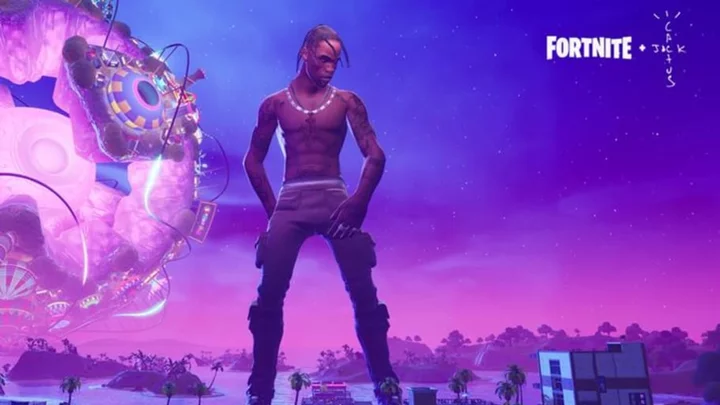

Here's When the Fortnite Festival Concert is Coming to Chapter 5
The leaked Fortnite Festival concert starts on Saturday, Dec. 9, 2023, at 9 a.m. ET in Chapter 5 with free rewards and possibly live music.
2023-11-16 23:56

Biggest-ever simulation of the universe could finally explain how we got here
It’s one of the biggest questions humans have asked themselves since the dawn of time, but we might be closer than ever to understanding how the universe developed the way it did and we all came to be here. Computer simulations are happening all the time in the modern world, but a new study is attempting to simulate the entire universe in an effort to understand conditions in the far reaches of the past. Full-hydro Large-scale structure simulations with All-sky Mapping for the Interpretation of Next Generation Observations (or FLAMINGO for short), are being run out of the UK. The simulations are taking place at the DiRAC facility and they’re being launched with the ultimate aim of tracking how everything evolved to the stage they’re at now within the universe. The sheer scale of it is almost impossible to grasp, but the biggest of the simulations features a staggering 300 billion particles and has the mass of a small galaxy. One of the most significant parts of the research comes in the third and final paper showcasing the research and focuses on a factor known as sigma 8 tension. This tension is based on calculations of the cosmic microwave background, which is the microwave radiation that came just after the Big Bang. Out of their research, the experts involved have learned that normal matter and neutrinos are both required when it comes to predicting things accurately through the simulations. "Although the dark matter dominates gravity, the contribution of ordinary matter can no longer be neglected, since that contribution could be similar to the deviations between the models and the observations,” research leader and astronomer Joop Schaye of Leiden University said. Simulations that include normal matter as well as dark matter are far more complex, given how complicated dark matter’s interactions with the universe are. Despite this, scientists have already begun to analyse the very formations of the universe across dark matter, normal matter and neutrinos. "The effect of galactic winds was calibrated using machine learning, by comparing the predictions of lots of different simulations of relatively small volumes with the observed masses of galaxies and the distribution of gas in clusters of galaxies," said astronomer Roi Kugel of Leiden University. The research for the three papers, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, was undertaken partly thanks to a new code, as astronomer Matthieu Schaller of Leiden University explains. "To make this simulation possible, we developed a new code, SWIFT, which efficiently distributes the computational work over 30 thousand CPUs.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-16 23:53
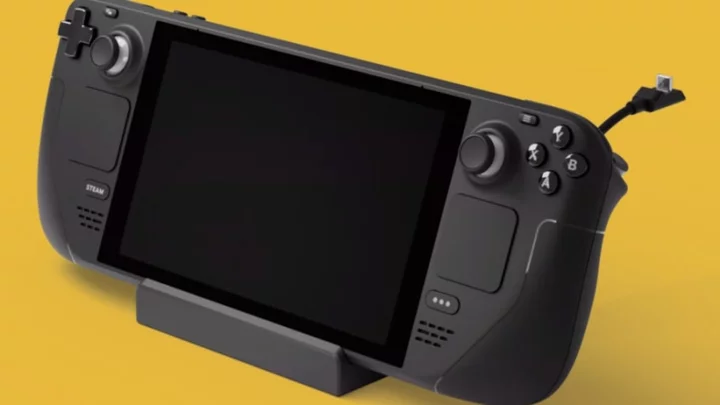

