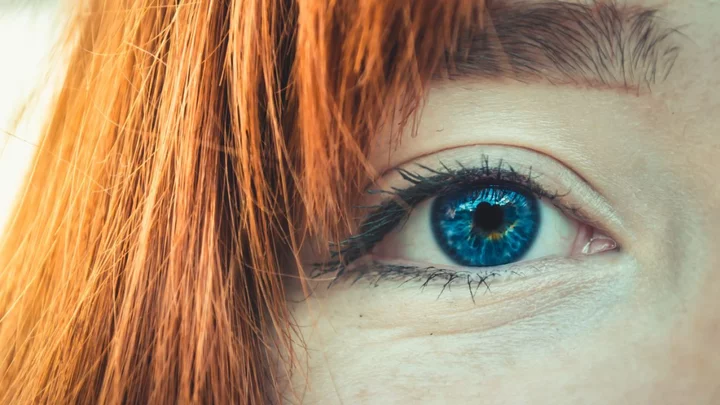

If you have blue eyes you may have a higher risk of alcoholism
Research from the University of Vermont suggests that there may be a link between those who have blue eyes and alcoholism. The study, conducted in 2015, was led by Dr Arvis Sulovari and assistant professor Dawei Li, and was the first to draw a direct connection between the colour of someone's eyes and their risk of developing alcoholism. Professor Li generated a database comprising of more than 10,000 individuals who have received a diagnosis for at least one psychiatric illness, including conditions such as addiction. Speaking of the conditions, Li - an expert in microbiology and molecular genetics - explained that they were "complex disorders" and that "many genes" and "environmental triggers" were involved. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The researchers used the database to identify those with a dependency on alcohol and discovered an interesting correlation. They found that those with lighter colour eyes - especially blue - had greater rates of alcohol addiction. The researchers even checked three times to be sure of their findings. "This suggests an intriguing possibility that eye colour can be useful in the clinic for alcohol dependence diagnosis," said Dr Sulovari. The study also found that the genetic components that determine eye colour and those associated with excessive alcohol use share the same chromosome. However, more tests and studies are going to have to take place in order for us to gain a deeper understanding of the potential link between eye colour and higher rates of alcohol dependency. Researchers are still unsure as to why there is such a link. With professor Li saying that much of genetics is "still unknown". Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-20 23:24

NFL Rumors: Dalvin Cook wants to team up with DeAndre Hopkins
Former Minnesota Vikings running back Dalvin Cook said he would love to play on the same team as free-agent wide receiver DeAndre Hopkins.All 32 NFL teams are over a month away until they host training camp, where they evaluate the talent on their rosters and bring the total number of players to...
2023-06-20 21:51

United States media guide
An overview of the media in the United States, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-06-20 17:15

Morocco media guide
An overview of the media in Morocco, including links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-06-20 16:19

Scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it
If you found water that was more than two billion years old, would your first instinct be to drink it? One scientist did exactly that after finding the oldest water ever discovered on the planet. A team from the University of Toronto, led by Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, came across an incredible find while studying a Canadian mine in 2016. Tests showed that the water source they unearthed was between 1.5 billion and 2.64 billion years old. Given that it was completely isolated, it marked the oldest ever found on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Remarkably, the tests also uncovered that there was once life present in the water. Speaking to BBC News, professor Sherwood Lollar said: “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Discussing the presence of life in the water, Sherwood Lollar added: “By looking at the sulphate in the water, we were able to see a fingerprint that’s indicative of the presence of life. And we were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology - and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” The professor also revealed that she tried the water for herself – but how did it taste? “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” Sherwood Lollar told CNN. She revealed that the water was "very salty and bitter" and "much saltier than seawater." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-20 14:58

How to Sell Your Android Phone Safely and Make the Most Money
So you're ready to move on from your current Android phone. Whether you're upgrading to
2023-06-20 00:18

Hackers threaten to leak stolen Reddit data if company doesn't pay $4.5 million and change controversial pricing policy
Reddit's month may be going from bad to worse.
2023-06-19 23:47

