
Mass event will let hackers test limits of AI technology
No sooner did ChatGPT get unleashed than hackers started “jailbreaking” the artificial intelligence chatbot – trying to override its safeguards so it could blurt out something unhinged or obscene
2023-05-10 22:49

Texas Startup ‘Slings’ into Business with First-Ever Retractable Smartphone Lanyard
PROSPER, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 22:49

ChatGPT creators try to use artificial intelligence to explain itself – and come across major problems
ChatGPT’s creators have attempted to get the system to explain itself. They found that while they had some success, they ran into some issues – including the fact that artificial intelligence may be using concepts that humans do not have named for, or understanding of. Researchers at OpenAI, which developed ChatGPT, used the most recent version of its model known as GPT-4 to try and explain the behaviour of GPT-2, an earlier version. It is an attempt to overcome the so-called black box problem with large language models such as GPT. While we have a relatively good understanding of what goes into and comes out of such systems, the actual work that goes on inside remains largely mysterious. That is not only a problem because it makes things difficult for researchers. It also means that there is little way of knowing what biases might be involved in the system, or if it is providing false information to people using it, since there is no way of knowing how it came to the conclusions it did. Engineers and scientists have aimed to resolve this problem with “interpretability research”, which seeks find ways to look inside the model itself and better understand what is going on. That has often required looking at the “neutrons” that make up such a model: just like in the human brain, an AI system is made up of a host of so-called neutrons that represent parts of the data it uses. Finding those is difficult, however, since humans have had to pick through the neurons and manually inspect them to find out what they represent. But some systems have hundreds of billions of parameters and so actually getting through them all with people is impossible. Now, researchers at OpenAI have looked to use GPT-4 to automate that process, in an attempt to more quickly pick through the behaviour. They did so by attempting to create an automated process that would allow the system to provide natural language explanations of the neuron’s behaviour – and apply that to another, earlier language model. That worked in three steps: looking at the neuron in GPT-2 and having GPT-4 try and explain it, then simulating what that neuron would, and finally scoring that explanation by comparing how the simulated activation worked with the real one. Most of those explanations went badly, and GPT-4 scored itself poorly. But researchers said that they hoped the experiment showed that it would be possible to use the AI technology to explain itself, with further work. The creators came up against a range of “limitations”, however, that mean the system as it exists now is not as good as humans at explaining the behaviour. Part of the problem may be that explaining how the system is working in normal language is impossible – because the system may be using individual concepts that humans cannot name. “We focused on short natural language explanations, but neurons may have very complex behavior that is impossible to describe succinctly,” the authors write. “For example, neurons could be highly polysemantic (representing many distinct concepts) or could represent single concepts that humans don’t understand or have words for.” It also runs into problems because it is focused on specifically what each neuron does individually, and not how that might affect things later on in the text. Similarly, it can explain specific behaviour but not what mechanism is producing that behaviour, and so might spot The system also uses a lot of computing power, the researchers note. Read More Google to unveil major new AI AI robots figure out how to play football in shambolic footage White House asks hackers to break ChatGPT White House reveals plan to ‘protect’ citizens from danger of AI DeepMind boss says human-level AI is just a few years away Regulator to probe use of artificial intelligence such as ChatGPT
2023-05-10 22:49
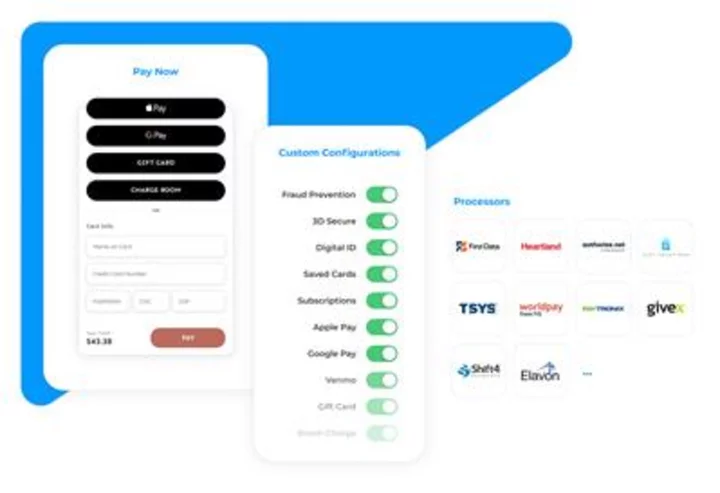
CardFree Launches ‘Checkout,’ The Most Comprehensive Wallet Offering for Merchants
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 22:24

