
The surprising reason it is bad to suck your stomach in
Self-conscious people may suck in their stomachs - but doing so can be unhealthy. Adam Taylor, Professor and Director of the Clinical Anatomy Learning Centre, Lancaster University, has explained that the habit can create abdominal imbalance and all sorts of problems. In an article, he explained: "This can lead to a condition called 'hourglass syndrome; – a detrimental change in the structure of the abdominal wall, which may cause a visible crease to form in the mid-abdomen. Not only that, but this change can also have a knock-on effect on the internal organs and other parts of the body if left untreated." He added: "When we suck our stomach in it causes our rectus abdominis (commonly referred to as our "six-pack" muscles) to contract. But since we tend to store more fat tissue in our lower abdomen, the muscles at the top of the stomach tend to be more active. This creates a fold or crease in the abdomen over a long period, with the belly button being pulled upwards. "Sucking the stomach in places greater pressure on the lower back and neck. This is because they now have to compensate for changes in core stability." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter He also said it may lead to changes in breathing capacity, though said more research needs to be done, and said sucking in the abdomen also puts strain on the pelvic floor which could cause incontinence. Fortunately, hourglass syndrome is reversible through exercises that strengthen core muscles like planks or bridges, he explained. And he also said the condition develops over weeks of consistently sucking in the stomach. "So occasionally sucking the stomach muscles in is not likely to cause problems," he said. Who knew it could have so many bad effects? Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-05 18:24

A crispy roast potatoes recipe could be the key to life on Earth
A chemical reaction that gives food flavour could have helped evolution, one study suggests. According to New Scientist, the Maillard reaction is when the temperature between sugars and amino acids rises above approximately 140°C. It often occurs in food such as toasted bread, meats and roasted vegetables. Caroline Peacock at the University of Leeds wanted to explore whether it could happen at lower temperatures. To do this, scientists added iron or manganese minerals to a solution made up of sugar glucose and the amino acid glycine. When the substance was incubated at 10°C, the process was sped up by around 100 times. The temperature is said to be similar to the seabed at the edges of continents. Peacock and the team discovered that the Maillard reaction also occurs on the ocean floor, where iron and manganese minerals are often found. If this is the case, it could cause the carbon in sugars and amino acids to be stored in "large, complex polymers that microbes find harder to ingest," Peacock said, as per the publication. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "If you can get your carbon through the 1-metre danger zone [at the top of the sea floor], where carbon generally is attacked and degraded and turned back into carbon dioxide by microbes, that will lock it away from the atmosphere," she explained. The team estimated that the minerals could lock away roughly 4 million tonnes of carbon every year. If this process didn't exist, the atmosphere could have warmed by a further 5°C over the past 400 million years, the study suggested. "This process has such a profound impact on atmospheric oxygen," she says. "Because complex life forms require higher levels of oxygen, as they’re more energetically demanding, we think it’s reasonable to surmise this process had a hand in creating conditions required for complex life." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-05 00:28
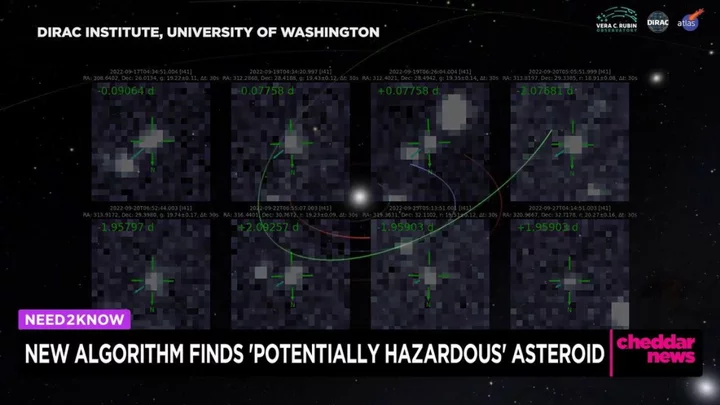
AI spots dangerous asteroid heading towards Earth that scientists missed
So far this year, we’ve mostly been seeing artificial intelligence pop up on our timelines as a tool for creating trivial things like odd news songs from classic bands or bizarrely sexualised images of classic artworks However, it looks like AI had a vital practical implementation recently after spotting a dangerous asteroid heading close to Earth that was originally missed by scientists. A 600-foot asteroid named 2022 GN1 was found thanks to a new algorithm, and it was revealed that our planet had a close shave with the object last year. As it’s now been revealed, 2022 GN1 flew a relatively close 4.5 million miles from Earth in September 2022. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It sounds like a huge distance, but it falls within the definition of a potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA). At the time, it was completely missed due to it being obscured by starlight from objects in the Milky Way. The algorithm, named HelioLinc3D, spotted the object after observing data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) telescope. The team leader behind the algorithm, Mario Jurić, released a statement saying: “This is just a small taste of what to expect with the Rubin Observatory in less than two years, when [the algorithm] HelioLinc3D will be discovering an object like this every night. “But more broadly, it’s a preview of the coming era of data-intensive astronomy. From HelioLinc3D to AI-assisted codes, the next decade of discovery will be a story of advancement in algorithms as much as in new, large, telescopes.” Meanwhile, scientists think they have come up with a new approach to mitigating global warming: put up a giant “umbrella” in space to protect the Earth from excess sunlight. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-04 23:22
What are semiconductors and how are they used?
Governments around the world are scrambling to boost semiconductor production.
2023-08-04 00:51

