
UK Will Widen Climate Aid Definition to Meet Target More Cheaply
The UK plans to expand its definition of what counts as climate aid in order to meet its
2023-09-21 18:22

Adin Ross and Andrew Tate laugh hysterically after Kim Jong Un impersonator makes unexpected comments about his sister: 'Having mid-life crisis'
Andrew Tate said, 'I go to Romanian jail and get woken up at three in the morning by Adin Ross to come and talk to a Kim Jong Un impersonator'
2023-09-21 18:17

Jumio Named a Representative Vendor in Fifth Consecutive Gartner® Market Guide for Identity Verification
SUNNYVALE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 21, 2023--
2023-09-21 18:17
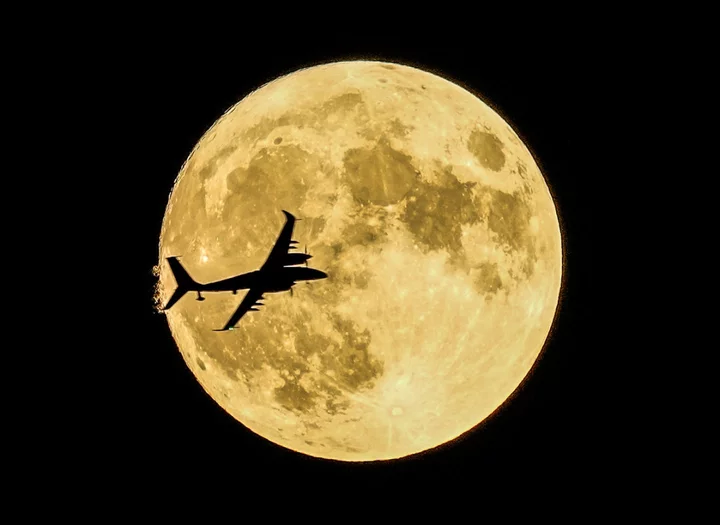

September Supermoon: When is it and how to view it?
The world is about to see the last Supermoon of the year. When the full Moon rises on 28 September, it will be bigger and perhaps brighter than usual, because it is relatively close to the Earth. Our nearest neighbour will be a mere 361,552km away. That compares with the average distance of 384,472km. Its relative proximity means that the Moon will appear larger and more clearly in the sky than usual, and can provide an exciting opportunity for people to get a good look at our satellite. Doing so is easier than with many other celestial phenomena: you can simply look up at the sky, and see whether you can spot the difference in the Moon’s size, though looking through telescopes or binoculars could provide a good look at its surface. It is best seen at Moonrise, when it begins to rise over the horizon. The other objects in front of it will help provide a sense of scale and can make the Moon look larger than normal. This month’s Moon is also known as the Harvest Moon, so named because it comes closest to the start of Autumn. As well as coming around harvest season, the bright reflections from the Moon can be a helpful way of working into the night. There is no formal definition of a Supermoon, and some astronomers have suggested that they are overhyped. What’s more, not all Supermoons are equal, and the lack of definition means that the word can be used for moons that are only slightly closer than normal. But they can bring significant increases in the amount of light that appears on Earth: Supermoons cast about 30 per cent more light than when the Moon is at its dimmest, according to the Natural History Museum. The museum’s planetary science researcher Sara Russell also noted that the Moon is actually moving slowly away from Earth. That means that what we call a Supermoon today was actually just the normal Moon a billion years ago. This year has been a busy one for fans of the Moon. Last month, for instance, also saw a supermoon – which also happened to collide with a Blue Moon, for the last time this decade. Read More MPs ask if Elon Musk ‘personally intervened’ on Russell Brand’s status on X Starship rocket launch window revealed by FAA India’s solar mission completes key manoeuvre, slingshots towards Sun
2023-09-21 18:16

HydrogenPro Completed Electrolyser Delivery to World Leading Validation Center
OSLO, Norway--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 21, 2023--
2023-09-21 18:15

The best dating apps of 2023: A guide to finding love, a hookup, or something in between
The success rate of throwing likes to somebody cute on Instagram definitely isn't zero. And
2023-09-21 17:59

