
HP announces outlook for fiscal 2024 and hikes annual dividend
HP Inc on Tuesday forecast fiscal 2024 earnings largely in line with estimates and raised its annual dividend,
2023-10-11 06:29

Prime Day 2023 isn't for a few weeks, but these deals aren't waiting
We all know someone who refers to their entire birth month as their birthday. That's
2023-06-22 05:15

In challenge to Tesla, major automakers launch EV charging network
A group of major automakers on Wednesday said they were forming a new company to provide electric vehicle
2023-07-27 00:51

US, Europe working on voluntary AI code of conduct as calls grow for regulation
The United States and Europe are drawing up a voluntary code of conduct for artificial intelligence, with a draft expected in weeks
2023-06-01 00:28

How to Hide Blue Checkmark on Twitter/X
Here's the easy way how to hide the blue checkmark on Twitter/X for all Twitter Blue subscribers on Elon Musk's platform.
2023-08-03 01:29

Are Adin Ross and Drake collaborating? Rapper DMs Kick star, fans say 'thought they were trolling'
The news spread rapidly across various platforms, sparking speculation about a potential collaboration between Adin Ross and Drake
2023-06-24 20:26

Setback for Ireland as EU legal adviser recommends revisit of Apple tax case
A legal expert at Europe’s top court has said a lower court committed “errors in law” when it threw out a decision by the European Commission which would force Apple to pay more than 13 billion euro in back taxes to Ireland. The non-binding opinion is seen as a significant setback to Ireland’s defence of its past tax treatment of the US technology giant. In 2016, following an EU investigation which launched in 2014, the commission concluded that Ireland gave undue tax benefits to Apple, which would be illegal under EU state aid rules. Ireland and Apple fought the commission on the matter and in July 2020, the General Court of the European Union annulled the decision. However, the European Commission subsequently appealed against the decision to the European Court of Justice (CJEU) saying the lower court’s ruling was legally incorrect. On Thursday, Giovanni Pitruzzella, an advocate general at the CJEU, agreed that the earlier ruling had contained “a series of errors in law”. He said the judgment should be set aside and referred the case back to the General Court for a new decision. While the opinion of the advocate general is non-binding, it is usually followed by the court and therefore could have significant implications for corporation tax bills. There was no sweetheart deal Finance Minister Michael McGrath The commission’s original position was that that tax rulings issued by Ireland to Apple in 1991 and 2007 substantially and artificially lowered the tax paid by the iPhone manufacturer in the country since the early 90s, in a way which did not correspond to economic reality. As a result, competition commissioner Margrethe Vestager said Ireland had granted illegal tax benefits which enabled it to pay substantially less tax than other business over many years. The investigation found that Apple had paid an effective corporate tax rate of 1% on its European profits in 2003, down to 0.005% in 2014, 50 euro for every one million euro of profit. The process involved recording almost all sales profits of two Irish incorporated companies, which the commission said only existed on paper. The companies, fully owned by Apple, held the rights to use the firm’s intellectual property to manufacture and sell its products outside North and South America. The commission said this situation allowed Apple to avoid taxation on almost all profits generated by sales of its products in the entire EU single market. It said this was due to Apple’s decision to record all sales in Ireland rather than in the countries where the products were sold. The findings were disputed by the Irish State, which said all tax owed had been collected, and Apple, which had come under scrutiny in the US for its tax practices years earlier. At the time, Apple’s chief executive, Tim Cook, branded the EU findings as “political crap”, maddening and untrue. The Irish Government, which was also used to defending a comparatively low 12.5% corporation tax rate, said Europe had overstepped the mark in attempting to dictate tax laws and enforce retrospective taxes decades later. Ireland and Apple fought the commission on the matter and in July 2020, the General Court of the European Union annulled the decision. The General Court found that the commission had not shown that there was an advantage deriving from the adoption of the tax rulings. However, the commission subsequently appealed the decision to the European Court of Justice with Ms Vestager saying the lower court’s ruling contained errors of law. On Thursday, the advocate general agreed the General Court had erred when it ruled that the Commission had not shown to the requisite legal standard that the intellectual property licences held by the two incorporated companies and related profits, generated by the sales of Apple products outside the US, had to be attributed for tax purposes to the Irish branches. The advocate general was of the view that the General Court also failed to assess correctly the substance and consequences of certain methodological errors that, according to the Commission decision, “vitiated the tax rulings”. It is the non-binding opinion of Mr Pitruzzella that it is necessary for the General Court to carry out a new assessment. The decision of the CJEU on the matter is expected next year and will have significant implications for how member states grant tax breaks to major firms. Apple has argued it has been paying tax on the profits in question in the US, while Ireland has seen it necessary to defend its reputation on taxation issues to protect foreign direct investment. Last weekend, Finance Minister Michael McGrath had said the advocate general’s opinion would be “significant” but added it is not the final step in the process. Mr McGrath said: “We are confident in our position in respect of the Apple case. “We take encouragement from the findings they have made so far, but it is a significant day.” He added: “There was no sweetheart deal. “This was the application of Ireland’s statutory corporation tax code.” In the interim, the 13.1 billion euro has been held in an escrow fund pending the outcome of the case. The money, with interest, is due to be entered into the Irish exchequer if the commission wins the case. However, other member states may make claims that they are owed some of the money. If the commission loses the appeal, the large sum will be returned to Apple. Read More Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’ Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute Guidance urges parents not to buy smartphones for primary school children William ‘blown away’ by futuristic technology from Singapore start-ups Return of original Fortnite map causes record traffic on Virgin Media O2 network NatWest creates new AI-powered chatbot capable of ‘human-like’ conversations
2023-11-09 18:22
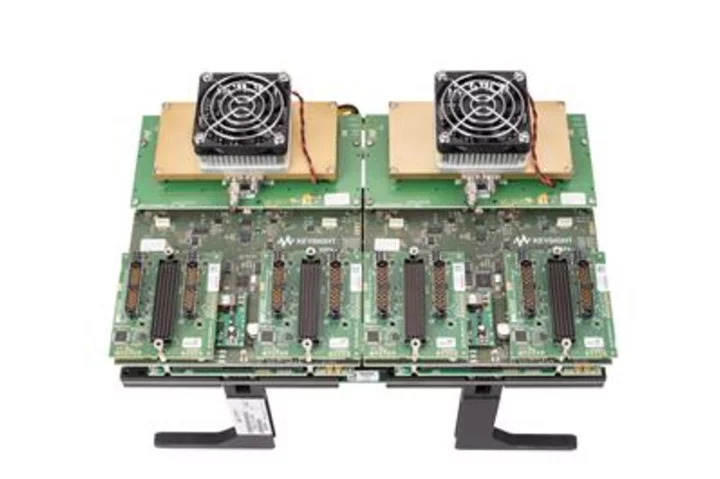

