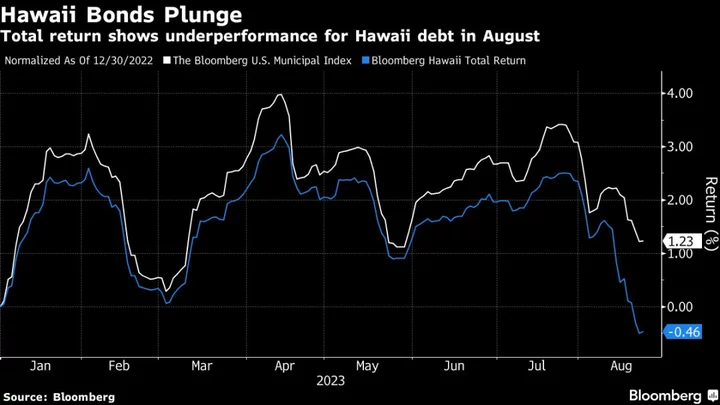
Hawaii Munis Plunge in Latest Investor Warning on Climate Risk
Hawaii state and local municipal bonds have surrendered all their 2023 gains in the past three weeks after
2023-08-26 00:54
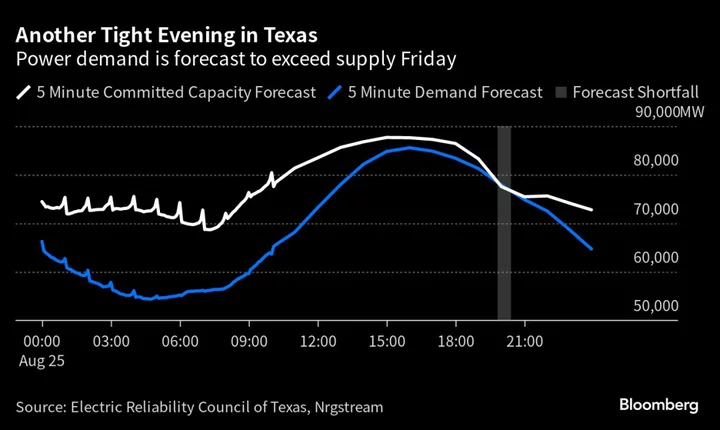
Blistering Heat Is Testing the Texas Power Grid for a Second Day
A punishing heat wave will test power supplies in Texas for a second day as triple-digit temperatures continue
2023-08-26 00:46

Simulation discovers what personality traits you would need to go to Mars
If the thought of jetting off to Mars to live doesn’t scare you enough, imagine what it would be like going with people whose personalities you cannot stand. To avoid that happening, scientists have come up with a simulation that can determine the right and, importantly, wrong, personality types to send up to colonize Mars. 28 different simulations of colonies on Mars were run as part of the study to establish which type of people stood the best chance of settlement and survival. While the study was published on pre-print server arXiv, it had not yet been peer-reviewed. The study worked on the assumption that there would already be some kind of infrastructure in place, including power, food, air and water being locally produced and available. As part of the model, there would also be regular supply deliveries from Earth. Those behind the simulation gave each agent their own attributes, skills and personalities and let the simulation run as they interacted, socialised and problem-solved together. In the paper, the researchers explained: “Each agent is granted skills associated with their civilian and military occupational specialities consistent with NASA’s Human Factors and Behavioral Performance Element research.” Different personality types included: “Agreeables” – they score low on levels of competitiveness and aggression. “Neurotics” – these people are highly aggressive, competitive, and are much less able to handle routine change or boredom. “Reactives” – they tend to have a “competitive interpersonal orientation”. “Socials” – people who are extroverted and require a lot of social interaction. As for the groups themselves, the numbers within each simulation differed with the lowest amount being 22 individuals. The study found that the presence of neurotics made the team have a worse chance of survival and that these people in particular “suffered during life on the colony”. The researchers: “Martians with the neurotic psychology and a high coping capacity benefit the least from interaction with other Martians, and are penalized the most if they have a low coping capacity. “Our results suggest that this effect is a driver of the Martian population decline, and once minimized or removed, can produce a stable settlement.” A lot to process there if you identify as neurotic. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 23:56

