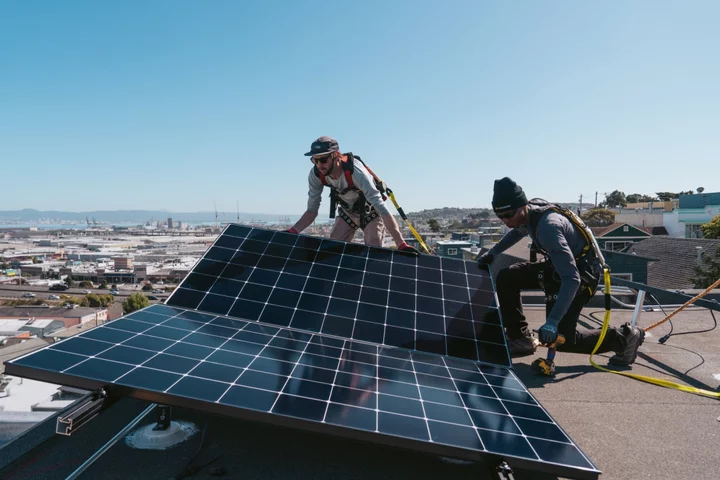

The World Has Already Crossed a ‘Tipping Point’ on Solar Power
Solar power is set to dominate global electricity markets within the next few decades, and may have already
2023-10-19 19:58

Larry Fink Leads CEOs Back to COP Talks They Snubbed Last Year
Wall Street is returning to climate talks that it largely snubbed last year, as the United Arab Emirates
2023-10-19 19:54

Giant heat-emitting mass discovered under the surface of the Moon
A huge mass of heat-emitting rock has been found buried beneath the surface of the Moon. The incredible discovery was made beneath one of the Moon’s craters, where a large mass of granite has slowly been releasing heat for years. Experts know that the Moon used to have eruptions and lava fields flowing from it, but until now, they have never uncovered evidence that is reminiscent of Earth-like volcanoes, underneath which granite forms when magma cools and crystalises deep beneath the surface. Now, that has changed after astronomers looked a bit more deeply at what lies beneath the Compton and Belkovich craters, located on the far side of the Moon. There they came across a large piece of granite rock that is emitting heat. The discovery excited experts as granite is not commonly found outside of Earth. Granite on the Moon was discovered using data from both Chinese and American lunar orbiters, and the information has revealed a whole new volcanic process never before witnessed. In a statement, one of the lead researchers, Dr Matt Siegler, from the Planetary Science Institute, said: “Using an instrument looking at microwave wavelengths – longer than infrared – sent to the Moon on both the Chinese Chang’E 1 and 2 orbiters, we have been able to map temperatures below the surface. “What we found was that one of these suspected volcanoes, known as Compton-Belkovich, was absolutely glowing at microwave wavelengths.” He continued: “What this means is that it is hot, not necessarily at the surface, as you would see in infrared, but under the surface. “The only way to explain this is from extra heat coming from somewhere below the feature within the deeper lunar crust. So Compton-Belkovich, thought to be a volcano, is also hiding a large heat source below it.” Using the data, they believe the 12-mile wide dip makes up the caldera, or depression, of the ancient volcano, where the surface temperature is 10°C higher than the surrounding areas. The volcano is thought to have last erupted 3.5 billion years ago and experts believe the heat that is emitting from the granite below is due to trapped radioactive material in the rock. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-19 19:54

Marvel's Spider-Man 2 disc players need to download this update before launch
'Marvel's Spider-Man 2' has some refinements that disc players will get from downloading the launch update.
2023-10-19 19:20

Super Mario Bros. Wonder almost had live commentary
The Nintendo team hired someone who worked on the project for six months, then decided it wasn't right.
2023-10-19 19:19

Meta, TikTok given a week by EU to detail measures against disinformation
By Charlotte Van Campenhout and Bart H. Meijer BRUSSELS (Reuters) -Meta and TikTok have been given a week by the
2023-10-19 18:59