A scientists found the oldest water on the planet and drank it
If you found water that was more than two billion years old, would your first instinct be to drink it? One scientist did exactly that after finding the oldest water ever discovered on the planet. A team from the University of Toronto, led by Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, came across an incredible find while studying a Canadian mine in 2016. Tests showed that the water source they unearthed was between 1.5 billion and 2.64 billion years old. Given that it was completely isolated, it marked the oldest ever found on Earth. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Remarkably, the tests also uncovered that there was once life present in the water. Speaking to BBC News, professor Sherwood Lollar said: “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Discussing the presence of life in the water, Sherwood Lollar added: “By looking at the sulphate in the water, we were able to see a fingerprint that’s indicative of the presence of life. And we were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology - and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” The professor also revealed that she tried the water for herself – but how did it taste? “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” Sherwood Lollar told CNN. She revealed that the water was "very salty and bitter" and "much saltier than seawater." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 22:55
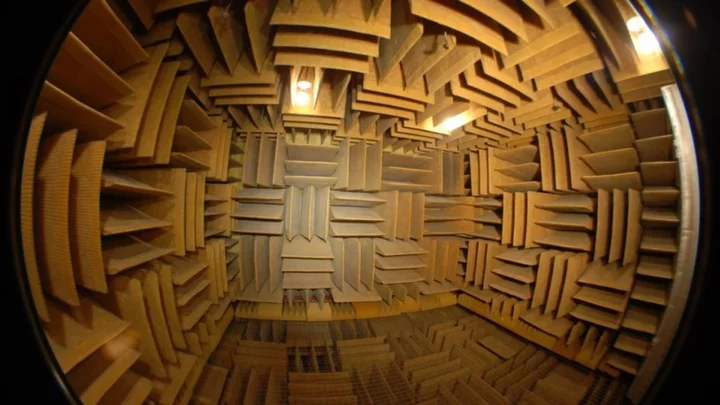

No one has been able to handle more than 45 minutes alone in this room
We all crave a bit of peace and quiet every now and then; just some time to be alone with our thoughts. But silence isn’t as golden as we’ve been led to believe, according to the people who’ve been to the quietest place on Earth. You might expect this to be in a remote part of some great desert whereas, in actual fact, it’s located in a research lab in Minnesota. Inside the anechoic chamber at Orfield Laboratories, it is so silent you can hear your own blood flowing and bones moving. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Made of 3.3ft-thick fibreglass acoustic wedges and double walls of insulated steel and thick concrete, the room absorbs 99.99 per cent of sound. The conditions within its Fort Knox-style walls are so intense that the longest amount of time anyone’s been able to endure in there is 45 minutes. “We challenge people to sit in the chamber in the dark,” the lab’s founder Steven Orfield told Hearing Aid Know. “When it’s quiet, ears will adapt. The quieter the room, the more things you hear. You’ll hear your heart beating, sometimes you can hear your lungs, hear your stomach gurgling loudly. “In the anechoic chamber, you become the sound." What he means by this is that, with the absence of external noise, your ears are forced to adapt to unimaginable silence and start to focus inwards on your own mind and bodily functions. Furthermore, after as little as 30 minutes subjects begin to hallucinate. Orfield explained that it is also impossible to stay in the room for more than half an hour without sitting down because a person’s orientation is largely grounded in the sounds they make when moving. "How you orient yourself is through sounds you hear when you walk," he told the Daily Mail. In the anechoic chamber, you don't have any cues. "You take away the perceptual cues that allow you to balance and manoeuvre. If you're in there for half an hour, you have to be in a chair." The Quietest Place on Earth: Orfield Laboratories youtu.be For anyone who reckons they could top that 45-minute record, it is possible to experience the chamber for yourself. The Laboratories offer a tour, named “The Anechoic Experience”, which enables participants to take on the challenge, provided they’re willing to fork out a cool $600 (around £470) per hour for the privilege. The Orfield website states: “We have witnessed many seeming miracles, some of which have explanations and some of which remain mysteries, as a result of time spent in our anechoic chamber. “We remain curious about the nature of the chamber's impact on all people, its therapeutic properties, and how it can influence human perception. While anechoic chambers are traditionally used to study products, ours is becoming also about the people. “The Anechoic Experience is designed to be an opportunity to personally inquire about the chamber's therapeutic and spiritual effects.” We reckon we might be better off just lying in bed with the duvet over our heads next time we want a moment's peace. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 21:49
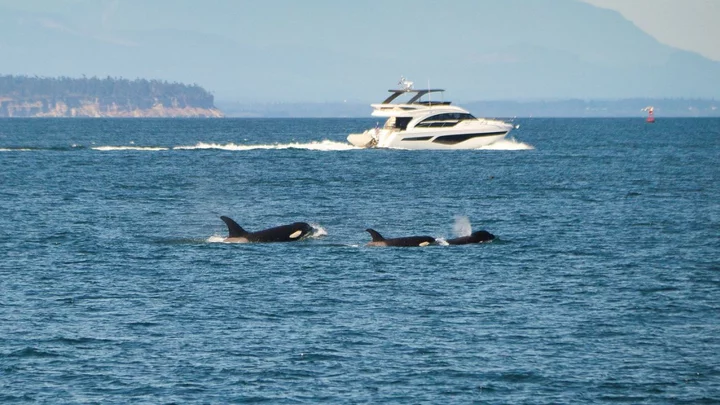

