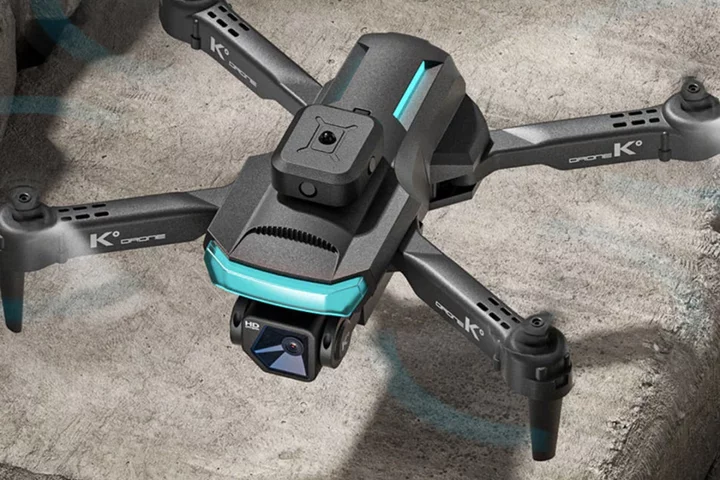

Gift your grad 4K drones with this 2-device bundle, on sale
TL;DR: As of June 9, get the Ninja Dragon Phantom K PRO + Alpha Z
2023-06-09 17:54
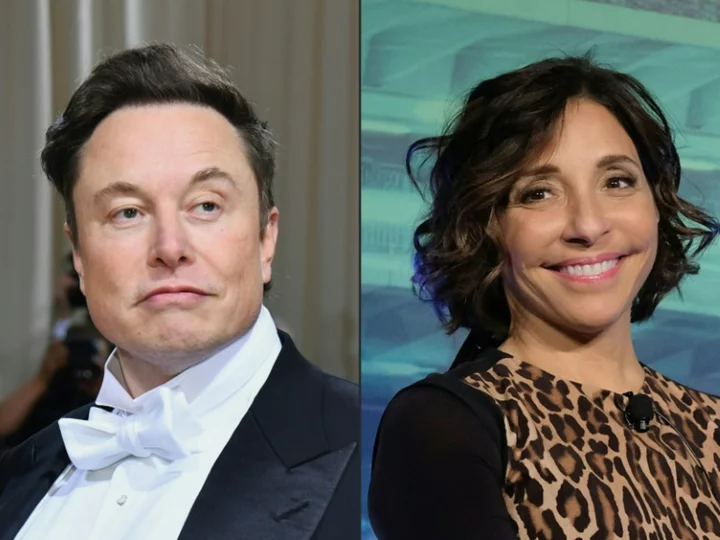

X chief Yaccarino claims renamed Twitter 'close' to break-even
Linda Yaccarino, CEO of social media platform X, said Thursday that the company formerly known as Twitter is "close" to breaking even and is hiring to beef up a...
2023-08-11 01:52
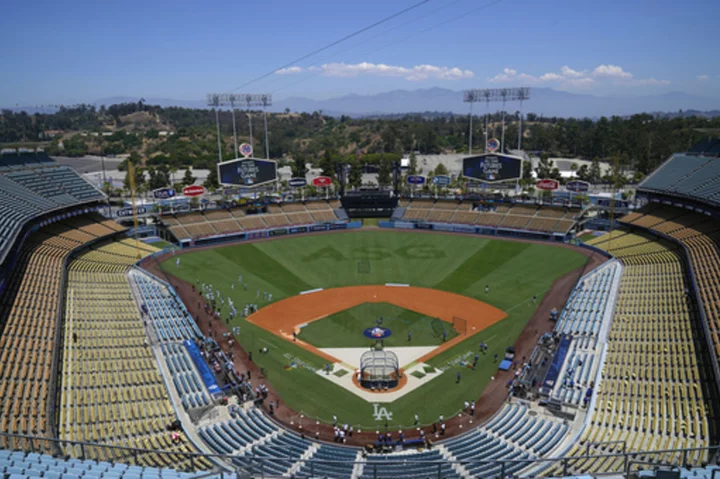

FACT FOCUS: Is Dodger Stadium flooded? No, it was just an illusion
A viral aerial video of Los Angeles’ Dodger Stadium has many social media users convinced that floodwaters submerged the ballpark amid Tropical Storm Hilary over the weekend
2023-08-22 09:51

Gastro Care Partners Chooses ModMed to Help Accelerate its Operational Excellence
BOCA RATON, Fla.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 7, 2023--
2023-09-07 20:15

