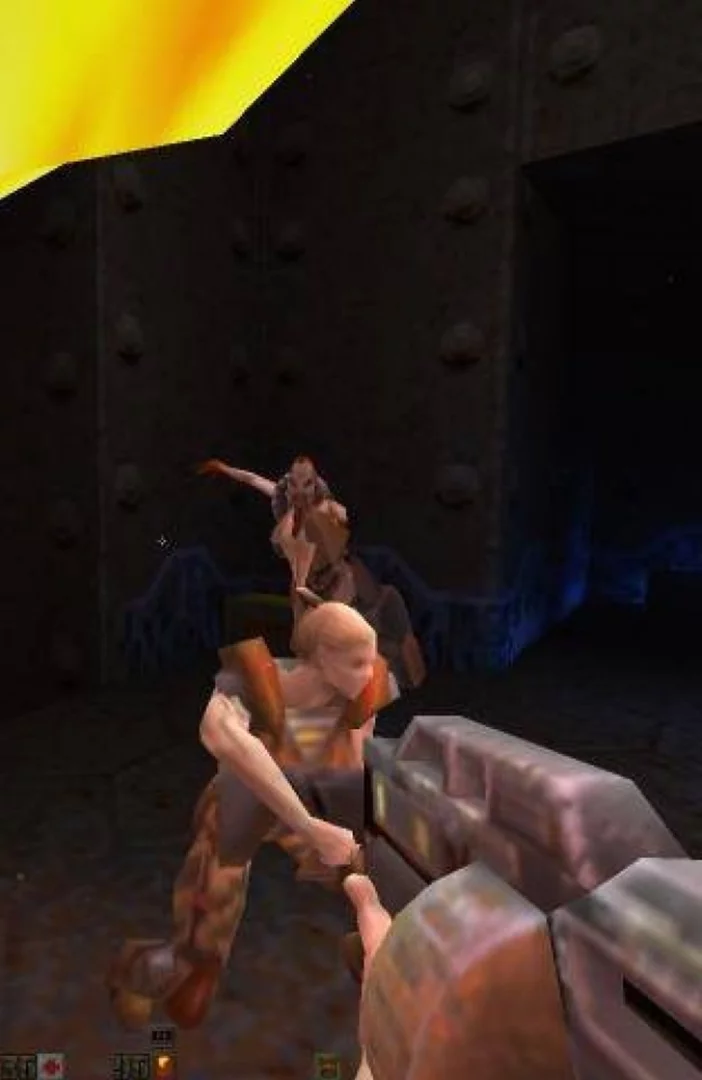

‘Quake 2’ remaster revealed at QuakeCon 2023!
A ‘Quake 2’ remaster featuring a raft of crowd-pleasing features has been revealed.
2023-08-11 20:28

FIS Named Top 200 Fintech Company for Digital Banking Solutions in Inaugural CNBC Ranking
JACKSONVILLE, Fla.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 11, 2023--
2023-08-11 20:22

Ant Group Expands Cross-Border Digital Payment Services in Asian Games Support Initiative
HANGZHOU, China--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 11, 2023--
2023-08-11 19:47
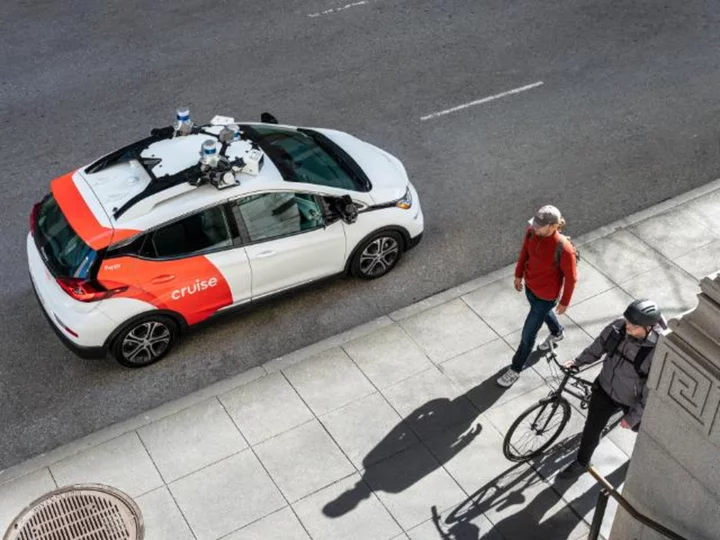