Man with 'projected age of 200' reveals he would drink alcohol for breakfast
A man who has spent 'millions' trying to biologically lower his age in order to live longer reveals he drinks alcohol every morning for breakfast. Bryan Johnson, 45, has the 'biological age' of an 18-year-old, and is projected to live to be 200. He made the shocking confession on Steven Bartlett's Diary Of A CEO podcast, where he told of how his final meal of the day is done by 11am. Johnson says he loves wine, and would have 3oz with his breakfast before it became too expensive. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter
2023-08-03 21:28

Star Wars Jedi: Survivor confirmed for PS4 and Xbox One
PlayStation 4 and Xbox One owners will be able to play 'Star Wars Jedi: Survivor'.
2023-08-03 20:29

A hidden iPhone setting has been discovered that drains your battery
There's nothing worse than the dreaded 10 per cent battery alert kicking in while out and about and no charger at hand. Well now, a hidden iPhone setting that could be draining your battery has been revealed – and most people don't even know it exists. The 'Wi-Fi Assist' setting is a program to monitor your phone's connection. When there's no Wi-Fi, your phone automatically switches to 4G/5G. All the while, it will be working overtime in the background to maintain a connection with the Wi-Fi, despite it being on one bar. "For example, if you're using Safari with a poor Wi-Fi connection and a webpage doesn't load, Wi-Fi Assist will activate and automatically switch to cellular so that the webpage continues to load," the Apple website explains. While this is a great feature for smooth internet browsing, it could very well be draining out the battery life and mobile data. To turn this off, all you need to do is head to Settings > Mobile Data > Wi-Fi Assist and simply switch it off. To really max iPhone battery life, you can also use Low Power Mode, turn down the brightness and limit Location Services, which can be found in Settings > Privacy. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter It comes after the news that the iPhone 15 Pro battery life could very set new records. According to reports, there are rumours of two major updates that involve prolonging that much-needed battery. Laptop Mag suggested that Apple users could expect a larger battery, without the need to bulk up the device. In June, Twitter leaker AppleTrack claimed to have information on the capacity of the iPhone 15. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-03 19:16

Abkhazia media guide
An overview of the media in Abkhazia, including links to broadcasters and a newspaper.
2023-08-02 23:53

Chechnya media guide
An overview of the media in Chechnya, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-08-02 22:52