Keysight Enables Advanced Pre-Tapeout Silicon Prototyping Using Digital Twin Signaling
SANTA ROSA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 23:18

Origin’s Top Investor to Reject Brookfield’s A$19 Billion Bid
Origin Energy Ltd.’s top investor AustralianSuper said it will reject an improved A$19.4 billion ($12.5 billion) takeover offer
2023-11-02 10:19

Meta is secretly building an AI chatbot with the personality of Abraham Lincoln
Facebook owner Meta is working on a ChatGPT-style chatbot with the personality of Abraham Lincoln, according to reports. The new AI bot is part of a series of prototypes under development at the tech giant, the Financial Times reported on Tuesday, with each one featuring a different human-like persona. The new chatbots form part of the company’s attempts to boost its engagement with its social media platforms, according to the report, citing people with knowledge of the plans. Beyond the chatbot based on the former US president, the California-based social media giant is also exploring a chatbot that advises on travel options in the style of a surfer. The purpose of these chatbots, which Meta employees have dubbed ‘personas’, will be to provide a new search function as well as offer recommendations. The report comes as Meta executives are focusing on boosting retention on its new text-based app Threads, after the app lost more than half of its users in the weeks following its launch on 5 July. The Facebook parent reported a strong rise in advertising revenue in its earnings last week, forecasting third-quarter revenue above market expectations. The company has been climbing back from a bruising 2022, buoyed by hype around emerging AI technology and an austerity drive in which it has shed around 21,000 employees since last fall. Meta launched a new version of its open-source artificial intelligence model in July called Llama 2 for commercial use, which will be distributed by Microsoft through its Azure cloud service and will run on the Windows operating system. Bloomberg News reported in July that Apple is working on AI offerings similar to OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard, adding that it has built its own framework, known as ‘Ajax’, to create large language models and is also testing a chatbot that some engineers call ‘Apple GPT’. Reports of a ‘Chat with an AI’ feature first emerged in June, when app researcher Alessandro Paluzzi shared screenshots of a new tool that offers users the option to ask questions and seek advice from up to 30 different AI chatbots on Instagram. Meta reportedly plans to launch the new AI chatbots in September. The Independent has reached out to Instagram for comment, though the company typically does not speak about unreleased products. Additional reporting from agencies Read More ‘I’ve got Elon Musk dying’: Voice clone baffles tech billionaire
2023-08-01 21:28
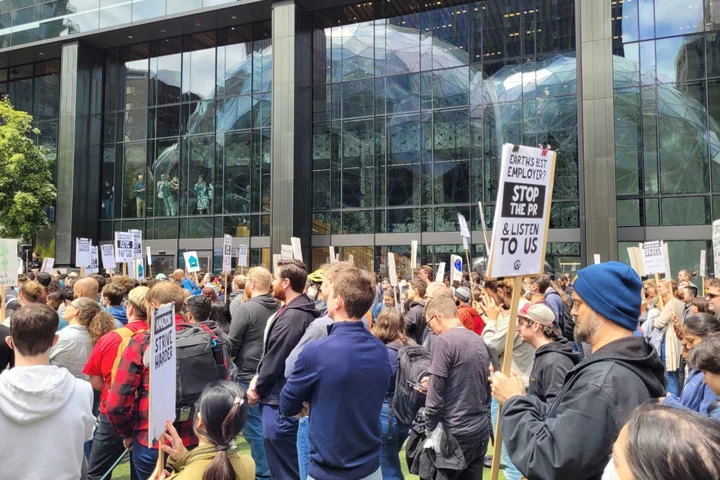