Vehicle scam reports surged by 74% in the first half of 2023, says Lloyds Bank
A major bank has recorded a 74% surge in the number of reports of vehicle scams in the first half of this year, with victims losing nearly £1,000 on average. The Ford Fiesta is the most commonly-reported model to feature in vehicle-related scams so far this year, according to Lloyds Bank. Bogus offers of BMWs and Audis also feature heavily among the fake ads, with motorbikes and classic cars also cropping up regularly, it added. There is also a thriving trade in fake ads for parts and accessories, such as alloy wheels, the bank said. According to the testimony of scam victims, vans are also often popular because people are seeking cheap models to be converted in campervans, Lloyds said. The findings were based on analysis of scams reported by Lloyds Banking Group customers during between January and June 2023. This was then compared with the same period in 2022 – and a 74% increase was found. Lloyds said victims are losing an average of £998, with people aged between 25 and 34 being the most likely age group to report being duped. Scams work by fraudsters creating fake posts on social media or online marketplaces to advertise vehicles that do not exist. They will include pictures of genuine cars or vans to convince the unsuspecting buyer that they are genuine. When a potential buyer responds, they will often be asked to make a deposit to “secure” the car, or even sometimes to pay the full amount, alongside excuses as to why the car cannot be physically viewed ahead of the payment being made. The fraudster will often apply pressure-selling tactics, telling the buyer the car is very popular, that they have several other offers, or that the payment must be made by a certain deadline, Lloyds said. Victims may be tricked into sending money via bank transfer. As soon as the payment is made, the buyer will be blocked and the seller’s profile will disappear. Occasionally, a fake address will be provided at which to collect the car, leaving buyers with a wasted trip alongside the financial loss. Ford Fiestas have been highly popular in the genuine sales market. Figures released by the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) in August indicated that the Ford Fiesta was the UK’s best-selling used car between April and June. The manufacturer recently ended production of the car at its factory in Cologne, Germany. If you do want to buy something you've found through social media, only transfer funds once the car is in your possession Liz Ziegler, Lloyds Bank Liz Ziegler, fraud prevention director at Lloyds Bank said: “Buying directly from approved dealers is the best way to guarantee you’re paying for a genuine vehicle, and always use your debit or credit card for maximum safety. “If you do want to buy something you’ve found through social media, only transfer funds once the car is in your possession.” Here are some tips from Lloyds Bank to avoid vehicle scams: 1. Fraudsters use social media to advertise vehicles that do not exist. Always do your own research and do not part with any money until you have viewed, and tested, the vehicle in person. 2. Check documents. Always ask to see the seller’s logbook, to verify that the seller is the legitimate owner. 3. The safest way to buy a new or used car is often from well-known, approved dealers. Organisations such as the AA offer specific guidance for buying cars unseen. 4. Low prices and pressure selling tactics are often used to target victims. Question if a deal looks “too good to be true” and compare prices from trusted sources. 5. Always use your debit or credit card when you shop online. This helps to protect your money should something go wrong. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Standard Life confirms plans for pensions dashboard BBC reviews Russell Brand’s time at corporation as YouTube demonetises content BBC removes some Russell Brand content as monetisation suspended on YouTube
2023-09-26 07:18

KIOXIA Showcases Storage Solutions That Unlock Server and Storage Potential at HPE Discover 2023
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 15, 2023--
2023-06-15 21:19
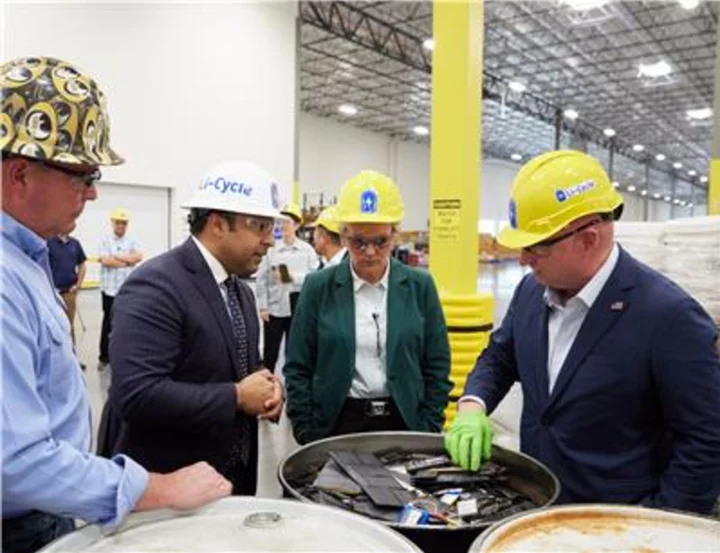

