
Google AI breakthrough could dramatically reduce planes’ global warming impact
Google says it has made a major artificial intelligence breakthrough that could dramatically reduce the climate impact from flying. The company partnered with an airline and data provider to build a new artificially intelligent system that looks to reduce the amount of contrails produced by planes. Contrails are the long, white lines that appear behind planes, and can sometimes make the sky appear cloudy. They are formed as soot from planes’ exhausts turn into ice – and when they merge together, they trap heat in the atmosphere and warm the Earth. Those contrails account for more than a third of the global warming impact of flying, according to the UN. If planes are able to avoid flying through areas that create contrails, however, then they will reduce the amount of warming. If the human-made clouds can be stopped, then their warming effects can be reduced. In an attempt to do so, Google researchers gathered satellite imagery, weather and flight path data and fed it into an AI system. That was then used to try and generate routes for pilots that avoided creating those contrails. Pilots at American then flew some 70 test flights over a period of six months, Google said, following those AI-generated routes. The researchers then examined satellite imagery and found that the contrails produced were reduced by 54 per cent. “This is the first proof point that commercial flights can verifiably avoid contrails and thereby reduce their climate impact,” Google said. The company did also note that the flights burned 2 per cent additional fuel, though Google suggested that the flights could be selectively chosen. Google said it would be “working across the aviation industry to use AI to make contrail avoidance a reality over the coming years” in its announcement. It said it has the “potential to be a cost-effective, scalable solution to reduce the climate impact of flying”. Airlines are currently not charged for their climate impact, however, and there is therefore no indication that they would opt to use the routes that help reduce global warming. Read More Google will now alert you if people are talking about you Google Assistant will be ‘supercharged’ with AI like ChatGPT and Bard Google warns Gmail users they could be about to lose their account
2023-08-09 23:51

Fortnite Lonely Labyrinth: How to Escape with Kinetic Ore Schematic
Slone's latest Fortnite quest forces players to escape Lonely Labyrinth with the Refined Kinetic Ore Schematic to earn 30,000 XP. Here's how to escape.
2023-08-09 23:47

LEAK: Fuse Heirloom Coming to Apex Legends
A Fuse Heirloom called Razor's Edge is coming to Apex Legends in the future, along with a new Collection Event, according to data miners.
2023-08-09 23:47
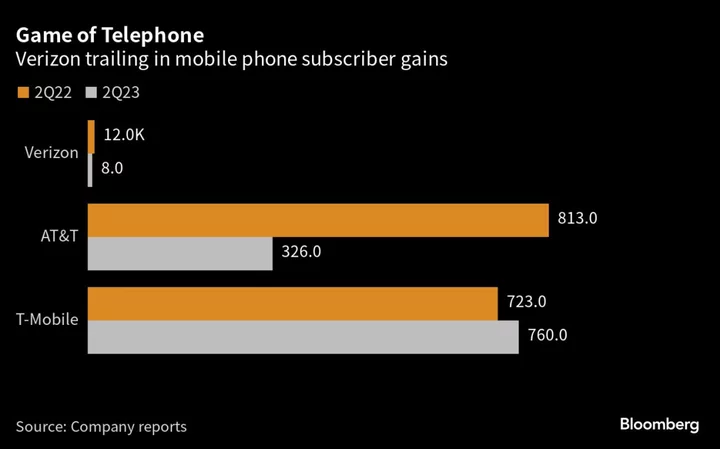
Verizon Raises Prices Again as Wireless Customer Growth Slows
Verizon Communications Inc. is raising prices on some existing wireless plans to help boost revenue and offset slumping
2023-08-09 22:52

Biden Decries Climate Threat But Does Not Declare Emergency
President Joe Biden stopped short of saying he would declare a national climate emergency, a move progressive lawmakers
2023-08-09 22:22

Roblox Misses Expectations on Daily Active Users and Engagement
Roblox Corp. reported a daily active user count and hours played that fell short of analysts’ expectations. The
2023-08-09 21:22

Roblox misses quarterly bookings estimates on lower spending, shares tumble
(Reuters) -Gaming platform Roblox missed estimates for second-quarter bookings on Wednesday as waning demand for its online games and intensifying
2023-08-09 20:55

Russia to widen scope of digital rouble testing from Aug. 15 -central bank
By Elena Fabrichnaya MOSCOW Russia will begin piloting its digital rouble with consumers on Aug. 15 after a
2023-08-09 20:52

Pope Francis warns about AI's dangers
Pope Francis warned that artificial intelligence could pose a risk to society, highlighting its "disruptive possibilities and ambivalent effects" and urging those who would develop or use AI to do so responsibly.
2023-08-09 20:45

IBM to launch Meta's Llama 2 on watsonx AI platform for businesses
International Business Machines said on Wednesday it would host Meta Platforms' artificial intelligence language program on its own
2023-08-09 20:26

UK retailer John Lewis boosts AI capability with Google deal
(Reuters) -British retailer John Lewis Partnership has agreed a five-year deal with Alphabet Inc's Google Cloud, enabling it to harness
2023-08-09 19:20

Bots are better than humans at cracking ‘Are you a robot?’ Captcha tests, study finds
Bots are better and significantly faster than humans at cracking Captcha tests, according to a comprehensive new study that inspected the security system deployed in over 100 popular websites. Automated bots pose a significant threat to the internet because they can masquerade as legitimate human users and perform harmful operations like scraping content, creating accounts and posting fake comments or reviews, as well as consuming scarce resources. “If left unchecked, bots can perform these nefarious actions at scale,” warned scientists, including those from the University of California, Irvine. For over two decades, Captchas have been deployed as security checks by websites to block potentially harmful bots by presenting puzzles that are supposed to be straightforward for people to solve – but very difficult for computers. Earlier forms of Captcha, for instance, asked users to transcribe distorted text from an image, but with advances in computer vision and machine learning, bots soon caught up to recognise the text with near perfect accuracy. Engaged in an arms race with bots, Captchas have since evolved into an annoying presence on the internet, becoming increasingly more and more difficult to solve for both bots and humans. However, the new yet-to-be peer-reviewed research, posted in arXiv, finds bots are able to quickly crack Captcha tests with ease, suggesting global effort users put into cracking these puzzles every day may be more trouble than its worth. In the study, scientists assessed 200 of the most popular websites and found 120 still used Captcha. They took the help of 1,000 participants online from diverse backgrounds – varying in location, age, sex and educational level – to take 10 captcha tests on these sites and gauge their difficulty levels. Researchers found many bots described in scientific journals could beat humans at these tests in both speed and accuracy. Some captcha tests took human participants between nine and 15 seconds to solve, with an accuracy of about 50 to 84 per cent, while it took the bots less than a second to crack them, with up to near perfection. “The bots’ accuracy ranges from 85-100 per cent, with the majority above 96 per cent. This substantially exceeds the human accuracy range we observed (50-85 per cent),” scientists wrote in the study. They also found that the bots’ solving times are “significantly lower” or nearly the same as humans in almost all cases. Since current Captchas do not meet the required security goal of keeping bots away, researchers have called for better and more dynamic approaches to protect websites. Read More Shock for millions of voters as details exposed in hack – which went undetected for a year AI-driven cyberattack can now steal your passwords with near 100 per cent accuracy, study warns More than a million NHS patients’ details compromised after cyberattack Many adults would struggle to understand video-sharing platforms’ rules – Ofcom Now even Zoom tells staff: ‘Come back to the office’ Ozzy Osbourne PlayStation tweet which failed to reveal link to Sony banned
2023-08-09 17:59