Armored Core 6 Share ID Catalog: Download These Popular Emblems
Armored Core 6 Share ID catalog detailing popular community created customizations.
2023-08-25 23:47

A new accent from 'Antarctica' has been discovered by scientists
Antarctica might be the only continent on Earth with no natural human habitation, but it’s emerged that an “Antarctica accent” is very much a thing. Despite having no locals, thousands of scientists have made up an ever-changing population in research stations over the years. The continent is so isolated and the level of interaction between researchers is so intense, that a common accent is beginning to emerge there despite people coming from different parts of the world. At its busiest points in the year during the summer, Antarctica is home to around 5,000 people. Only around 1,000 people live there during the winter months. The idea of accents changing due to human interaction on Antarctica is no different to the phenomenon seen throughout history at a glacial pace. However, given the very specific sample size, it’s an opportunity for scientists to study it at a much quicker rate and on a much smaller scale. Experts at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich published a study in 2019 which focused on the change in accents observed in 11 people who took part in the British Antarctic Survey. @human.1011 There’s an Antarctic Accent! #language #linguistics #english #antarctica Of the 11 who were studied, eight came from England, one from the US, one from Germany and one from Iceland. Their voices were recorded every six weeks, and the team found that over time they developed longer vowel sounds. There was a physical change too, with participants pronouncing the “ou” sound in the front of their mouths rather than the back of their throats. Speaking to IFL Science, Jonathan Harrington, study author and Professor of Phonetics and Speech Processing at the Ludwig-Maximilians University of Munich said: "The Antarctic accent is not really perceptible as such – it would take much longer for it to become so – but it is acoustically measurable. "It's mostly an amalgamation of some aspects of the spoken accents of the winterers before they went to Antarctica, together with an innovation. It's far more embryonic [than conventional English accents] given that it had only a short time to develop and also, of course, because it's only distributed across a small group of speakers.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 23:45

Armored Core 6 BALTEUS Boss Guide: How to Beat First Boss
Armored Core 6 BALTEUS boss guide for the Chapter 1 boss that's been giving players a ton of trouble early on.
2023-08-25 23:20
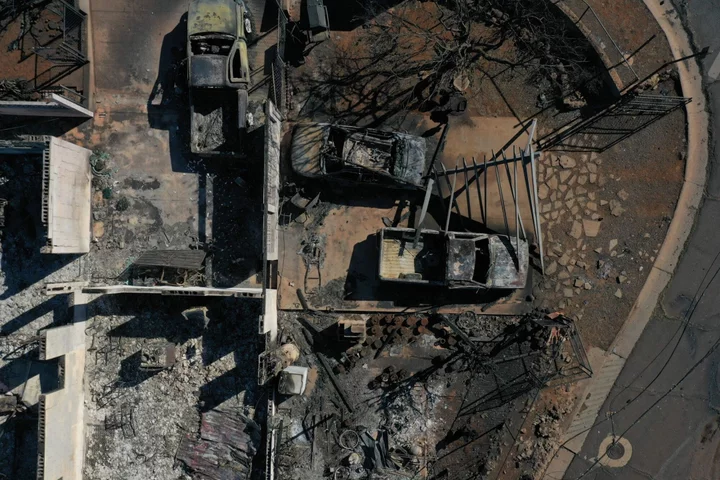

Maui Fire’s Missing-Person List Falls to 388 After FBI Vetting
The list of people who remain unaccounted for after Maui’s wildfire disaster dropped to 388, a significant decline
2023-08-25 23:18