Where to Buy a Steam Deck on Black Friday 2023
Steam Decks are getting price cuts! Here's where you can buy one.
2023-11-16 23:51
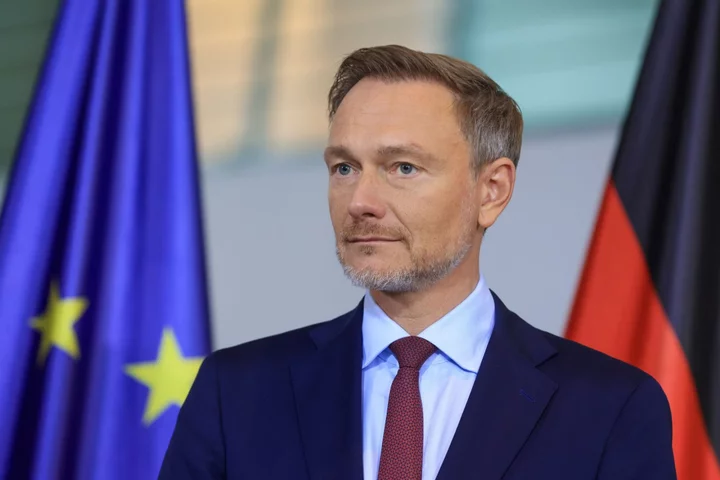

German Finance Chief Sees Budget Ruling as “Turning Point”
Finance Minister Christian Lindner said Wednesday’s ruling by Germany’s top court curbing the use of off-budget special funds
2023-11-16 23:50

Redwood inks long-term EV battery materials supply deal with Toyota
By Paul Lienert Redwood Materials has signed a long-term contract to supply Toyota Motor with recycled materials for
2023-11-16 22:53

Carbon-Capture Firm Deep Sky Gets $55 Million of Fresh Capital
A Canadian startup raised $55 million from venture capital firms and governments to begin a carbon-capture plant in
2023-11-16 22:47

UAE to Set Up Carbon Registry to Gauge Companies’ Emission Cuts
The United Arab Emirates is developing a carbon registry that will measure companies’ progress in reducing emissions, and
2023-11-16 22:29

Nintendo Download: Wish Upon a Star Road
REDMOND, Wash.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Nov 16, 2023--
2023-11-16 22:15

A 125-Year-Old European Carmaker Starts Over to Democratize EVs
Renault SA started with a daring wager. On Christmas Eve in 1898, a young mechanic named Louis Renault
2023-11-16 21:59
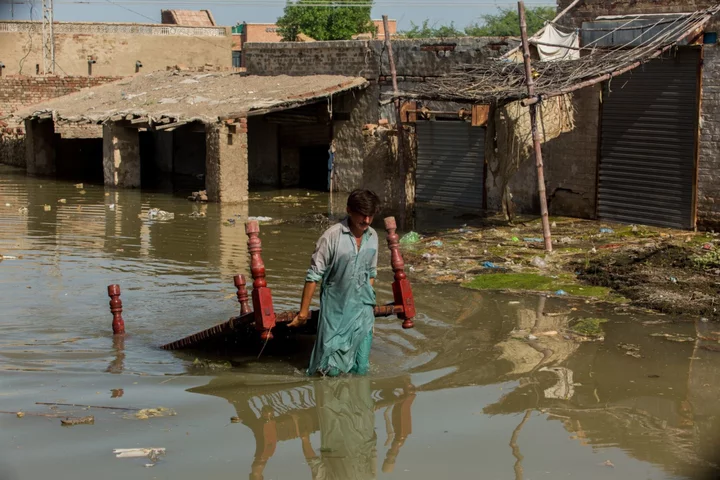

World Needs $172 Billion More to Face Climate Impacts Than Estimates Show
The UN Environment Programme recently published its annual Adaptation Gap Report, examining how much funding the world’s developing
2023-11-16 21:45
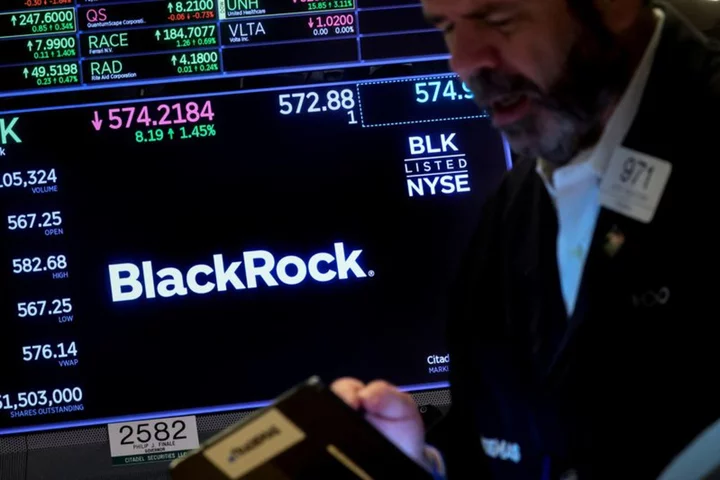

