
A top product executive at Microsoft who launched its Surface line of devices and Windows 11 is leaving the company
2023-09-18 23:21

Fortinet, rivals fall on concerns around cybersecurity spending
By Samrhitha A (Reuters) -Fortinet sank nearly 18% and sparked a selloff in cybersecurity stocks with a dismal forecast that
2023-11-08 13:48
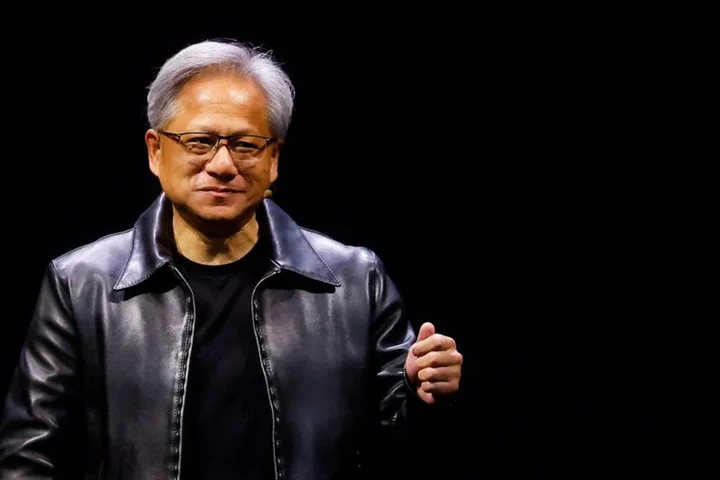

AI means everyone can now be a programmer, Nvidia chief says
TAIPEI Artificial intelligence means everyone can now be a computer programmer as all they need to do is
2023-05-29 16:16

Is Adin Ross dating again? Kick star's girlfriend and family background explored
Here's a look at Adin Ross' dating life and his delightful family, who often appear on his videos
2023-06-07 20:22
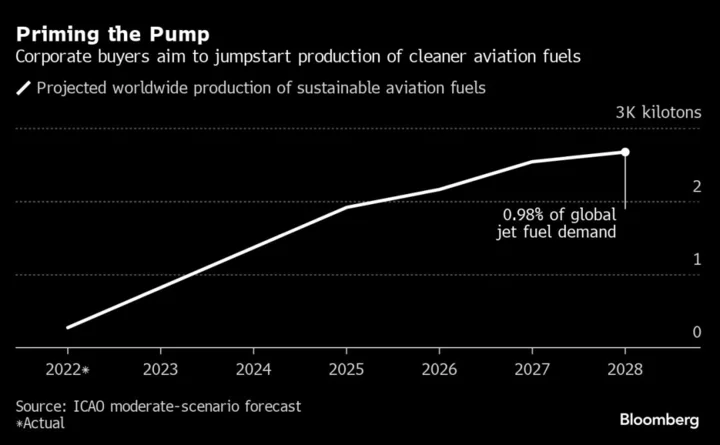
Microsoft Is On Pace to Buy More Clean Jet Fuel Than Most Airlines
Some of the world’s biggest corporate consumers of air travel are investing in cleaner jet fuel, using a
2023-10-27 17:25
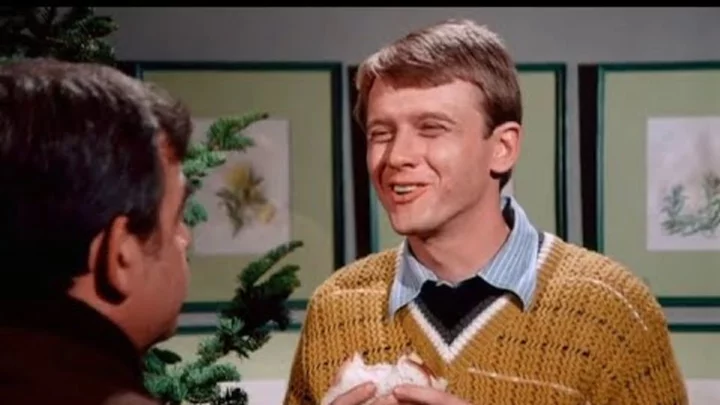

