
Exclusive-Geely's Zeekr edges closer to US IPO, to make filing public this week - sources
SHANGHAI (Reuters) -Zeekr, Chinese automaker Geely's premium electric car brand, will this week publicly release some details of its plans
2023-11-09 18:16
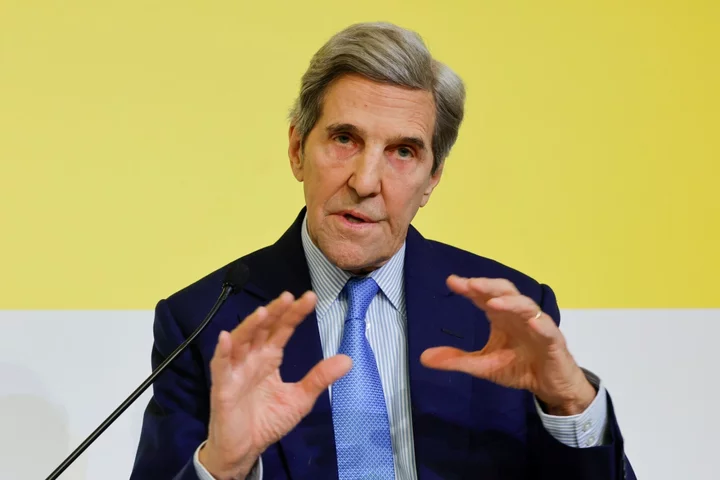

US-China Climate Talks Wrap Up With Warm Words But Few Details
The top climate envoys from the US and China ended five days of face-to-face talks late Wednesday, hailing
2023-11-09 16:58

Sony Raises Outlook Yet Sounds Cautious Note on PS5 Holiday Goal
Sony Group Corp. raised its full-year outlook for sales and profit after its media divisions outperformed, yet warned
2023-11-09 16:54
ESG Veteran Says Purge Has Further to Go With ETFs Next in Line
The bad year that a lot of ESG investors are having may be about to get even worse.
2023-11-09 16:54
Soap may be key for longer-lasting batteries, study finds
The key to longer-lasting batteries may lie in soap, according to a new study. Scientists have developed a new promising substance used for designing batteries. They said it acts in a manner similar to soap removing grease, dirt and germs. Localised high-concentration electrolytes could be the “missing piece” that fully open the door to building longer-lasting batteries, said a recent study published in the journal Nature Materials. The key to longer-lasting batteries may lie in understanding how soap gets rid of dirt. It forms tiny structures called micelles that act as a bridge between water and what is being cleaned away by wrapping them into small structures. Scientists from Brown University said a similar process plays out in localised high-concentration electrolytes – described as one of the most promising substances for designing batteries. Electrolytes are key in the energy-storing process as they allow an electrical charge to pass between a battery’s two terminals. This sparks the chemical reaction needed to convert stored chemical energy to electricity. Batteries made from lithium metal have a greater energy storage capacity than today’s lithium-ion batteries. But the electrolytes commonly used to power lithium-ion batteries don’t do this effectively in metal-based batteries, researchers explained. “The big picture is that we want to improve and increase the energy density for batteries, meaning how much energy they store per cycle and how many cycles the battery lasts,” said study co-author Yue Qi from Brown University. “To do this, materials inside of traditional batteries need to be replaced to make long-life batteries that store more energy a reality – think batteries that can power a phone for a week or more, or electric vehicles that go for 500 miles,” Dr Qi said. Electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries are made of low-concentration salt dissolved in a liquid solvent. The new type of electrolytes, however, are created by mixing high concentrations of salt in a solvent with another liquid called a diluent. Scientists said this makes the electrolyte flow better so the power of the battery can be maintained. They also found the electrolyte functions like soap. “The paper provides a unified theory to why this electrolyte works better and the key understanding of it came by finding that micelle-like structures form within this electrolyte – like they do with soap,” said study co-author Bin Li from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. “Here we see that the role of the soap or surfactant is played by the solvent that binds both the diluent and the salt,” Dr Li explained, “wrapping itself around the higher concentration salt in the center of the micelle”. While in lab tests, this type of electrolyte has shown promising results, how it works has remained elusive. This has put a cap on how effective it can be and how it can be further developed. The new understanding has, however, helped scientists develop the right concentrations needed to bring about optimal reactions for the batteries. “The concept of the micelle may be new for the electrolyte, but it’s actually very common for our daily life,” Dr Qi said. “Now we have a theory, and we have guidelines to get interactions we want from the salt, the solvent and the diluent in the electrolyte, and what concentration they have to be at and how you mix them.” Researchers said this new understanding could lead to introducing a proper balance of the three battery ingredients and also help extend the life of lithium-metal batteries. Read More Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute Apple just released an iPhone update you should download right now Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’ Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute Apple just released an iPhone update you should download right now Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’
2023-11-09 15:53
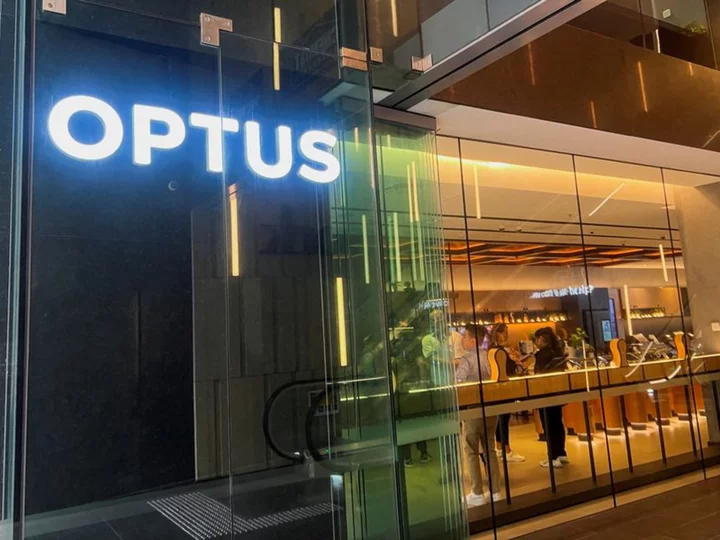