Mysterious galaxy resembling a giant ‘question mark’ discovered by Webb telescope
Nasa’s James Webb telescope’s most recent image of a distant star system has thrown up more questions than answers – literally. The image is of the star system Herbig Haro 46/47, and includes a cosmic object that is shaped like an actual question mark. Scientists think the entity could be a distant galaxy, or two galaxies interacting with one another. One larger galaxy could be distorting the cosmic cloud and gas of the other, for example, forming a shape similar to a question mark. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The red colour of the unusually shaped object in the image suggests it is more distant than the other stars in the picture. “This may be the first time we’ve seen this particular object. Additional follow-up would be required to figure out what it is with any certainty. Webb is showing us many new, distant galaxies – so there’s a lot of new science to be done,” the US’s Space Telescope Science Institute, which manages Webb’s science operations, told Space.com. The star system in the foreground, dubbed Herbig-Haro 46/47, was captured by the Webb telescope’s powerful infrared cameras and consists of two young stars pulled to each other by gravity as they spin. An image reveals the stars as buried deeply, appearing as an orange-white splotch, surrounded by a disk of gas and dust that continued to add to their mass. JWST Finds a Cosmic Question Mark and a Starry Fountain www.youtube.com “Herbig-Haro 46/47 is an important object to study because it is relatively young – only a few thousand years old,” Nasa said in a statement. The pair of actively forming stars have two-sided orange lobes which were created by earlier ejections from these stars. Scientists said the two young stars could give more insight into how stars gather mass over time, given the fact that the process usually takes millions of years. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-02 22:25

Amazon expands its virtual health clinic nationwide
Amazon's virtual clinic is now available in all 50 states and Washington, D.C., the company announced on Tuesday.
2023-08-02 01:53
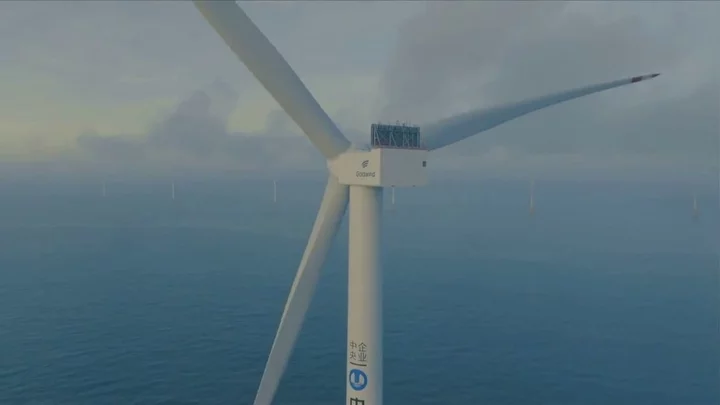

Mega wind turbine with blades twice the size of a football pitch switched on for first time
In the week that it was announced that Rishi Sunak will be granting new oil and gas licences in the North Sea, new commitments to renewable energy are being made elsewhere in the world. The China Three Gorges Corporation just turned on a mega wind turbine with blades twice the size of a football pitch in the Taiwan Strait. The state-owned energy firm has activated the biggest wind turbine on the planet offshore in a move which could produce up to 16 megawatts of energy, and it’s now been connected and hooked up to the energy grid. The MySE 16-260 turbine stands at an incredible 500ft (152m) tall and it could power thousands of homes every year. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter In fact, it’s thought that around 36,000 homes will be served by electricity from the turbine. It’s not surprising given that each blade weighs around 54 tons and covers nearly 540,000 square feet when they rotate. Mingyang Smart Energy is the company that designed the turbine, and they released a message on LinkedIn making clear just how much wind the structure could deal with – stating that it can withstand “extreme wind speeds of 79.8 [meters per second]”. It’s a staggering feat of engineering and it’s thought that the turbine could save around 54,000 tons of carbon dioxide compared to coal power plants. More structures like one are being planned, too. Executive Director Lei Lei Zengjuan told the media: “In the next step, the 16 [megawatt] unit will be applied in batches in the second phase of the Zhangpu Liuao Offshore Wind Farm Project constructed by China Three Gorges Corporation.” It comes a few weeks after work was stopped on one of the UK’s largest offshore wind farms after its developer said that the cost of the project had soared by so much that it no longer made financial sense to push forward. Swedish energy giant Vattenfall, one of Europe’s biggest wind producers, shut down work on the development of the Norfolk Boreas site. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-02 00:19
