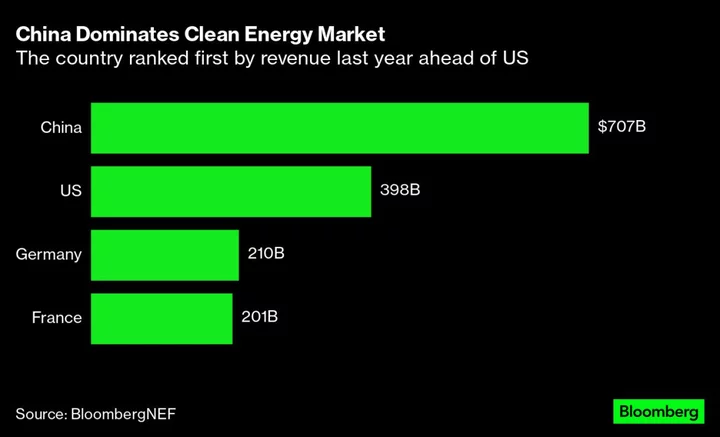
China Leaves Everyone Behind in Race for Renewables Income
The biggest US companies are badly trailing their Chinese counterparts when it comes to generating income from solar,
2023-09-04 07:59

Money and Politics Put World’s Biggest Climate Deal at Risk
When Indonesia agreed last year to clean up its energy system with an estimated $20 billion of help
2023-09-04 07:55

Dell Precision 5680 Review
While the Lenovo ThinkPad P16 Gen 1 is our most recent Editors' Choice honoree among
2023-09-04 07:28

Alipay+ Payment Tech to Debut in the Middle East Market With Its Full Suite of E-Wallet Solutions at Seamless Saudi Arabia 2023
RIYADH, Saudi Arabia--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 3, 2023--
2023-09-04 07:27

Asus TUF Gaming Z790-Plus Wi-Fi Review
The Asus TUF Gaming Z790-Plus Wi-Fi ($229.99) is an affordable Intel Z790 motherboard that promises
2023-09-04 07:24
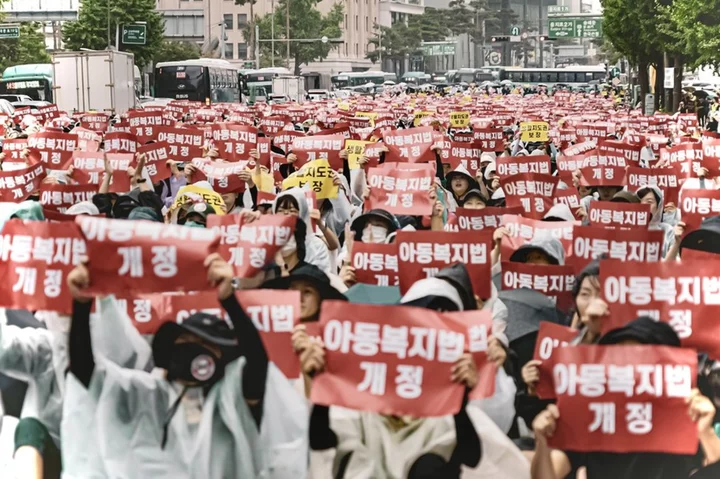

Teacher suicide exposes parent bullying in S Korea
The tragedy has unleashed a wave of anger from primary school teachers across the country.
2023-09-04 07:17
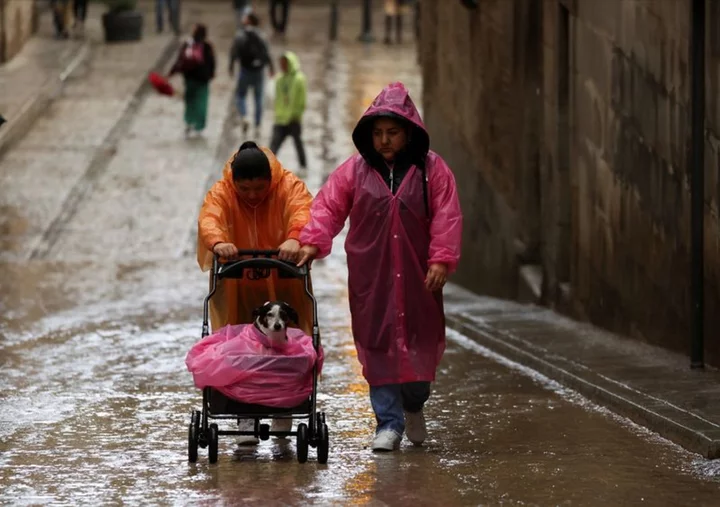