Microsoft signs power purchase deal with nuclear fusion company Helion
By Timothy Gardner WASHINGTON (Reuters) -Private U.S. nuclear fusion company Helion Energy will provide Microsoft with electricity in about five
2023-05-10 22:22
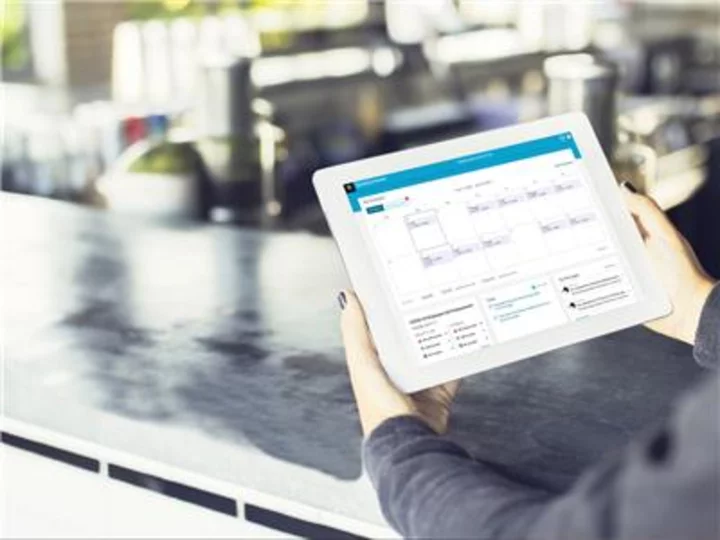
Fourth’s HotSchedules Named Leading Employee Scheduling and Workforce Management Solution
AUSTIN, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 22:20
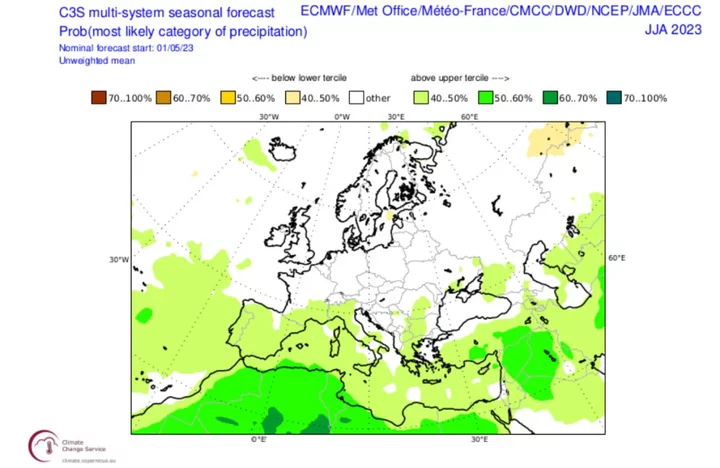
Searing Summer Temperatures Forecast in Europe and Northeast US
Much of Europe and the northeast US are in store for sweltering summer temperatures well above historical norms,
2023-05-10 22:20

James Han Joins Triage Partners as President in Latest Broadtree Partners Acquisition
CHARLOTTE, N.C.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 22:18
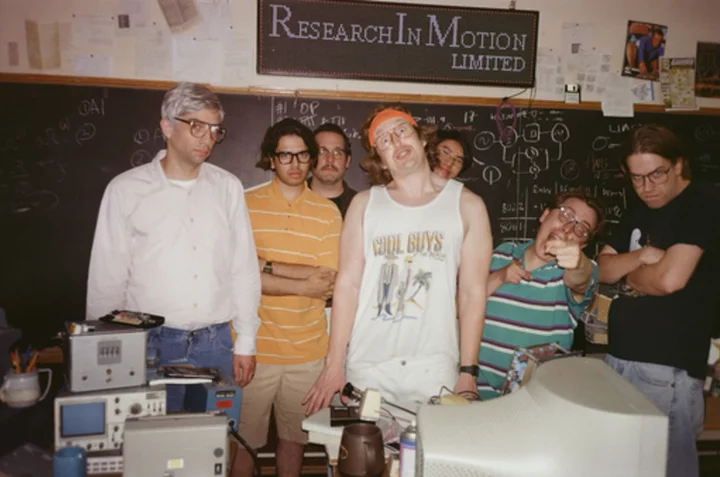

'BlackBerry' film taps into device that ruled pre-iPhone era
Almost everyone knows the backstory of the iPhone, a breakthrough that continues to reshape culture 16 years after late Apple co-founder Steve Jobs introduced the device to the world
2023-05-10 22:18
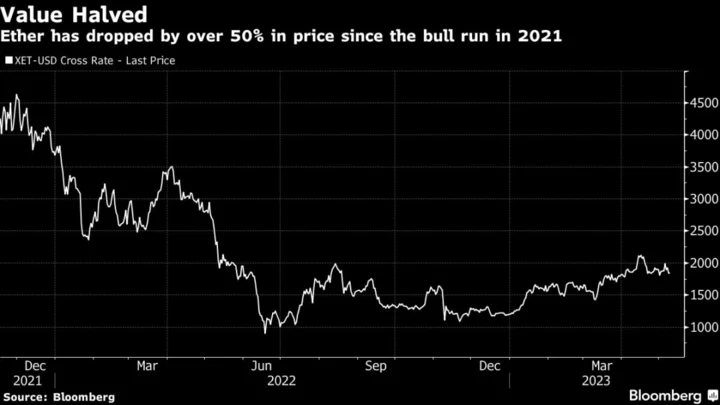
AI Needs Specialized Processors. Crypto Miners Say They Have Them
When the Ethereum blockchain moved away from using a technique for verifying transactions known as proof of work
2023-05-10 21:56