Former Elon Musk employee speaks out on 'ridiclous' death of Neuralink's monkeys
A new report from Wired has alleged that Elon Musk's Neuralink - a neurotechnology company developing a brain-computer interface - euthanised the company's macaque subjects after they suffered various complications from the implant. The report comes after human-test subjects were recently approved for Neuralink's clinical trial. Elon Musk had claimed earlier this month that "no monkey has died as a result of a Neuralink implant, but public documents obtained by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) and seen by Wired, suggest that the primate subjects suffered complications including "bloody diarrhoea, partial paralysis, and cerebral edema." Musk had acknowledged the deaths on September 10 on Twitter/X, denying the deaths were "a result of a Neuralink implant", and that researchers had selected subjects who were already "close to death." However an anonymous former employee called this "ridiculous" if not a "straight fabrication." However, the public records reviewed by Wired suggest a different story. The PCRM, a nonprofit aiming to abolish live animal testing, claim that Musk knew his comments about the primate subjects deaths "to be false". They write that investors deserve to hear the truth about the safety, "and thus the marketability," of Neuralink's product. A December 2019 experiment outlined in one of the documents mentioned a subject known as Animal 15. The documents said that the subject "began to press her head against the floor for no apparent reason" just days after receiving the implant. Her condition only worsened as she "began to lose coordination" and "would shake uncontrollably when she saw lab workers." Staff finally euthanised her months later. Last year, the PCRM filed a complaint with the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) alleging that Neuralink's practices violate the Animal Welfare Act. The US Department of Transportation is also investigating Neuralink over allegations contimanted devices that were removed from monkeys' brains were illegally transported. Indy100 have reached out to Neuralink for comment. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:59

Get two durable 4K drones on sale for $150
TL;DR: As of Sept. 21, you can snag the Ninja Dragon Phantom K Pro and
2023-09-21 17:59

Amazon Alexa gets new AI powers, with the same kind of brain as ChatGPT
Amazon is adding the same kind of brain that powers ChatGPT into Alexa. The new technology is intended to allow the virtual assistant to be more powerful and able to speak with its owners in more natural conversations. The announcement were part of a wide array of new devices launched by Amazon this week. It also revealed new tablets and Echos, including those with screens, as well as plans to use generative artificial intelligence to create art to show on those screens. Every year, Amazon announces a number of Alexa devices, which have in the past included everything from soundbars to microwaves. This year, much of its focus was on artificial intelligence. While Alexa was one of the first virtual assistants of its kind to go mainstream, Amazon has lagged behind rivals such as Microsoft and Google in integrating new large language models into those systems. The sudden rise of such technology has sparked greater scrutiny of AI from regulators, given its explosion into general use and concerns over its potential impact on human life as well as industry, jobs and education. During a live event to unveil its latest range of Alexa-powered devices, Amazon looked to reaffirm its position as a market leader in AI by showing off an update to the assistant that will allow for more natural conversations with Alexa, rather than just the transactional request fulfilment it currently runs on. In a live demonstration of Alexa’s new large language model (LLM), Amazon devices boss Dave Limp showed how the new version of the assistant will be able to be more expressive in its responses - for example sounding happier when returning a positive sporting result for a user’s favoured team. Based within a new section of the service called “Let’s Chat”, Alexa will respond without the use of a wake word first, be able to pick up a conversation after a break and still understand the context, as well as understand inferences and more vague prompts in a way that Limp said is “like talking to a friend”. For example, the new Alexa will respond to the prompt “I’m cold” by turning on the heating in a connected home. Amazon has not confirmed a general release date for the new version of Alexa, instead focusing on an early preview programme in the US to try out the new capabilities among some users. Technology expert Ben Wood, chief analyst at CCS Insight, said it was “little surprise” to see Amazon discussing the power of its AI assistant in this way. “It undoubtedly knows that it needs to keep pace with rivals such as Google and Microsoft so articulating what it is doing in this area was essential for this event,” he said. “The upgraded way to talk to Alexa certainly makes it a more personal experience but success will depend on Amazon being able to get consumers to engage with the Echo devices in a very different way to the transactional and basic requests used today. “Some users may find it a little intimidating, but if successful it could make interactions a lot more conversational.” Elsewhere at its hardware event, Amazon unveiled a string of new hardware products, including several new Alexa-powered Echo smart speakers and smart home hubs, as well as new Fire tablets and updated Fire TV Stick devices. Read More Neuralink’s monkeys may have died due to brain implants contrary to Musk’s claims Facebook changes logo to ‘make F stand apart’ – but can you tell the difference? What is ‘Rumble’, where Russell Brand is posting videos? Neuralink’s monkeys may have died due to brain implants contrary to Musk’s claims Facebook changes logo to ‘make F stand apart’ – but can you tell the difference? What is ‘Rumble’, where Russell Brand is posting videos?
2023-09-21 17:58