Amazon Workers Walk Out to Protest Climate, Office Return Policy
Amazon.com Inc. employees walked off the job Wednesday to protest the company’s return-to-work policies, impact on the climate
2023-06-01 03:51
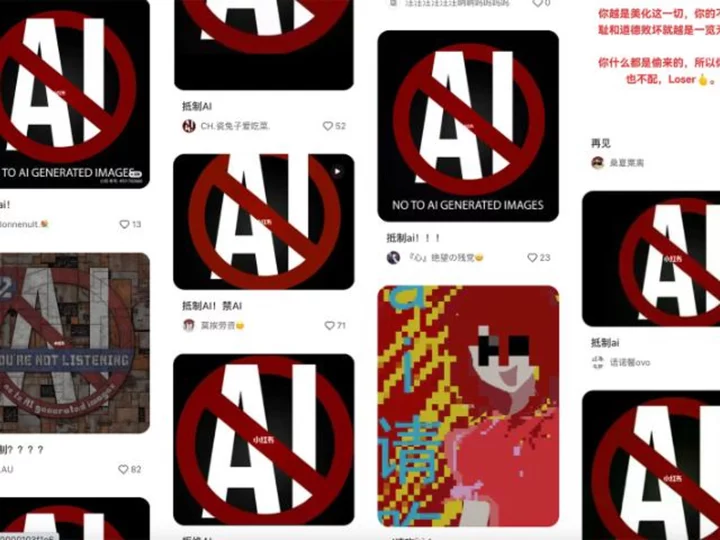
Chinese artists boycott big social media platform over AI-generated images
Artists across China are boycotting one of the country's biggest social media platforms over complaints about its AI image generation tool.
2023-09-29 06:24
You Might Like...

CapVest to Buy UK Software Provider Kerridge in $1 Billion Deal

Kick trolling Pokimane in TikTok promotional video leaves Internet in splits: 'Honestly a banger ad'

Options and Mercurius Solutions Empower Trading Firms with Automated Trading as a Service

Dell shares hit record high after report, forecasts impress with AI in mix

U.S. students trailing pre-pandemic learning levels, new study shows

Lumos Awarded GREAT Grant Funding to Expand Fiber Optic Network in Wayne County Ahead of Service Launch
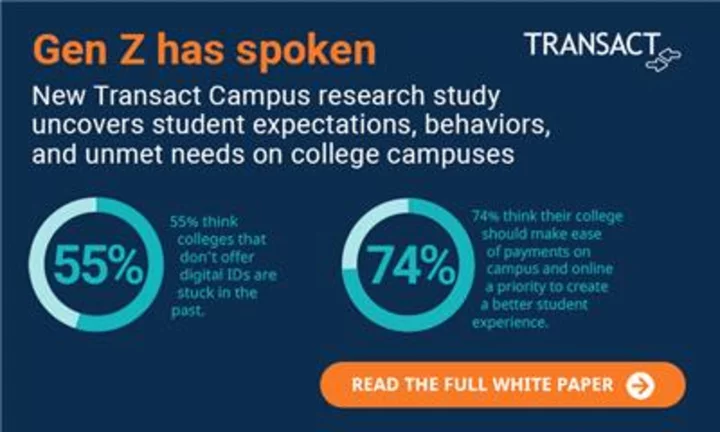
CORRECTING and REPLACING Transact Campus Announces National Study of Current College and High School Students Examining Financial Habits and Technology Use

China Chip Firms Surge on Report of Technology Breakthrough