Australia to investigate Optus outage as customers seek compensation
By Renju Jose SYDNEY (Reuters) -Australia said on Thursday it would investigate an outage at telco Optus that cut off
2023-11-09 15:19

Honda posts 31% Q2 operating profit jump, raises full-year forecast
TOKYO (Reuters) -Japan's Honda Motor posted a 31% increase in operating profit for the September quarter on Thursday, lifted by
2023-11-09 14:56

Sony Q2 profit falls 29%, hit by chips division
By Sam Nussey TOKYO Sony's operating profit fell 29% in the July-September quarter, below estimates, as the company
2023-11-09 14:26

Smartphones ‘may be able to detect how drunk a person is with 98% accuracy’
Sensors in smartphones may be able to detect how drunk a person is based on changes in their voice, according to a small study. Following experiments involving 18 adults aged 21 and above, scientists said they were able to predict a person’s level of intoxication with 98% accuracy based on an analysis of their voice patterns. Brian Suffoletto, an associate professor of emergency medicine at Stanford University in the US, said the accuracy of the findings of his research “genuinely took me by surprise”. He added: “While we aren’t pioneers in highlighting the changes in speech characteristics during alcohol intoxication, I firmly believe our superior accuracy stems from our application of cutting-edge advancements in signal processing, acoustic analysis, and machine learning.” While Prof Suffoletto said larger studies are needed to confirm the validity of the findings, he added his work has the potential to deliver “just-in-time interventions” to prevent alcohol-related road injuries and deaths in the future. Prof Suffoletto said: “Imagine if we had a tool capable of passively sampling data from an individual as they went about their daily routines and survey for changes that could indicate a drinking episode to know when they need help.” Imagine if we had a tool capable of passively sampling data from an individual as they went about their daily routines and survey for changes that could indicate a drinking episode to know when they need help Prof Brian Suffoletto For the research, published in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, the scientists tailored alcohol doses based on the body weight of each person taking part and were given an hour to finish their drink. Each individual was randomly given a series of tongue twisters to read out loud and a smartphone was used to record their voices. Recordings were made before drinking, and each hour up to seven hours after drinking. The researchers also measured each person’s breath alcohol levels at the beginning of the study and every 30 minutes for up to seven hours. Using digital programmes, the researchers were able isolate the speaker’s voices and analyse measures such as frequency and pitch in one-second increments. When checked against breath alcohol results, the researchers found that the model they developed was a good predictor of how drunk a person was – with 98% accuracy. Prof Suffoletto believes that other behaviours such as gait and texting could be combined with voice pattern sensors to gauge intoxication levels. He said: “Timing is paramount when targeting the optimal moment for receptivity and the relevance of real-time support. “For instance, as someone initiates drinking, a reminder of their consumption limits can be impactful. “However, once they’re significantly intoxicated, the efficacy of such interventions diminishes.” Read More Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute Guidance urges parents not to buy smartphones for primary school children William ‘blown away’ by futuristic technology from Singapore start-ups Return of original Fortnite map causes record traffic on Virgin Media O2 network NatWest creates new AI-powered chatbot capable of ‘human-like’ conversations Succession star Sarah Snook says AI use in film industry needs ‘stringent rules’
2023-11-09 14:21
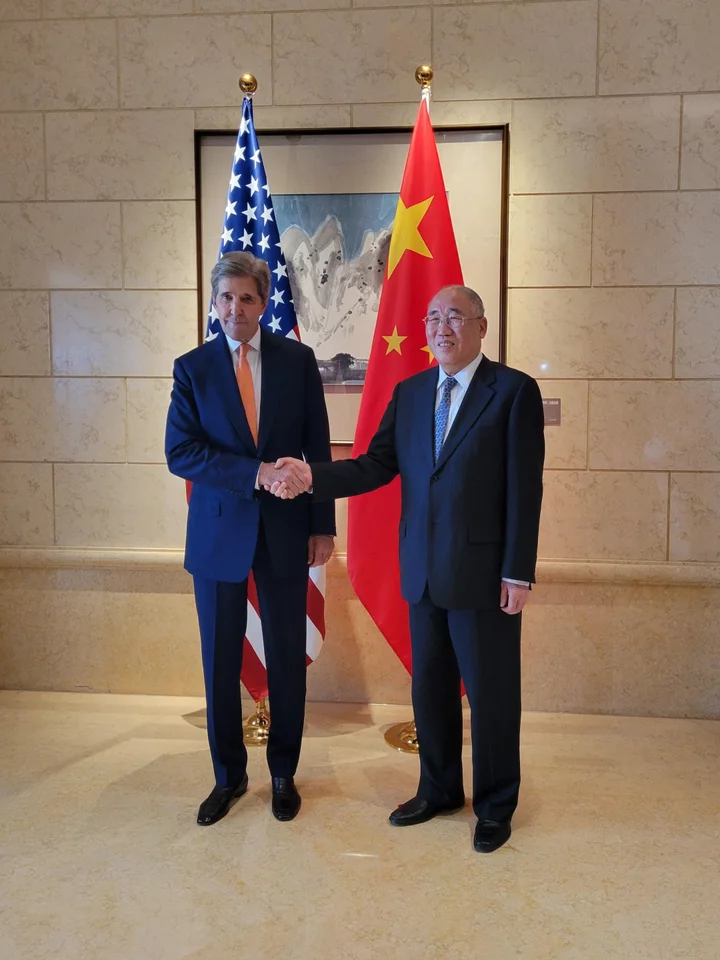