Regulators give green light to driverless taxis in San Francisco
California regulators gave approval Thursday to two rival robotaxi companies, Cruise and Waymo, to operate their driverless cars 24/7 across all of San Francisco and charge passengers for their services.
2023-08-11 18:54
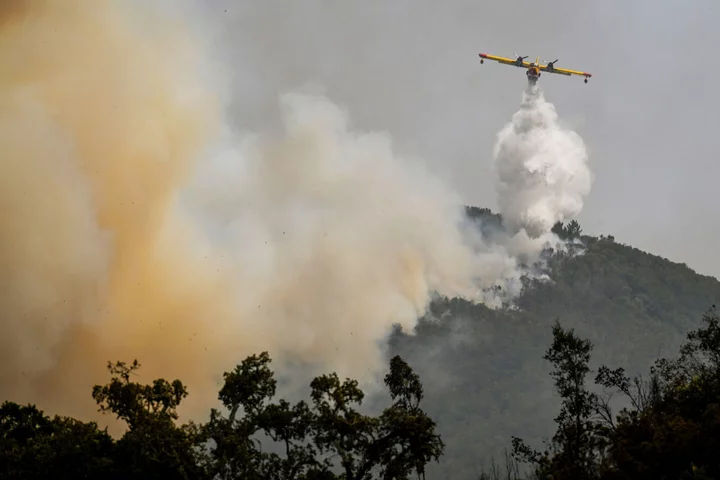

Portuguese Firefighters on Alert After Containing Border Blaze
Portuguese firefighters are on high alert after containing a blaze that threatened to cross the border into neighboring
2023-08-11 18:29
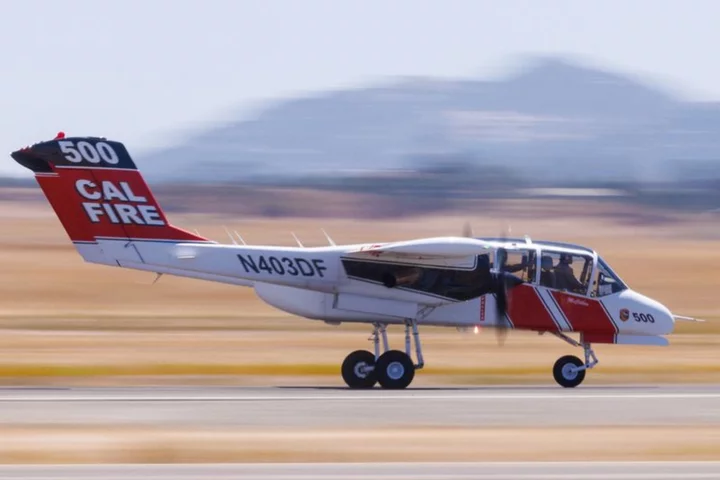

California turns to AI to help spot wildfires
By Daniel Trotta EL CAJON, California California firefighters are using artificial intelligence to help spot wildfires, feeding video
2023-08-11 18:23
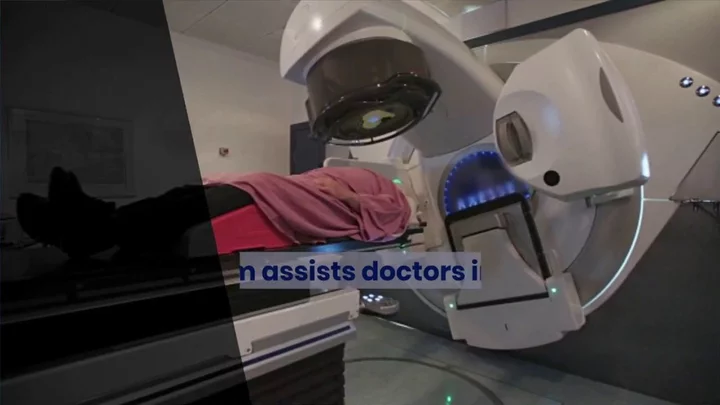