Learn a new language via audiobook with this app, now $30
TL;DR: Through Sept. 24, a lifetime subscription to the Beelinguapp language learning app is on
2023-09-21 17:57

Carbon Offsets Undercut California’s Climate Progress, Researchers Find
Since the passage of its landmark climate regulations 17 years ago, California has been a leader in the
2023-09-21 17:55

A scientist has discovered when Earth's first continent was formed
A researcher has figured out that the Earth’s first continent was formed 3bn years ago, in a new paper that sheds fresh light on the early stages of the planet’s life. Jane Greaves, an astronomy professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at Cardiff University in Wales, was examining continent formation on distant stars and planets. It is thought that exoplanets with continents that formed in a similar way to Earth’s are more likely to be habitable, and perhaps even contain alien life. In the process, she calculated when several distant planets’ continents were born, as well as those a little closer to home. Continents on Earth sit on top of the planet’s hot, viscous mantle. Heat from the inner core stops the mantle from solidifying. The reason the core is hot is because it contains radioactive elements that came from neutron star collisions billions of years ago such as forms of Uranium, Thorium and Potassium. By analysing how many materials like this are present on Earth and on other planets, we are also able to estimate when the continents formed. On Earth, that was about 9.5 billion years since the beginning of the universe. Meanwhile, in Greaves' sample, the first continents appeared 2bn years before Earth’s on the exoplanets of younger, so-called thin disk stars. Older, thick disk stars analysed in her work produced rocky planets with continents that appeared even earlier: about 4 to 5bn years before Earth’s. “The outlook seems very promising for finding rocky exoplanets with continents, given that nearby Sun-like stars have already produced a few candidate hosts,” she wrote. The study, “When were the First Exocontinents?” is published in Research Notes of the American Astronomical SocietySign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:19
You Might Like...

Senate to Vote on Stripping Mountain Valley Pipe From Debt Bill

New Indie Game ‘Polaroid: Pieces of Memory’ Enters Early Access on Steam
Did Mizkif sign a deal with Rumble? Streamer says 'it's not about money but about growing the platform'

Where is Sunswoon Lagoon in Fortnite?

Amazon's AWS appeals to corporate customers with new chatbot, AI safety measures
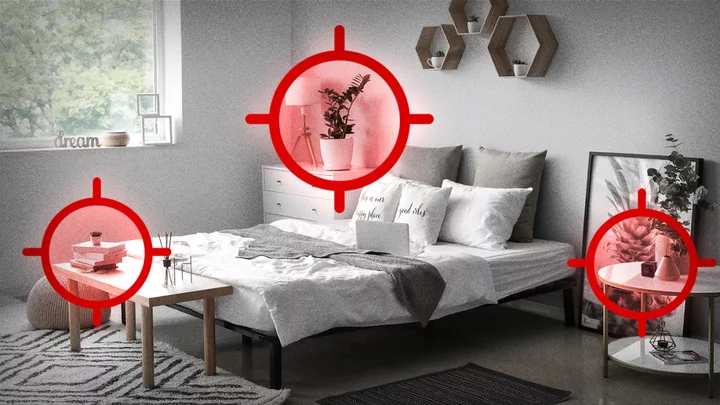

Does Your Airbnb Have Hidden Cameras? Here's How to Check

Huge Xbox leak reveals Microsoft’s plans for the future of the console

How to Get Cyberpunk 2077 Phantom Liberty Early Access