'Orca wars': Why are killer whales attacking boats, and are they really rising up?
A spate of recent orca attacks has fuelled concern among scientists in recent weeks for animal safety, and even led to speculation that the ocean mammal could be trying to rise up against humans. But are they? In a new trend – dubbed "orca wars" by some on social media – a population of orcas has recently been smashing into boats off the coast of Portugal and near the Strait of Gibraltar at a rate of nearly one per day. That's according to researcher Rui Alves, who collects data on the attacks. In June alone there have been 12 orca attacks on boats and 12 other encounters. In May, there were 21 attacks, says his website, orca.pt. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Of course, social media reacted just how you might expect: by picking a team. One person tweeted: “If you an orca whale reading this, i am on your side. I have always been on your side.” Researchers don’t know exactly why this is happening, but there are two main hypotheses. The first is that killer whales – highly intelligent and social creatures – have invented a new fad, something that younger members of orca pods have been known to do. The other, more concerning possibility, is that it is a response to trauma involving a boat, Dr Alfredo López Fernandez, of Grupo Trabajo Orca Atlántica (GTOA, or Atlantic Orca Working Group), told the Guardian. “[It could be a] response to an adverse situation; one or several individuals have had a bad experience and are trying to stop the boat so as not to repeat it. This behaviour coincides with the profile of adults,” he said. If it is the latter, there is even one key suspect in starting the trend: a white orca called Gladis Blanca (or White Gladis), who is thought to have had a bad collision with a vessel at some stage. Other adult orcas in the region also have injuries consistent with boat collisions or entanglement, López added. “All this has to make us reflect on the fact that human activities, even in an indirect way, are at the origin of this behaviour,” he said. In fact, the attacks are not such a new thing. Back in 2020, a group of orcas were seen pursuing sailboats in the region, in an act of aggression that was previously thought to be extremely rare. Since then, it has grown more and more common. The orcas have tended to ram into the hulls of boats, but they have also been seen scraping them with their teeth. The attacks sometimes snap the boats’ rudders, leaving sailors unable to navigate. In three cases, the animals damaged a boat so badly that it sank. However, for all the concern that the orcas might be getting, erm, orca-nised, scientists remain concerned that the attacks could come back to bite the ocean mammals eventually. The Iberian orca subpopulation is considered critically endangered, according to GTOA, with only 39 animals the last time a full census was carried out in 2011. López and his colleagues fear boaters may lash out, or that the orcas might hurt themselves in the process of ramming the vessels. Either way, it doesn’t look like the attacks will stop any time soon. So who knows: maybe the ocean world really is rising up… Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 16:19