AI could soon be used to treat cancer in the NHS
Artificial intelligence could soon be used to perform radiotherapy to treat certain cancers for the first time. Draft guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice) has given approval to nine AI technologies for performing external beam radiotherapy in lung, prostate and colorectal cancers, which could save radiographers hundreds of thousands of hours and help relieve pressure on radiotherapy departments. Currently therapeutic radiographers outline healthy organs on digital images of a CT or MRI scan by hand so that the radiotherapy does not damage healthy cells by minimising the dose to normal tissue. Nice found that using AI to create the contours could free up between three and 80 minutes of radiographers’ time for each treatment plan, and that AI-generated contours were of a similar quality to manually drawn ones. Nice said that the contours would still be reviewed by a trained healthcare professional. It comes after a study found AI was safe to use in breast cancer screenings with evidence growing that it can be more effective in detecting cancers. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Meanwhile, Nice said it was also examining the evidence for using AI in stroke and chest scans. Dr Sarah Byron, the programme director for health technologies at Nice, said using AI could help reduce waiting lists. She added: “NHS colleagues working on the frontline in radiotherapy departments are under severe pressure with thousands of people waiting for scans. “The role imaging plays in radiotherapy treatment planning is quite pivotal, so recommending the use of AI technologies to help support treatment planning alongside clinical oversight by a trained healthcare professional could save both time and money. “We will continue to focus on what matters most and the recommendations made by our independent committee can help to bring waiting lists down for those needing radiotherapy treatment.” The health secretary, Steve Barclay, welcomed the announcement. He said: “It’s hugely encouraging to see the first positive recommendation for AI technologies from a Nice committee, as I’ve been clear the NHS must embrace innovation to keep fit for the future. “These tools have the potential to improve efficiency and save clinicians thousands of hours of time that can be spent on patient care. Smart use of tech is a key part of our NHS long-term workforce plan, and we’re establishing an expert group to work through what skills and training NHS staff may need to make best use of AI.” Charlotte Beardmore, the executive director of professional policy at the Society of Radiographers, welcomed the draft guidance but said it was not a replacement for staff and caution was needed. “It is critical there is evidence to underpin the safe application of AI in this clinical setting,” she said. Using AI would still require input by a therapeutic radiographer or another member of the oncology multi-professional team, she added. “Investment in the growth of the radiography workforce remains critical.” Science is pretty amazing. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-11 18:21
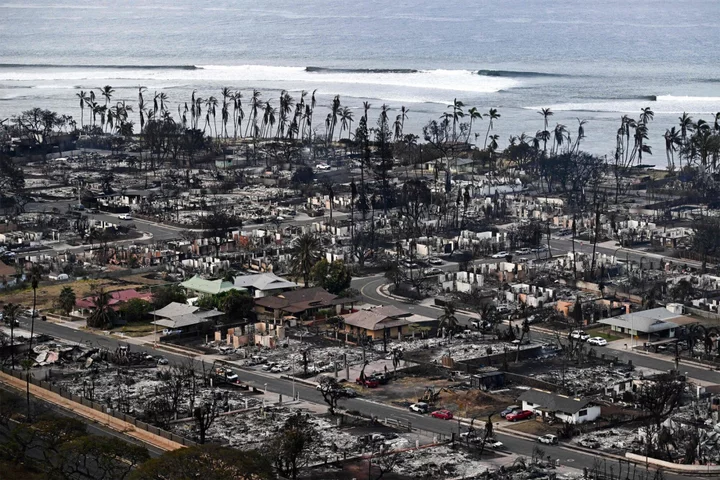