When Chuck Cunningham Vanished From ‘Happy Days’
Richie Cunningham’s older brother not only disappeared from the show, he was wiped from the minds of the entire cast.
2023-07-08 03:19
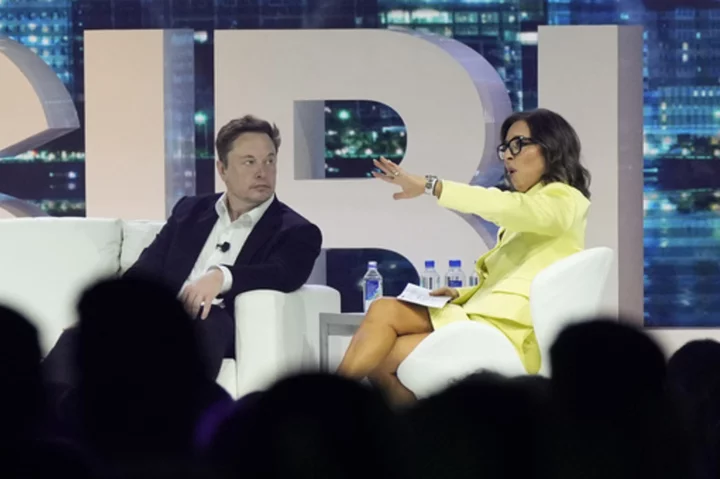

Elon Musk sparred with new CEO Linda Yaccarino in on-stage interview: 3 takeaways from the exchange
Elon Musk sat down in April for an on-stage interview with Linda Yaccarino, the advertising executive he named as Twitter's new chief executive on Friday
2023-05-13 13:28
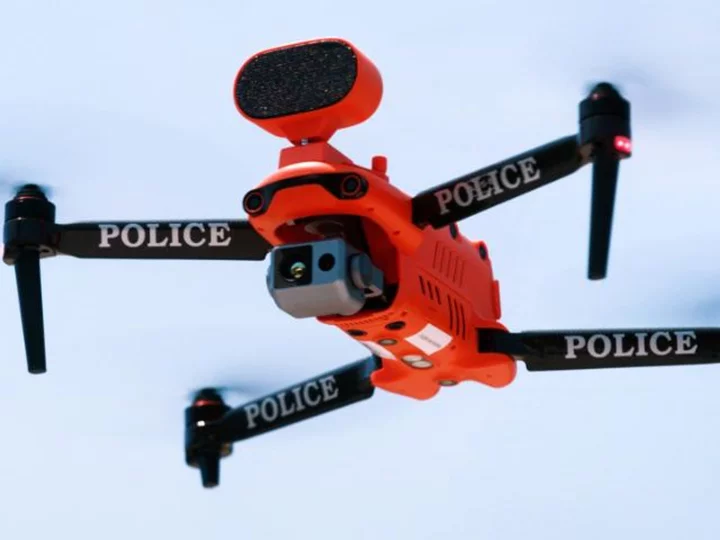

After a string of shark attacks, here's how officers at one New York beach use drones to keep swimmers safe
Warmer and cleaner waters off the coast of Long Island, New York, in recent years have brought growing numbers of bait fish to the area — and with them, the bigger fish that eat them, including sharks. In some ways, it's a good sign for the environment. But it's a different story for swimmers, surfers and beach goers.
2023-08-14 19:58

Best gay dating apps for hookups, relationships, and everything in between
Most people have at least one horror story about online dating. It's a rite of
2023-08-16 17:47
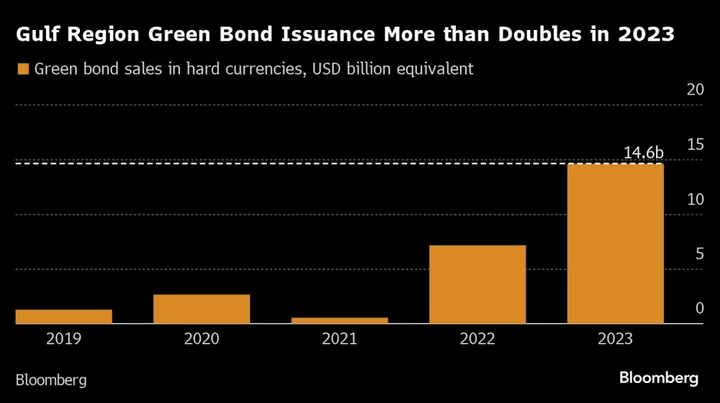
Green Bond Sales Surge in UAE Before It Hosts Climate Summit
A record amount of green debt has been raised this year by issuers in the United Arab Emirates
2023-11-23 18:17
Aiosyn Launches AI-Powered Mitosis Detection Solution to Support Cancer Research, Improving the Efficiency and Consistency of Results
NIJMEGEN, Netherlands--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 20:46
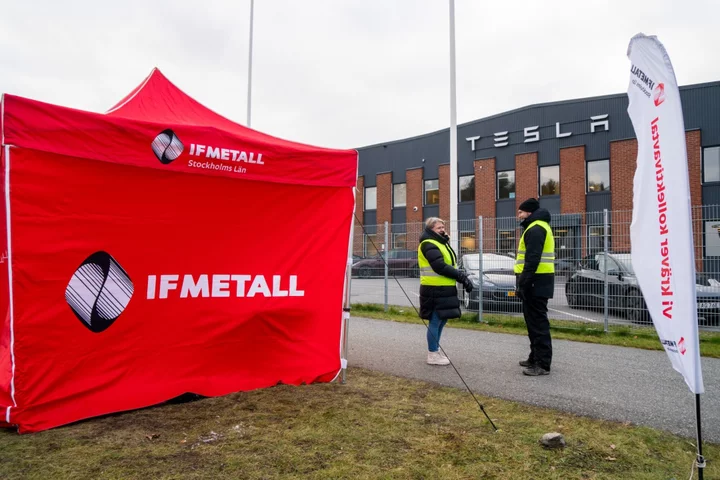

