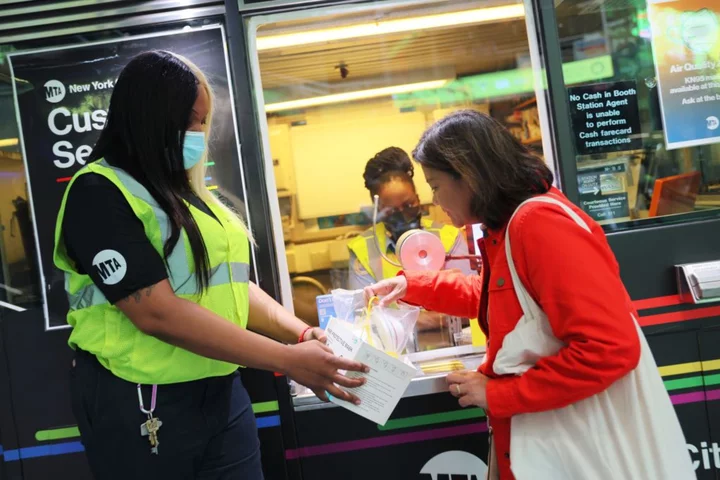

What East Coast Cities Can Learn About Wildfire Policies From the West
Hazardous smoke from wildfires has become a near-annual occurrence on the West Coast since 2017. But the hazy
2023-06-10 00:25
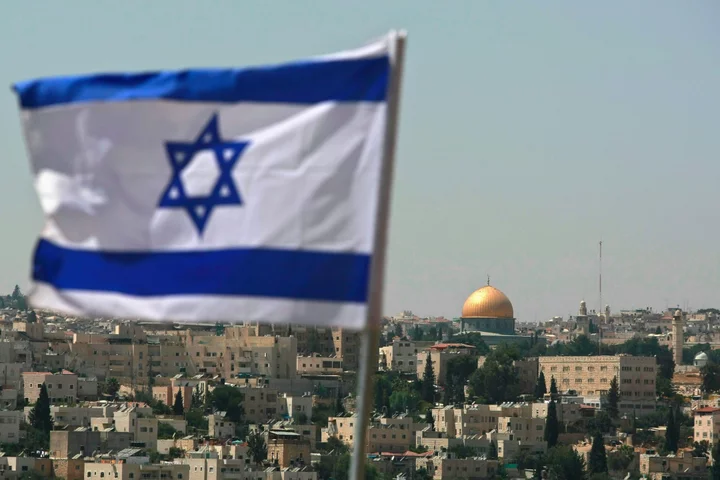

Israel Illegally Storing Millions of People’s Photos, Audit Says
Israel’s immigration authorities are illegally storing millions of photos of citizens and foreign nationals, according to a government
2023-05-16 21:29

KUBTEC® Launches MOZART iQ® - A Next Generation 3D Margin Management System for Breast Surgery
STRATFORD, Conn.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 11, 2023--
2023-05-11 22:46

Where to watch the Apple event livestream revealing expected iPhone 15, Apple Watch, more.
The annual Apple Event is tantalizingly close. Best get your plans for watching it figured
2023-09-12 16:51

Hate returning packages? Uber will now do it for you
Uber is looking to help with a much-dreaded chore: returning packages.
2023-10-04 19:18
Anthropic releases Claude Pro, a paid version of its ChatGPT rival
ChatGPT's competitor, Claude now has a paid version with premium features. On Thursday, Anthropic announced
2023-09-08 04:27
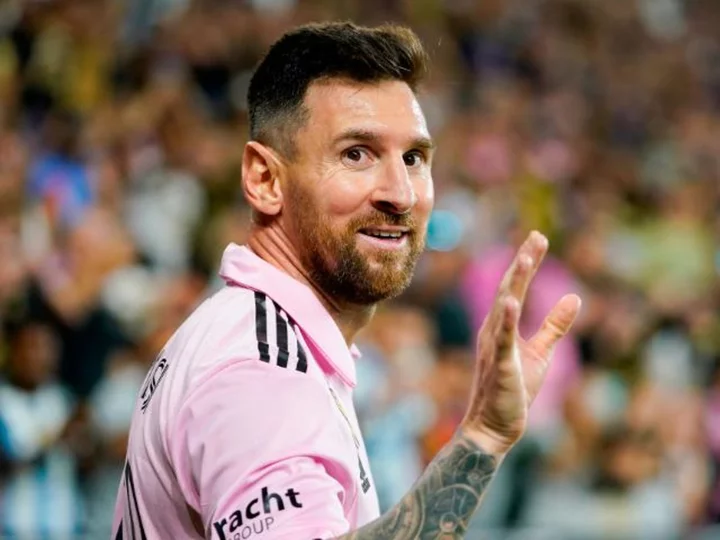