Vanta Expands Partnership with CrowdStrike, Announces New Integration to Secure Access for Automated Compliance
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 10, 2023--
2023-05-10 21:50
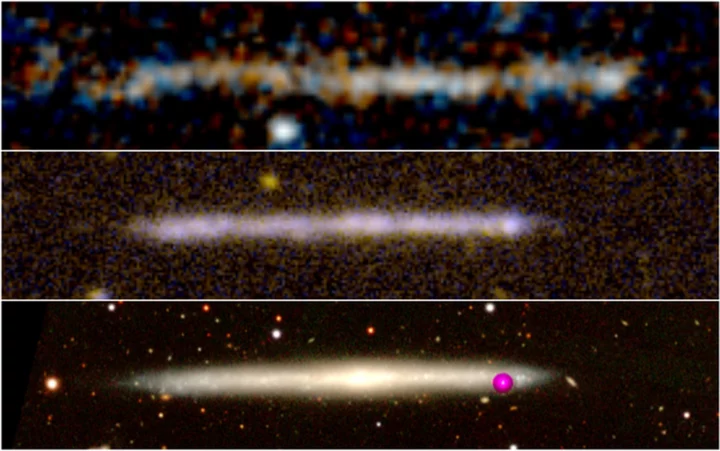

‘Runaway supermassive black hole’ mystery solved: Scientists find new explanation for unusual star structure
Scientists think they have found an explanation for what scientists thought was a “runaway” black hole speeding through the universe. Last month, scientists reported that they had seen what appeared to be an object unlike anything seen before. What originally appeared to be scratches on Hubble images was actually a black hole that had been thrown out from its home galaxy and was now speeding through the cosmos, scientists said. Astronomers had come to that conclusion after spotting a long trail of stars, formed 8 billion years ago. It was a stretched out, narrow shape, roughly the same size as our own Milky Way. Last month’s study suggested that those stars were the wake left behind from that runaway black hole. As the black hole travelled through a gas cloud, it left behind the right conditions to start forming stars, that study suggested. It was shock and a breakthrough for a number of reasons: it was unprecedented, and required a number of different conditions for it to be true. That led astronomers both to celebrate and question the theory, and in the time since other researchers have been working on their own ideas. Now scientists at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) have suggested their own, more ordinary explanation of the unusual, long star structure. They suggest that it is in fact just a flat or thin galaxy – one without a bulge that makes it wider – that is being seen from its side. “The motions, the size, and the quantity of stars fits what has been seen in galaxies within the local universe,” said Jorge Sanchez Almeida, an IAC researcher who is the first author of the article, in a statement. “It’s a relief to have found the solution to this mystery, the new proposed scenario is much simpler. In one sense it is also a pity, because the existence of fleeing black holes is expected, and this could have been the first one to be observed.” The team compared the mystery structure with another, much better known galaxy, named IC5249. That is near to us, has a similar mass of stars, and doesn’t have a galaxy either. They found that it was surprisingly similar. The stars were moving in similar ways to those found in closer, comparative galaxies, researchers said. That led scientists working on the new paper to suggest that it is a relatively normal and expected galaxy, rather than an out-of-control black hole. But they hope that further observations will shed further light on what exactly it is doing – and could still allow the galaxy to prove of interest to astronomers. “We also looked at the relation between the mass of the assumed galaxy and its maximum velocity of rotation, and discovered that indeed it is a galaxy which behaves like a galaxy,” said Ignacio Trujillo, an IAC researcher who worked on the study. “It is an interesting object, because it is quite a large galaxy at a very large distance from Earth, where the majority of the galaxies are smaller.” The proposal is reported in a paper, ‘Supermassive black hole wake or bulgeless edge-on galaxy?’, published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics. Read More Aliens may intercept human communication ‘within next 100 years’, study says Powerful auroras likely this week due to rare ‘backward’ sunspot Meteorite crashes through roof of New Jersey home Aliens may intercept human communication ‘within next 100 years’, study says Powerful auroras likely this week due to rare ‘backward’ sunspot Meteorite crashes through roof of New Jersey home
2023-05-10 21:45