Tesla Business Grinds to a Halt Where Unions Still Hold Sway
For the past week, not a single Tesla has passed through Sweden’s four biggest ports. Starting Friday, broken
2023-11-17 18:23
You Might Like...
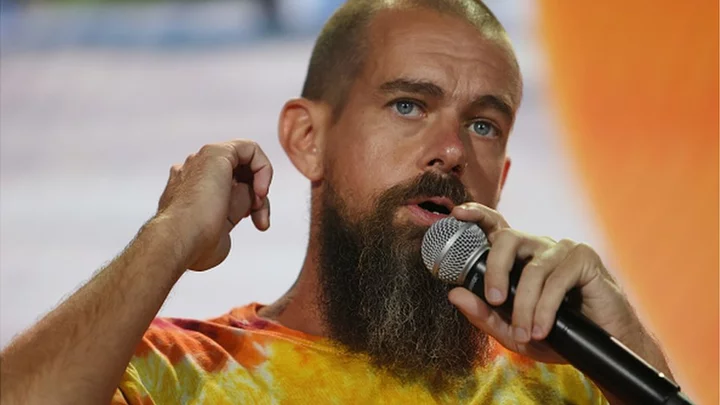

Jack Dorsey: India threatened to shut Twitter and raid employees

Who is Farrah Safari? Meghan Markle accused of faking her 'Archetypes' podcast

ChatGPT Plus: OpenAI stops premium signups after major update

YouTube Is Letting AI Write Video Summaries
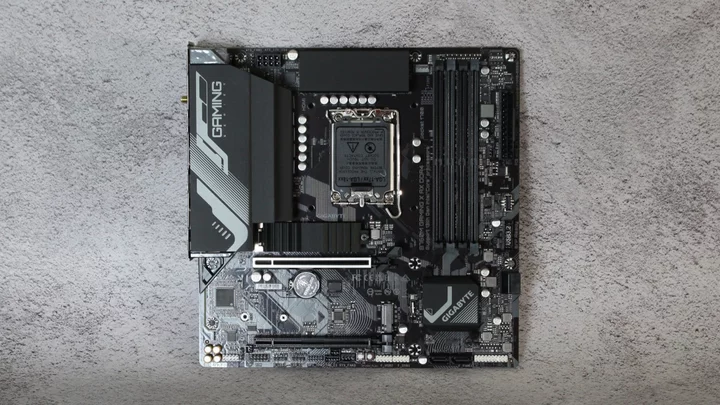

Gigabyte B760M Gaming X AX DDR4 Review

Keysight Accelerates Open RAN by Co-Organizing First Global OTIC Summit

South Korea Reverses Paper Cup Ban in Unusual Green Backtrack
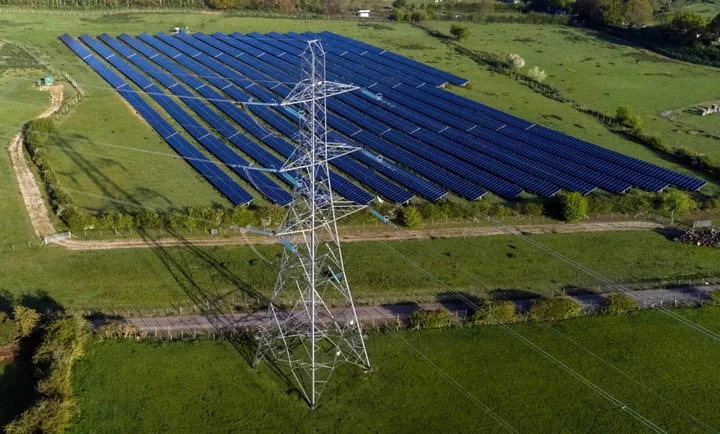

Nearly Half of Tory Voters Still Favor Net Zero, Study Says