Leo Messi sparks a surge in Major League Soccer subscription sign-ups
Soccer superstar Leo Messi's arrival in America has sparked a surge in ticket prices, apparel and now, streaming subscriptions.
2023-09-05 23:24

Talkdesk Appoints Graham Smith to Board of Directors
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 27, 2023--
2023-07-27 21:20
Pets pose a serious health threat that we've all been overlooking
While millions of people own cats and dogs and wouldn’t dream of getting rid of them, pets pose a health risk to humans that is massively overlooked, according to a new study. Since the Covid-19 pandemic swept the world with devastating impact, it has become evident how much of a risk new viruses can pose to our well-being. However, experts are warning that it is not just the wildlife trade or exotic animals that we should be concerned about, as pets could also be sources of zoonotic diseases (which jump from animals to humans). Back garden pets, house pets, working animals and even rodents and pests could host new viruses that could affect humans, according to a new study. It warns that the urbanisation of our habitats and climate change will have an impact on diseases and their dynamics. The study was shared in Science Translational Medicine and penned by disease ecologist Amandine Gamble along with a group of colleagues, who gave examples of how companion animals (aka pets) and stray animals carried a risk of zoonotic spillover. While the risk is thought to be small, experts warn it is significantly underappreciated, especially given the frequent proximity human beings have to pets and strays. The study said: “These animals can play critical roles in zoonotic spillover by enabling the maintenance of a zoonotic pathogen, facilitating its spatial spread, acting as a bridge between otherwise unconnected species, or providing particular opportunities for its evolution.” While the zoonotic spillover that caused Covid-19 sparked a global pandemic, any instance of infection that jumps from animal to human is known as a zoonotic, regardless of the numbers affected. Pet parrots are a known transmitter of the Chlamydia psittaci bacterium to humans. Elsewhere, bats and horses are also known sources of zoonotic diseases. In terms of common household pets, cats can act as a link to a number of fatal diseases. The experts explained: “Numbers of infections are low, but plague is endemic in 17 western U.S. states, and many of the small mammals on which cats prey carry Y. pestis. “Consequently, outdoor cats and cats with incomplete veterinary care, combined with human interaction, suggest that cat-transmitted plague can be considered an increasing public health risk.” They conclude that “it is critical to implement surveillance programs allowing us to track changes in pathogen dynamics”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-19 17:21
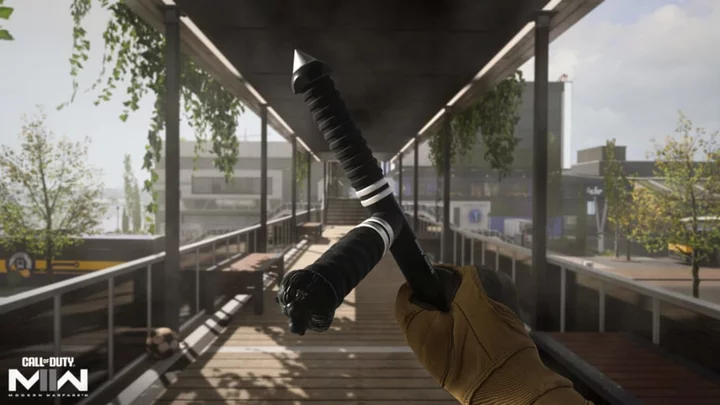

How to Unlock Tonfa Melee Weapon in Warzone Season 4
Players can unlock the Tonfa Melee weapon in Call of Duty: Warzone Season 4 by completing the final challenge in the Assault on Vondel Event.
2023-06-15 00:53

Alibaba Saw Singles Day Sales Growth, but Don’t Call It a Win for China’s Economy
Chinese e-commerce giants may have eked out another year of sales growth on Singles Day, but the data isn't all encouraging.
2023-11-13 21:45

Align Ranked in Top 100 of the Channel Futures 2023 MSP 501 List—Tech Industry’s Most Prestigious List of Managed Service Providers Worldwide
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 27, 2023--
2023-06-27 20:46
You Might Like...

Summer Heat Waves Are Far From Over in the Mediterranean Sea

xQc: Was Twitch streamer legally married to Adept? Ex couple's relationship timeline explored
Musk's X to fund legal bills of people 'unfairly treated' for posting on platform

Altman Says AI Can Improve Government Service and Deserves Backing

Top Green Fund Backs Deforestation-Free Crops With $189 Million

proteanTecs to Present in Open Compute Project (OCP) Webinar on Silent Data Errors for Resilient Data Centers

Where is Midas' Drum Gun in Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 4?
Google AI-powered search gets better at citing its sources