Scientists think there could be an 'anti-universe’ where time runs backwards
It sounds like something straight out of a Christopher Nolan film, but scientists have suggested that there could actually be an 'anti-universe' where time runs backwards. And if you’re anything like us, your brain is probably starting to hurt already. It comes from experts studying symmetries, and the new research is all to do with the fundamentals of symmetry in nature – the most significant of which are charge, parity and time. Bear with us… According to LiveScience, a new paper recently accepted for publication in the journal Annals of Physics suggests that there is a combined symmetry to the entire universe. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter As the research attests, the early universe was so uniform that time looks symmetric going backwards and forwards. The paper argues that the way we understand the world and wider universe around us, moving forwards in time, must also be expanded to include a mirrored version which runs backwards in time. It could also provide a deeper understanding of dark matter, too. The theory suggests that it is an invisible particle which only interacts via gravity and provides a pairing to the electron-neutrino, muon-neutrino and tau-neutrino. The research suggests that the conditions in a mirrored universe where time runs backwards would be full of these paired neutrinos, which would account for dark matter. Of course, we’d never be able to experience time running backwards even if it did definitely exist, but it’s a pretty cool theory none-the-less. It comes after Elon Musk made headlines in the world of science and space travel, after giving his estimation for when humans will land on Mars for the first time. The first moon landing famously took place in 1969, but space enthusiasts have been debating when they think the first Mars landing will be – now, the SpaceX CEO thinks we’ll be up there by 2029. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-19 00:17
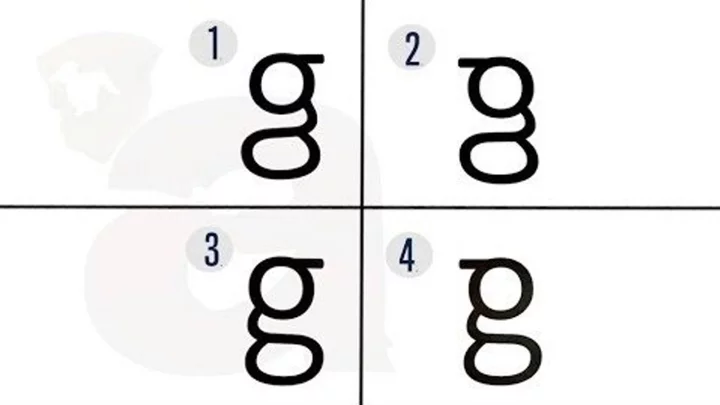
Can you find which letter 'G' is written correctly? Most people can't
We use letters every day of our lives, but apparently, there's one lowercase letter that we do not recognise. Psychologists at Johns Hopkins University have discovered that most people aren't aware that there are two types of the lowercase letter g. One of them is the open tail 'g' which most of us would have written out by hand with its image comparable to "a loop with a fishhook hanging from it. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Then, there is the loop tail 'g' which appears in print form e.g. books and newspapers as well as in Serif fonts such as Times New Roman and Calibri - we've all seen this type of letter millions of times, but it seems remembering it is an entirely different challenge altogether. There were 38 volunteers in the study published by the Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance and they were asked to list letters that they thought had two variations in print. In the first experiment, "most participants failed to recall the existence of looptail g" while only two people could write looptail g accurately. "They don't entirely know what this letter looks like, even though they can read it," co-author Gali Ellenblum said. Next participants were asked to look for examples of the looptail g in the text and were asked to reproduce this letter style after this and in the end, only one person could do this while half the group wrote an open tail g. Finally, those taking part in the study were asked to identify the letter g in a multiple-choice test with four options of the letter where seven out of 25 managed to do this correctly. So how can we know a letter but not recognised it? It could be to do with the fact we are not taught to write this kind of 'g," according to Michael McCloskey, senior author of the paper. "What we think may be happening here is that we learn the shapes of most letters in part because we have to write them in school. 'Looptail g' is something we're never taught to write, so we may not learn its shape as well," he said. "More generally, our findings raise questions about the conditions under which massive exposure does, and does not, yield detailed, accurate, accessible knowledge." In a play-along video on John Hopkin's YouTube channel, four different g's labelled from one to four appear on the screen where it asked viewers to guess which is the correct looptail 'g'. (*Spoiler ahead*) The correct answer is number 3. Meanwhile, this study has also led research to question the impact that writing less and using more devices has on our reading abilities. "What about children who are just learning to read? Do they have a little bit more trouble with this form of g because they haven't been forced to pay attention to it and write it?" McCloskey said. "That's something we don't really know. Our findings give us an intriguing way of looking at questions about the importance of writing for reading..." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-18 23:49