Madrid residents told to stay at home as torrential rain sweeps across Spain
MADRID Madrid's mayor on Sunday advised all residents to stay at home as the capital braced itself for
2023-09-04 01:28
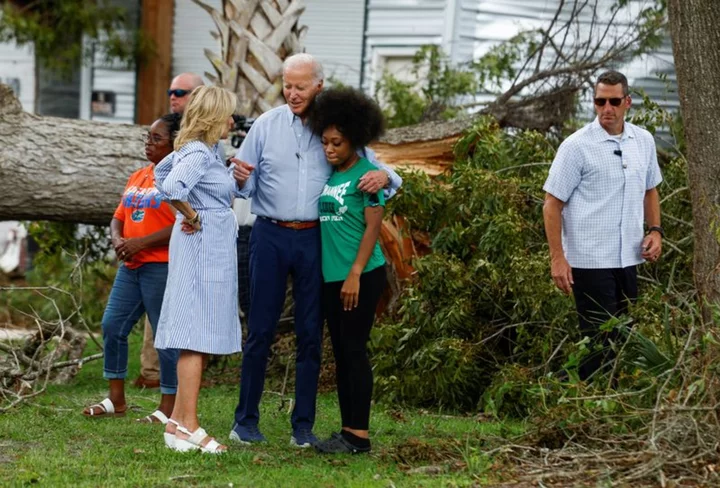

Biden surveys storm damage in Florida, without DeSantis
By Jeff Mason LIVE OAK, Florida (Reuters) -President Joe Biden traveled to Florida on Saturday to survey the destruction from
2023-09-03 21:46

The terrifying time our early ancestors almost became extinct
New research has shown that our early ancestors almost went extinct some 900,000 years ago. Using a new method called FitCoal (fast infinitesimal time coalescent process), researchers analysed the likelihood of present-day genome sequences to project current human genomic variation backwards in time. They applied the technique to the genomes of 3,154 people from 10 African and 40 non-African populations, and found a massive crash in genetic diversity during the transition between the early and middle Pleistocene. “Results showed that human ancestors went through a severe population bottleneck with about 1,280 breeding individuals between around 930,000 and 813,000 years ago,” the study authors wrote in the journal Science. “The bottleneck lasted for about 117,000 years and brought human ancestors close to extinction,” they say. Wiping out roughly 98.7 percent of the ancestral human population, “the bottleneck could also have increased the inbreeding level of our ancestors, thus contributing to the 65.85 percent loss in present-day human genetic diversity,” explained the researchers. This probably happened because of changes in the global climate as short-term glaciations became longer-lasting, triggering a drop in ocean temperatures, prolonged drought, and the loss of large numbers of species that humans might have relied on for food. Then, around 813,000 years ago, populations finally recovered, with a 20-fold increase in numbers because of fire combined with the return of warmer temperatures, researchers reckon. What a near miss, eh? Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-03 19:22
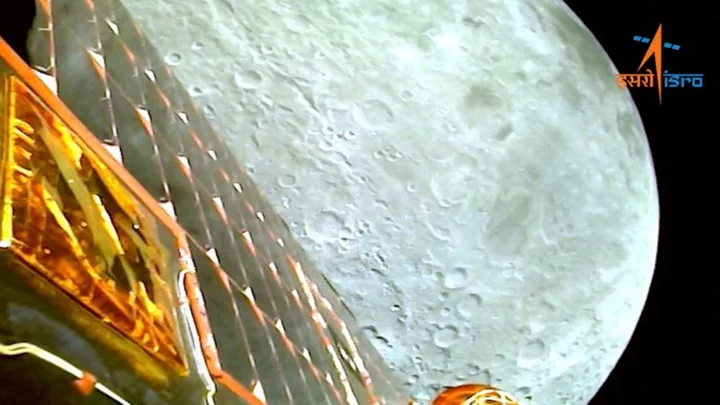

Mission accomplished, India puts moon rover to 'sleep'
By Arpan Chaturvedi NEW DELHI India switched off its moon rover, the first craft to reach the lunar
2023-09-03 16:45

'19 Kids and Counting' alum Amy King slammed for making son Daxton, 3, work as child model
'Amy's profile includes 'children's advocate.' That obviously doesn't include protecting children from child labor and exploitation,' a netizen said
2023-09-03 14:52
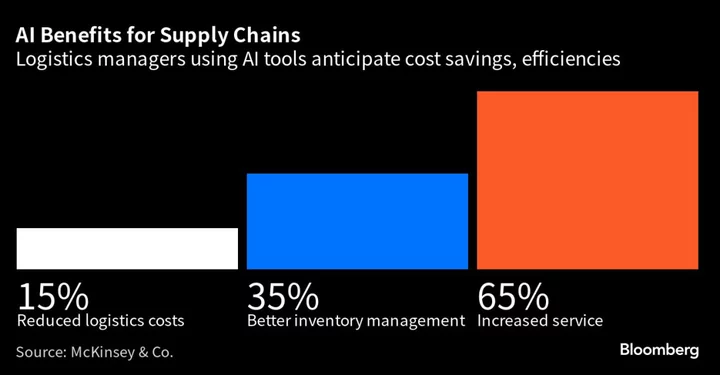
AI Fused With Trade Data May Finally Smooth Clunky Supply Chains
The dawn of artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT may revolutionize the way both the public and private sector
2023-09-03 14:47