How the Maui Wildfires Became So Destructive, So Fast
At least 55 people are dead and hundreds of homes incinerated after tail winds from a hurricane stoked
2023-08-11 18:21
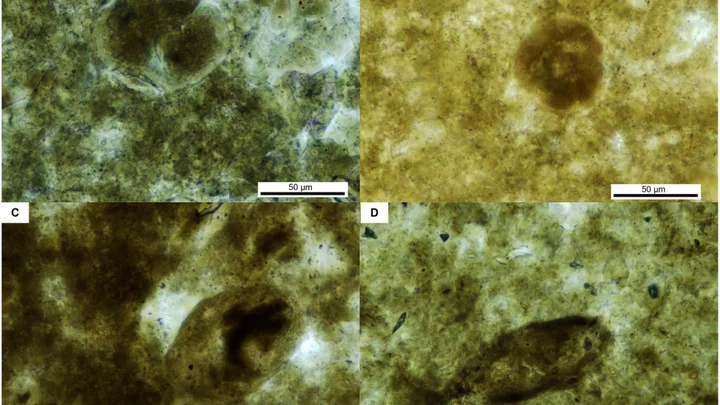
Scientists are cutting open parasitic eggs from 200 million years ago
A 200 million-year-old parasite has been discovered in fossilised poo, in the latest not-at-all-scary instance of scientists unearthing a species which blighted the Earth in ancient times. Researchers found that the earliest predators on the planet were infested with roundworm, also known as nematodes, among multiple other parasites. The fossilised poo, which is known to palaeontologists as coprolite, is thought to belong to a type of semi-aquatic phytosaur, which was a crocodile-like predator. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It comes weeks after another team revived a prehistoric worm – the catchily named Panagrolaimus kolymaensis – which was found dormant in the Siberian permafrost in a state of “cryptobiosis”. The latest study saw researchers from Mahasarakham University, Thailand, analyse a three-inch-long portion of ancient poo and discover five types of parasitic remnants. The group sliced open the parasitic egg fossils with a diamond saw using a “standard thin section method,” their report said. The ultra-thin slices allowed the palaeontologists to look at cross-sections of the ancient infectious microbes under a microscope. One was identified as a nematode worm egg, while the others are thought to be either more eggs, protozoan cysts or spores from moss and ferns. While modern parasites are often an important part of ecosystems, it is usually more difficult to work out what their ancient equivalents did, because there are so few examples in the fossil record. The creatures often inhabited the soft tissues of their hosts, but are rarely preserved as fossils, making the latest discovery all-the-more significant. This fossilised late Triassic-era coprolite (the poo), was shielded from the elements in the Huai Hin Lat geological formation in Thailand, which is over 200 million years old. It was found by local villagers, according to the study's lead author, paleontologist Thanit Nonsrirach. “The peculiar appearance of these findings intrigued the villagers, who considered them potentially auspicious and capable of bestowing good luck if repurposed as talismans,” Nonsrirach told news outlet Inverse. “In 2010, our team received word of this discovery and embarked on a field expedition, guiding the villagers to the actual fossil site.” The discovery is the first record of parasites in a terrestrial vertebrate host from the late Triassic period in Asia, and provides a rare look at the life of an ancient creature that was infected by multiple species. This discovery also adds to the few known examples of nematode eggs preserved within the coprolites of Mesozoic animals. “Parasites of several species, including Ascaridida (roundworm) eggs were found in a coprolite, probably produced by a crocodile-like reptile and possibly a phytosaur,” said Nonsrirach, who works at Mahasarakham University's Palaeontological Research and Education Center. “This is therefore the first discovery of Ascaridida eggs and evidence of multi-infection in a host assignable to the Crurotarsi from the Late Triassic of Asia. “Coprolite is a significant palaeontological treasure trove, containing several undiscovered fossils and expanding our understanding of ancient ecosystems and food chains. “These findings are therefore a significant contribution to scientific understanding of the distribution and ecology of parasites of the distant past.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-11 18:21
Alphabet’s $118 Billion Cash Pile Poses a New Problem
Alphabet Inc. is facing a new and, by most accounts, welcome problem — how to spend its rapidly
2023-08-11 17:53
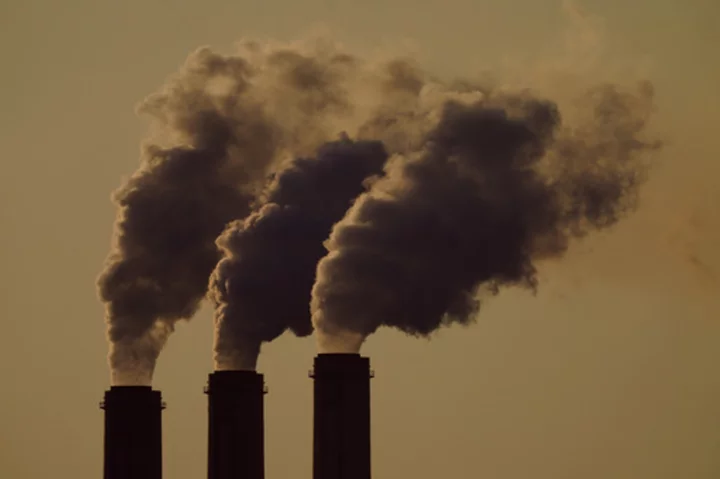

Energy Department announces largest-ever investment in 'carbon removal'
The Department of Energy announced Friday it is awarding up to $1.2 billion to two projects that promise to remove carbon dioxide from the air in what officials said was the largest investment in “engineered carbon removal” in history
2023-08-11 17:16

ChatGPT fever spreads to US workplace, sounding alarm for some
By Richa Naidu, Martin Coulter and Jason Lange LONDON/WASHINGTON Many workers across the U.S. are turning to ChatGPT
2023-08-11 16:55