U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm and U.S. Senator Mark Kelly Visit Li-Cycle’s Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Facility in Arizona
TORONTO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 24, 2023--
2023-05-24 18:20

Who is JustaMinx? Streamer goes live with black eyes and broken nose: 'My face hurts'
Twitch streamer JustaMinx's mysterious facial injuries spark concern and speculation among fans
2023-06-16 20:47

Musk’s X Sues Non Profit That Tracks Hate Speech Over Report
Elon Musk’s X Corp. sued a nonprofit group that monitors online hate speech, accusing it of falsely describing
2023-08-01 13:59

Why has Rex Heuermann's DNA not been put into CODIS? Cops wrap up search of Gilgo Beach murders suspect's home
While DNA evidence was crucial in connecting Rex Heuermann to the heinous crimes, the suspect's DNA could not be entered into the database
2023-07-26 17:56

Surfaceink Qualified as an Authorized Test Lab for Alexa
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 20, 2023--
2023-06-20 22:19

SoundHound AI Launches Fully Automated Smart Answering Service That Lets Any Business Handle Customer Service Calls With Voice AI
SANTA CLARA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 10, 2023--
2023-08-10 21:18
You Might Like...

Microsoft CEO Says Smaller Companies Can Still Compete in AI
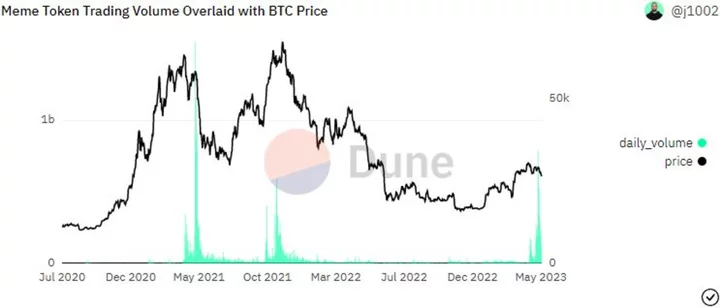
Bitcoin Bulls Trip on a Frog as Pepe Memecoin Frenzy Signals Market Top

Unauthorized Debits Hit Popular Philippine E-Wallet GCash
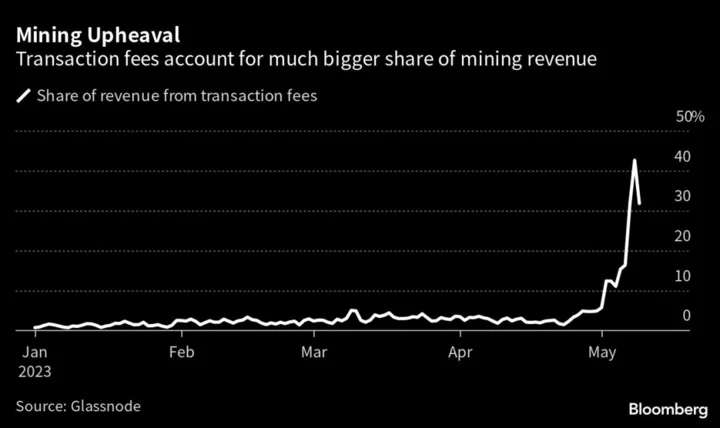
Memecoin Mania and NFTs Bring a ‘Seismic Shift’ for Bitcoin Mining

Musk Says Discriminated X Users Will Get Help With Legal Bills

Key facts about Neuralink, Musk's cyborg gamble

US Must Widen China Chip Curbs in Micron Response, Lawmaker Says
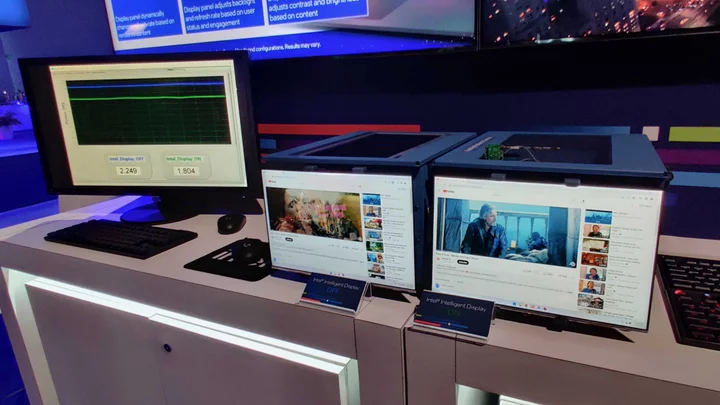

New Intel Tech Can Lower a Laptop's Brightness When You're Not Looking