EU Proposes Delaying Some ESG Reporting Rules
Europe’s executive arm is proposing a two-year delay in implementing a key element of its sustainable finance framework,
2023-10-19 17:24
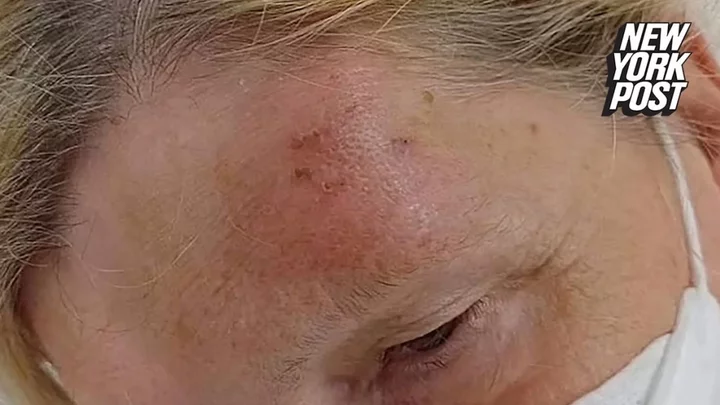
Pets pose a serious health threat that we've all been overlooking
While millions of people own cats and dogs and wouldn’t dream of getting rid of them, pets pose a health risk to humans that is massively overlooked, according to a new study. Since the Covid-19 pandemic swept the world with devastating impact, it has become evident how much of a risk new viruses can pose to our well-being. However, experts are warning that it is not just the wildlife trade or exotic animals that we should be concerned about, as pets could also be sources of zoonotic diseases (which jump from animals to humans). Back garden pets, house pets, working animals and even rodents and pests could host new viruses that could affect humans, according to a new study. It warns that the urbanisation of our habitats and climate change will have an impact on diseases and their dynamics. The study was shared in Science Translational Medicine and penned by disease ecologist Amandine Gamble along with a group of colleagues, who gave examples of how companion animals (aka pets) and stray animals carried a risk of zoonotic spillover. While the risk is thought to be small, experts warn it is significantly underappreciated, especially given the frequent proximity human beings have to pets and strays. The study said: “These animals can play critical roles in zoonotic spillover by enabling the maintenance of a zoonotic pathogen, facilitating its spatial spread, acting as a bridge between otherwise unconnected species, or providing particular opportunities for its evolution.” While the zoonotic spillover that caused Covid-19 sparked a global pandemic, any instance of infection that jumps from animal to human is known as a zoonotic, regardless of the numbers affected. Pet parrots are a known transmitter of the Chlamydia psittaci bacterium to humans. Elsewhere, bats and horses are also known sources of zoonotic diseases. In terms of common household pets, cats can act as a link to a number of fatal diseases. The experts explained: “Numbers of infections are low, but plague is endemic in 17 western U.S. states, and many of the small mammals on which cats prey carry Y. pestis. “Consequently, outdoor cats and cats with incomplete veterinary care, combined with human interaction, suggest that cat-transmitted plague can be considered an increasing public health risk.” They conclude that “it is critical to implement surveillance programs allowing us to track changes in pathogen dynamics”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-19 17:21

Google bets on India with Pixel smartphone manufacturing
By Tanvi Mehta and Blassy Boben NEW DELHI (Reuters) -Alphabet Inc's Google will start manufacturing smartphones in India and its
2023-10-19 17:20

Science recreate mysterious ice found on Neptune that only melts at extreme temperatures
Five years ago, scientists managed to recreate what is known as superionic ice, in lab experiments for the first time. Superionic ice is believed to form within Uranus and Neptune as familiar materials are subjected to extreme pressures and heat, with iron atoms forming hot, black, heavy ice. But just last year researchers at several universities in the United States discovered a new phase of superionic ice. The discovery helps broaden our understanding of why Uranus and Neptune have off-kilter magnetic fields with multiple poles. Different to forms of water on Earth, the oxygen atoms in superionic ice are locked in a solid cubic lattice, while the ionised hydrogen atoms are loose, flowing through the lattice. This gives superionic ice conductive properties as well as raising its melting point, meaning the frozen water remains solid at temperatures up to 4704 Degree Celsius (8500 Fahrenheit). In this latest study, Stanford University's Arianna Gleason and colleagues blasted thin slivers of water, sandwiched between two diamond layers, with some extremely powerful lasers. "Recent discoveries of water-rich Neptune-like exoplanets require a more detailed understanding of the phase diagram of [water] at pressure–temperature conditions relevant to their planetary interiors," Gleason and colleagues explain in their paper, from January 2022 X-Ray diffraction revealed the hot, dense ice's crystal structure, and confirmed the ice crystals were in fact a new phase, distinct from the superionic ice that was observed in 2019. This newly discovered superionic ice, Ice XIX, has increased conductivity compared to its 2019 predecessor. The conductivity is important because it helps us understand why certain off-kilter magnetic fields are generated on planets such as Neptune and Uranus. You can read the paper, published in Scientific Reports here. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-19 16:53

Climate Science in Arctic ‘Broken’ as US and Europe Isolate Russia
Irina Panyushkina is a dendrochronologist — a scientist who studies tree-ring dating to understand past environmental conditions —
2023-10-19 16:50

Netherlands, Denmark to Help Pay for South Africa’s Energy Transition
South Africa’s cabinet said that the Netherlands and Denmark have joined the Just Energy Transition Partnership, a landmark
2023-10-19 16:15