Mystery of how a meteor left Earth thousands of years ago, then came back
Baffled scientists are trying to unravel the mystery of how a meteorite left Earth’s atmosphere and somehow came back again. Unlike boomerangs, meteorites don’t have a reputation for coming back around again, so when a black rock found in Morocco in 2018 seemed to have done just that, it left the scientific community confused. The rock, whose official name is Northwest Africa (NWA) 13188, is a scientific first (that we know of) to have left the Earth’s atmosphere, gone into outer space and returned again. The 646-gram piece of rock is remarkable not only for its journey but also its makeup. NWA 13188 has a bubbly texture and contains crystals. Its chemical components suggest that the rock is made out of the minerals produced by molten minerals that come from volcanic activity. It also possesses trace elements and oxygen isotopes, which suggests to scientists that it is not the typical meteorite that originates in space, but instead, it originated on Earth itself. However, according to a geophysicist from the French National Centre for Scientific Research, Jérôme Gattacceca, who studied the rock and presented the findings, it has undergone an interesting journey in orbit. Scientists can identify this because of the presence and concentration levels of Helium-3, Beryllium-10, and Neon-21, which suggest exposure to cosmic rays that are not present in Earth’s atmosphere. Compared to other more traditional meteorites scientists have studied, the concentrations are lower on NWA 13188 but are still higher than rocks on Earth. It is thought that NWA 13188 could have been expelled from Earth and in orbit for thousands of years. Scientists said, “We consider NWA 13188 to be a meteorite, launched from the Earth and later re-accreted to its surface”. Despite the rock originating on Earth, the team said it fits the definition of a meteorite since it has achieved orbit. The definition states: “Material launched from a celestial body that achieves an independent orbit around the Sun or some other celestial body, and which eventually is re-accreted by the original body, should be considered a meteorite. “The difficulty, of course, would be in proving that this had happened, but a terrestrial rock that had been exposed to cosmic rays and had a well-developed fusion crust should be considered a possible terrestrial meteorite.” It is not yet understood how the rock came to be launched from Earth into space, as researchers said it still “remains to be determined”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 23:17

Scientist shares routine that can 'make you better at everything'
The emphasis on a good night's sleep is nothing new. But now, neuroscientist, Dr Andrew Huberman, has shared one routine that he suggested can make you "better at everything." In a YouTube talk on After Skool, Dr Huberman said he immediately starts his day with a sunrise walk at 6.30am. "Getting outside for a 10-minute walk or a 15-minute walk is absolutely vital to mental and physical health," he shared. Despite coffee being the get-up-and-go drink for most, Huberman says the first beverage he consumes is salty water, as he claims it helps improve bodily functions. "There are certain foundational behaviours - certain dos and don'ts that set the stage for you to be better at everything," he continued. "It always comes back to two elements - that's sleep and what I call non-sleep deep rest. Sleep is the fundamental practice or part of our 24-hour cycle where if you don't get it on a consistent basis, you are down-regulating your ability to do everything." He went on to discuss a "90-minute bout of work," in which he says he turns his phone off to fully optimise this time. "You'd be amazed how much you can get done in 90 minutes if you are focused," he said. Huberman then ensures he gets in an hour's worth of exercise before exposing himself to cold temperatures such as an ice bath. The NHS states that there are no official guidelines regarding how much sleep a person should get each night as everyone is different. "On average, a 'normal' amount of sleep for an adult is considered to be around seven to nine hours a night. Children and babies may sleep for much longer than this, whereas older adults may sleep less," they wrote. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-25 21:58

St Kitts and Nevis media guide
An overview of the media in St Kitts and Nevis, as well as links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-08-25 21:56

Dropbox Advanced Plan No Longer Offers 'as Much Space as You Need'
Dropbox will no longer offer unlimited storage on its Advanced plan due to a growing
2023-08-25 20:27

New PointsBet NFL Promo: Five $100 Bonus Bets on ANY Game!
PointsBet is rewarding new users with five days of $100 bonus bets! Find out how to claim this exclusive NFL promo here.
2023-08-25 20:26