World’s Two Biggest Emitters Hold Key to Success at COP28 Summit
There’s been an unwritten rule during the past decade of climate diplomacy: Good things can happen when the
2023-11-09 13:20
Japan's efforts to foster chip sector are 'impressive' - research org head
By Sam Nussey TOKYO Japan's efforts to regain its position as a leading manufacturer of chips are "impressive",
2023-11-09 12:48

Ireland and Apple await major development in long-running EU tax dispute
EU lawmakers are awaiting an announcement which is seen as major step in the drawn-out dispute over tax arrangements between technology giant Apple and Ireland. The advocate general at the European Court of Justice is to issue an opinion on Friday morning about whether Apple will be forced to pay more than 13 billion euro in back taxes to Ireland. While the opinion of the advocate general is non-binding, it is usually followed by the court and therefore could have significant implications for corporation tax bills. Ireland had fought the European Commission over the matter due to concerns over an intrusion on Irish sovereignty and potential impacts to investment in the country. There was no sweetheart deal Finance Minister Michael McGrath In 2016, following an EU investigation which launched in 2014, the commission concluded that Ireland gave undue tax benefits of 13.1 billion euro to Apple, which is illegal under EU state aid rules. The commission said that tax rulings issued by Ireland to Apple in 1991 and 1997 substantially and artificially lowered the tax paid by the iPhone manufacturer in the country since 1991, in a way which did not correspond to economic reality. As a result, competition commissioner Margrethe Vestager said Ireland had granted illegal tax benefits which enabled it to pay substantially less tax than other business over many years. The investigation found that Apple had paid an effective corporate tax rate of 1% on its European profits in 2003, down to 0.005% in 2014 – 50 euro for every one million euro of profit. The process involved recording almost all sales profits of two Irish incorporated companies, which the commission said only existed on paper. The companies, fully owned by Apple, held the rights to use the firm’s intellectual property to manufacture and sell its products outside North and South America. The commission said this situation allowed Apple to avoid taxation on almost all profits generated by sales of its products in the entire EU single market. It said this was due to Apple’s decision to record all sales in Ireland rather than in the countries where the products were sold. The findings were disputed by the Irish State – which said all tax owed had been collected – and Apple, which had come under scrutiny in the US for its tax practices years earlier. At the time, Apple’s chief executive, Tim Cook, branded the EU findings as “political crap”, maddening and untrue. The Irish Government, which was also used to defending a comparatively low 12.5% corporation tax rate, said Europe had overstepped the mark in attempting to dictate tax laws and enforce retrospective taxes decades later. Ireland and Apple fought the commission on the matter and in July 2020, the General Court of the European Union annulled the decision. However, the commission subsequently appealed the decision to the European Court of Justice with Ms Vestager saying the lower court’s ruling contained “errors of law”. The European Court of Justice’s advocate general is to give a legal opinion on the dispute ahead of the court’s final decision. That decision is expected next year and will have significant implications for how member states grant tax breaks to major firms. Apple has argued it has been paying tax on the profits in question in the US, while Ireland has seen it necessary to defend its reputation on taxation issues to protect foreign direct investment. Last weekend, Finance Minister Michael McGrath said the advocate general’s opinion will be “significant” but added it is not the final step in the process. Mr McGrath said: “We are confident in our position in respect of the Apple case. We take encouragement from the findings they have made so far, but it is a significant day.” He added: “There was no sweetheart deal. This was the application of Ireland’s statutory corporation tax code.” In the interim, the 13.1 billion euro has been held in an escrow fund pending the outcome of the case. The money, with interest, is due to be entered into the Irish exchequer if the commission wins the case. However, other member states may make claims that they are owed some of the money. If the commission loses the appeal, the large sum will be returned to Apple.
2023-11-09 11:18