BlackRock woos investors for ethereum trust to further crypto push
Asset management giant BlackRock on Thursday began courting public investors for an ethereum trust, doubling down on its
2023-11-16 21:23

Water discovered to be leaking from Earth's crust into the planet's core
There is much we still don’t know about the inside of our planet – but scientists recently discovered water is slowly leaking down there from the surface. It’s not a simple journey. The liquid is dripping down descending tectonic plates, before eventually reaching the core after a 2,900 kilometre journey. And while the process is slow, it has over billions of years formed a new surface between the molten metal of the outer core and the outer mantle of the Earth. In a new study, scientists at Arizona State University have said the water is triggering a chemical reaction, creating the new layer, which is “few hundred kilometres thick”. (That’s “thin” when it comes to the inner layers of the Earth.) “For years, it has been believed that material exchange between Earth's core and mantle is small. Yet, our recent high-pressure experiments reveal a different story. “We found that when water reaches the core-mantle boundary, it reacts with silicon in the core, forming silica," co-author Dr Dan Shim wrote. “This discovery, along with our previous observation of diamonds forming from water reacting with carbon in iron liquid under extreme pressure, points to a far more dynamic core-mantle interaction, suggesting substantial material exchange.” So what does it mean for all of us up on the surface? The ASU release said: “This finding advances our understanding of Earth's internal processes, suggesting a more extensive global water cycle than previously recognised. “The altered ‘film’ of the core has profound implications for the geochemical cycles that connect the surface-water cycle with the deep metallic core.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-16 21:16
You Might Like...

Orsted’s $2.3 Billion Charge Exposes US Offshore Wind Woes
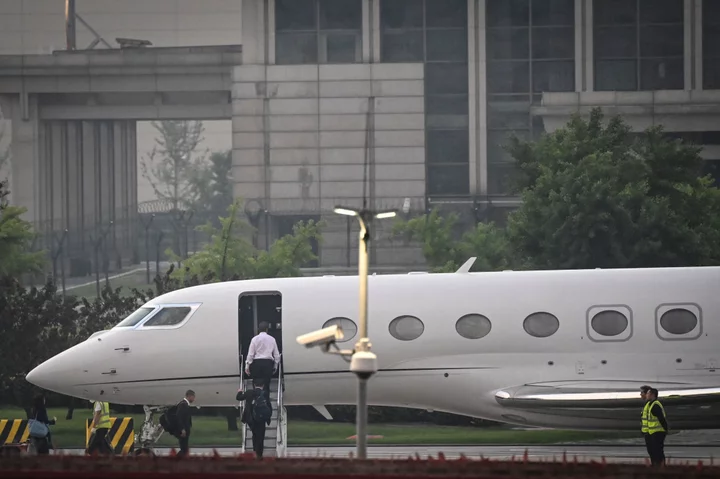

Elon Musk Goes Silent on Twitter After Arriving In China
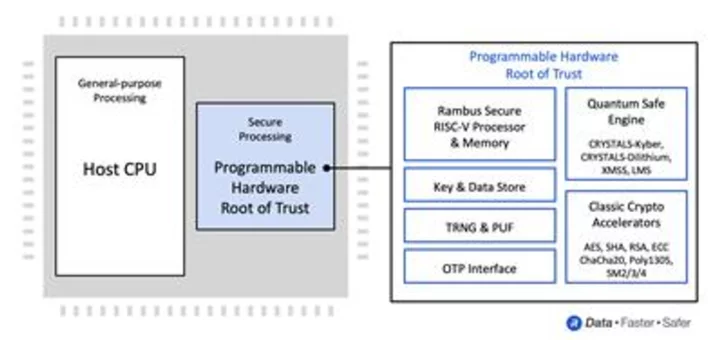
Rambus Delivers Quantum Safe IP Solutions with Next-Generation Root of Trust for Data Center Security

Synopsys Could Sell More to China Without Export Rules, CEO Says

Toshiba Launches Motor Driver ICs with Small Package and Reduced External Parts that Save Space on Circuit Boards

EU asks Meta for more details on efforts to stop illegal and inaccurate content on Israel-Hamas war

Is Pleasant Park Coming Back to Fortnite?

10 of the best online Photoshop courses you can take for free this week
